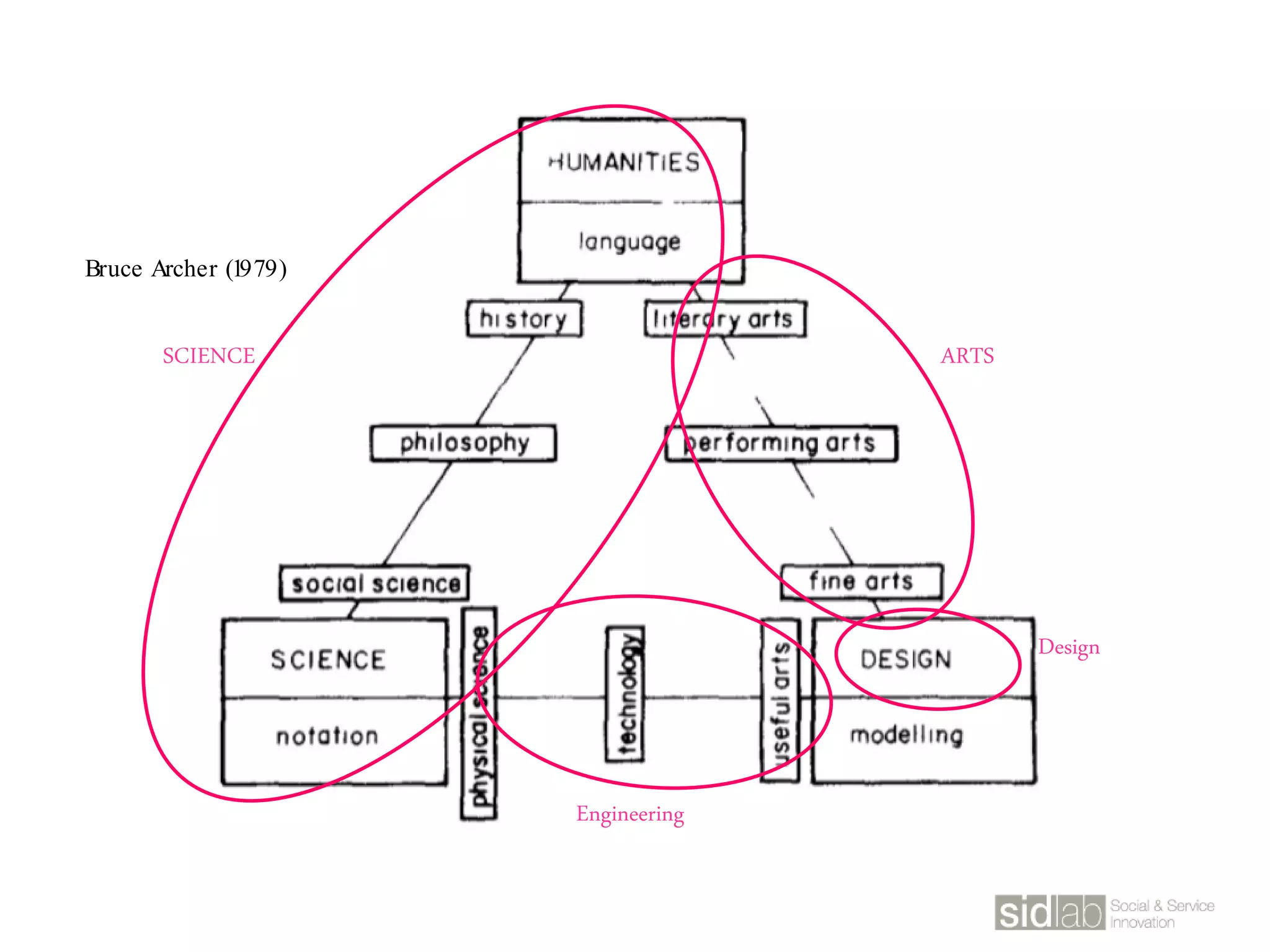
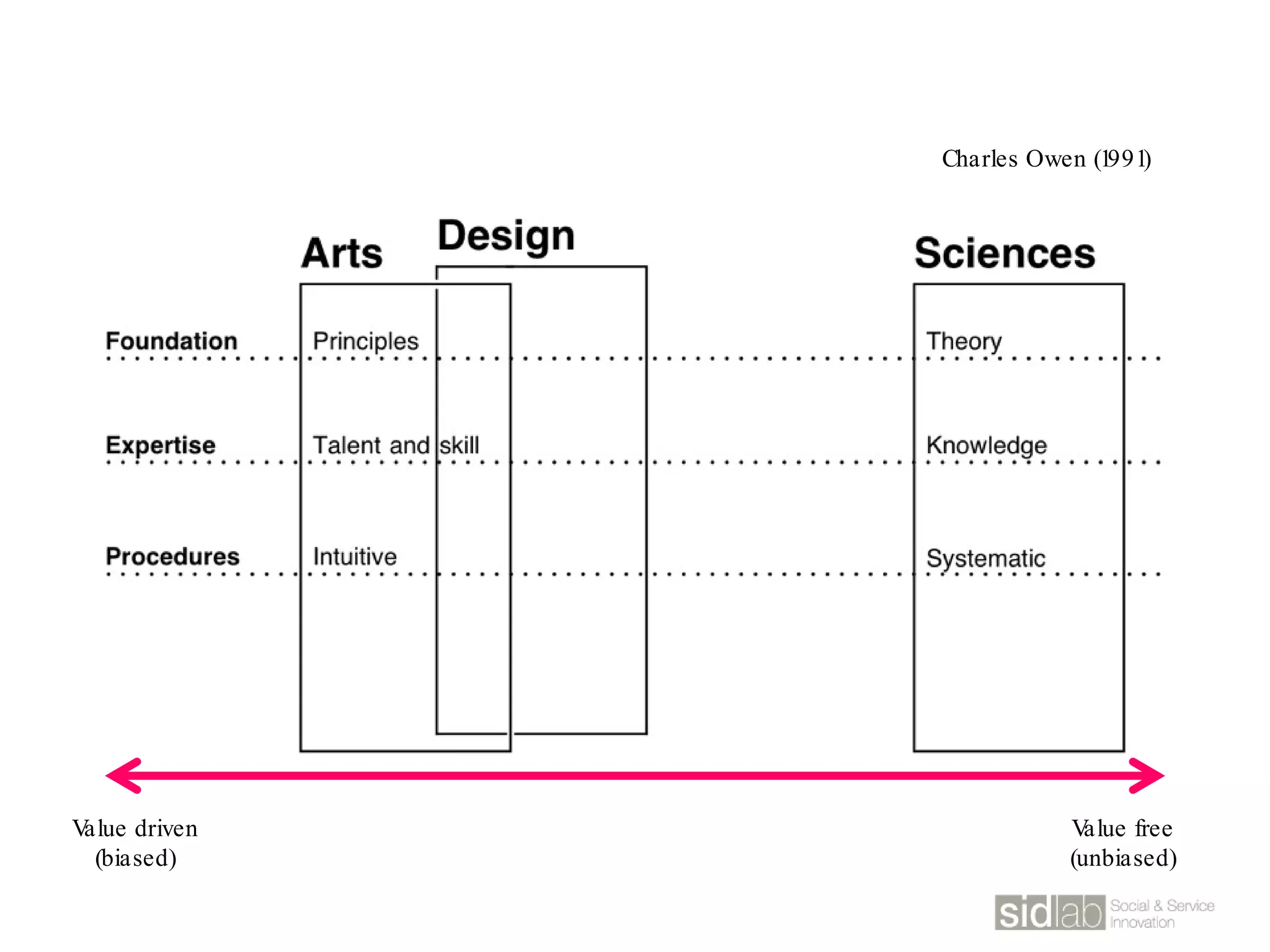
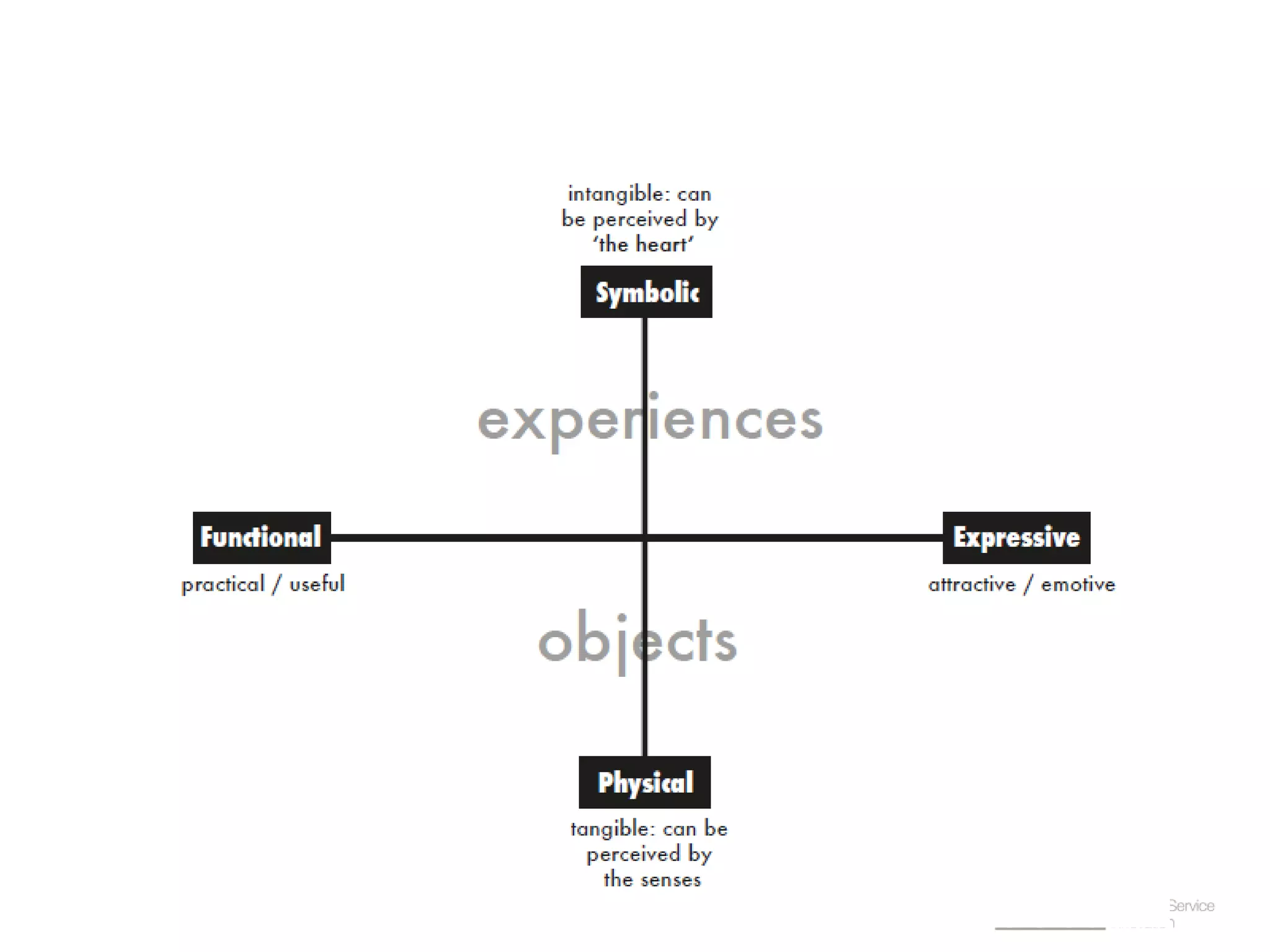
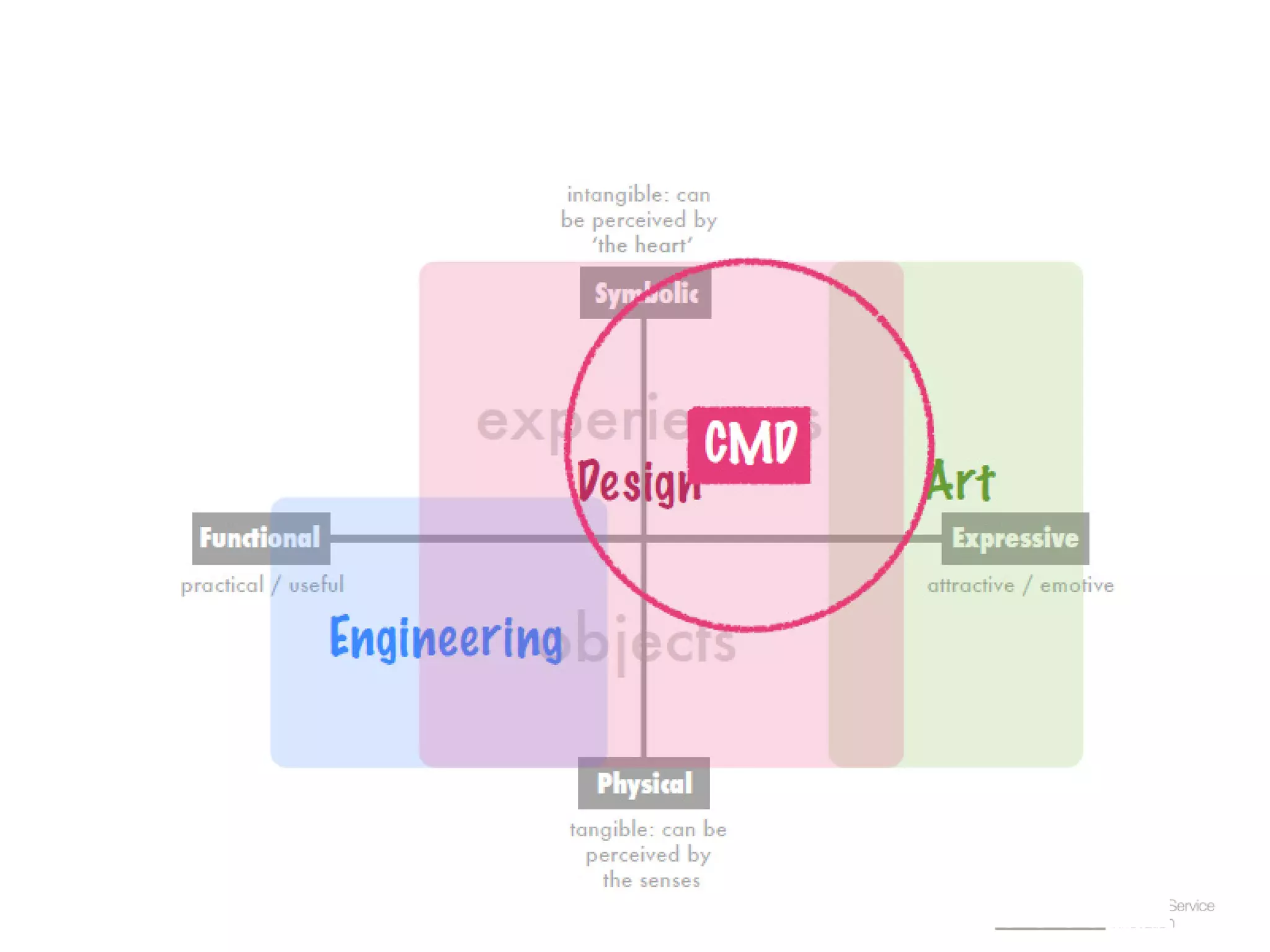
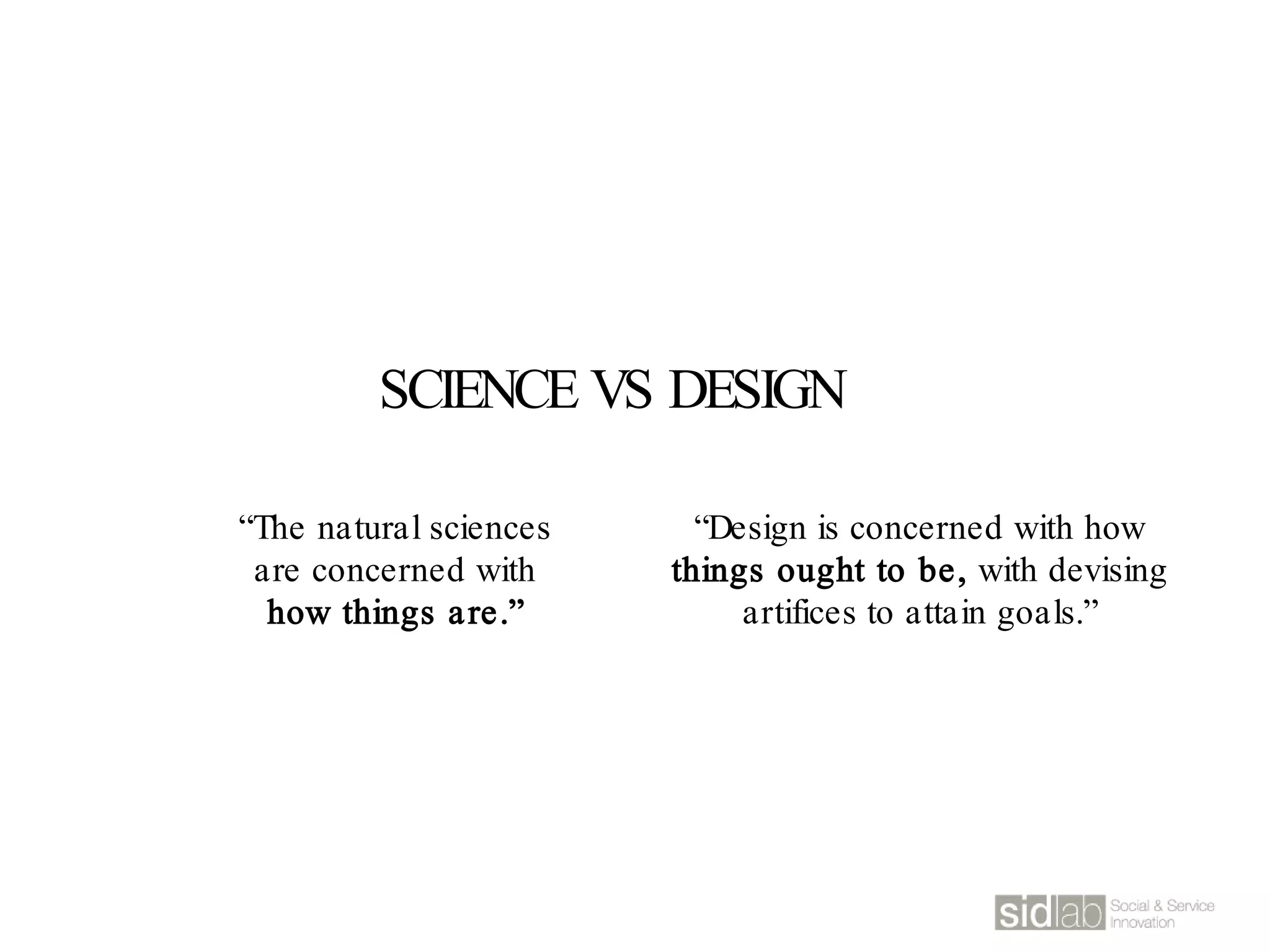
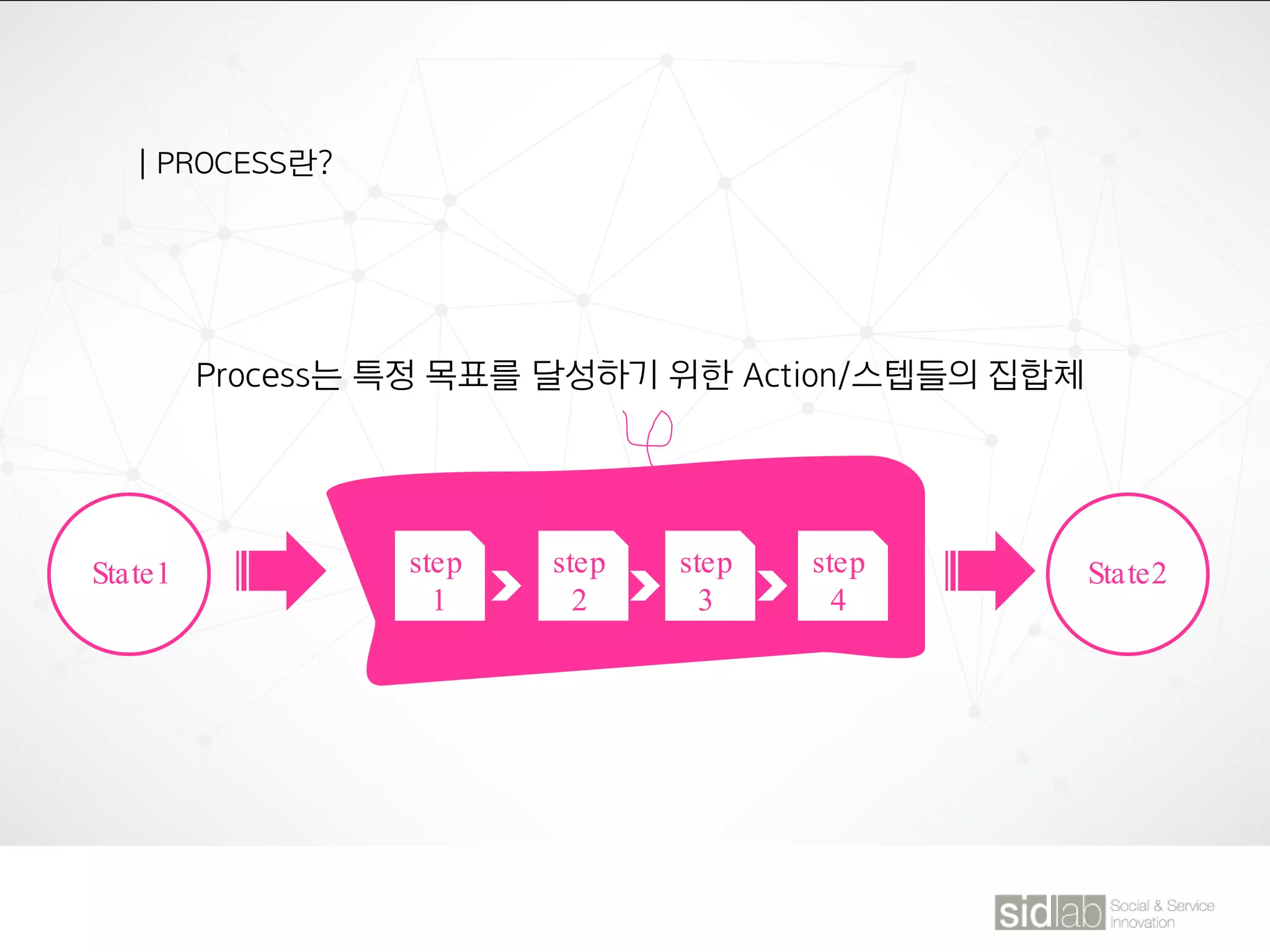
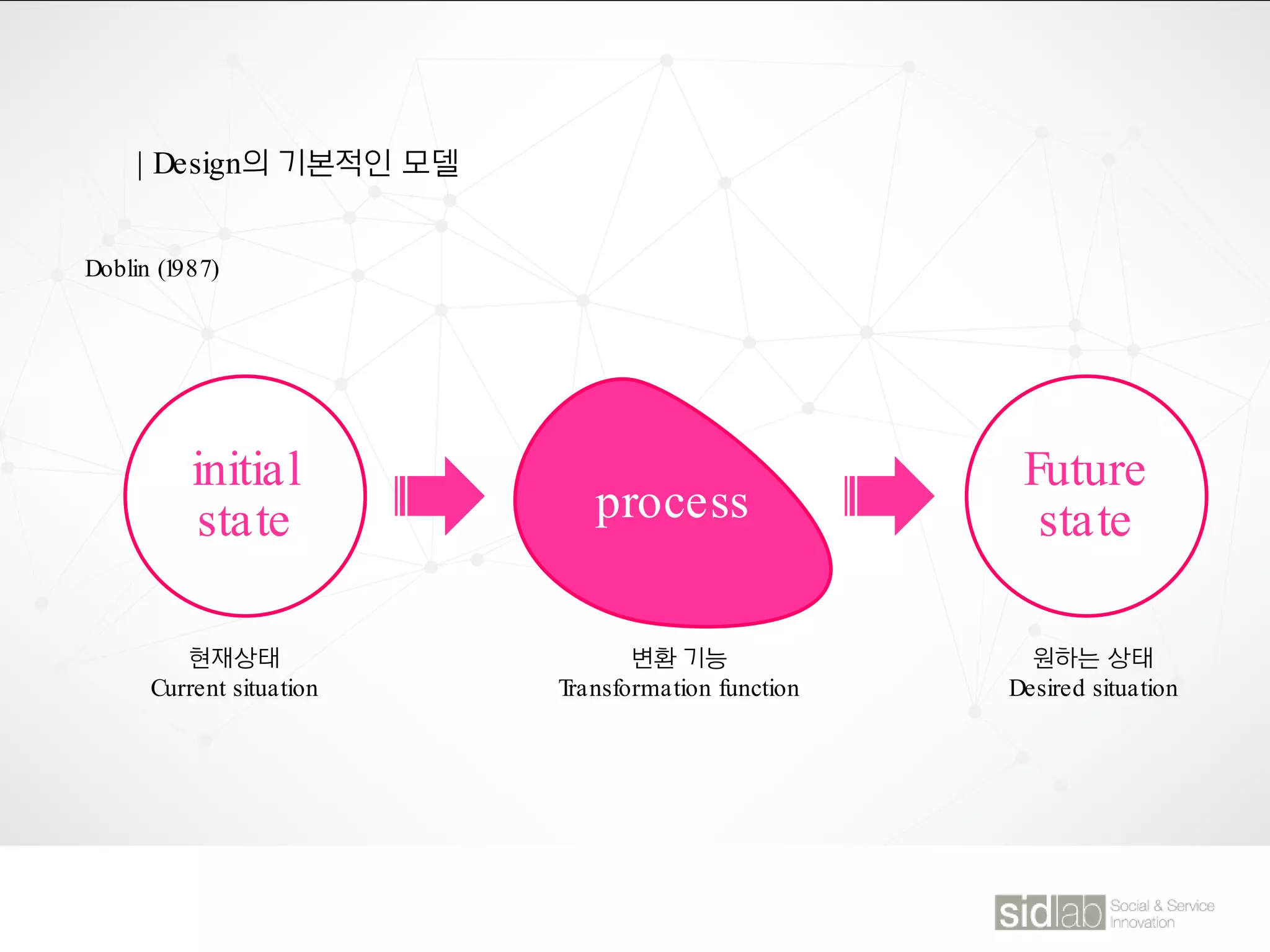
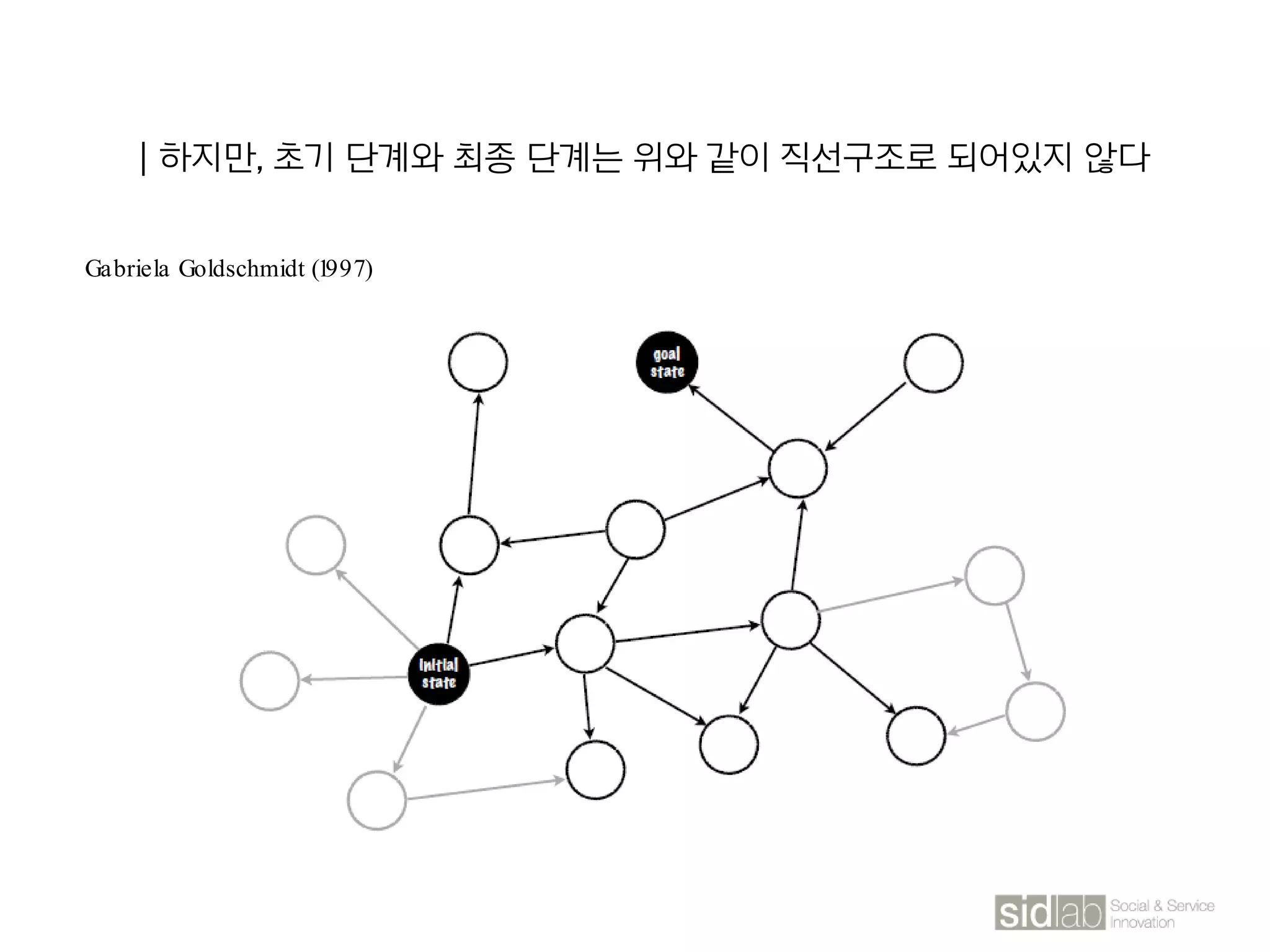
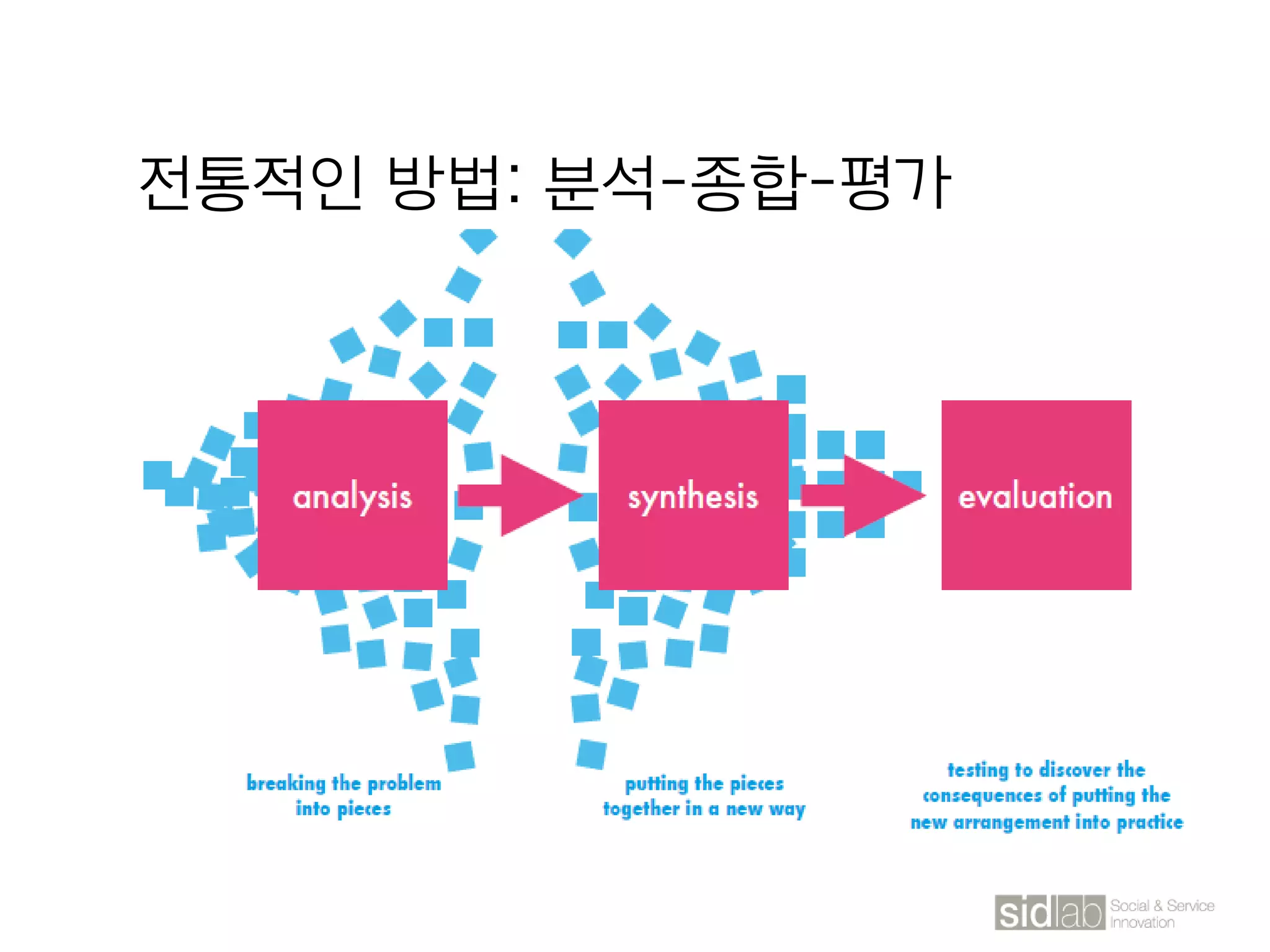
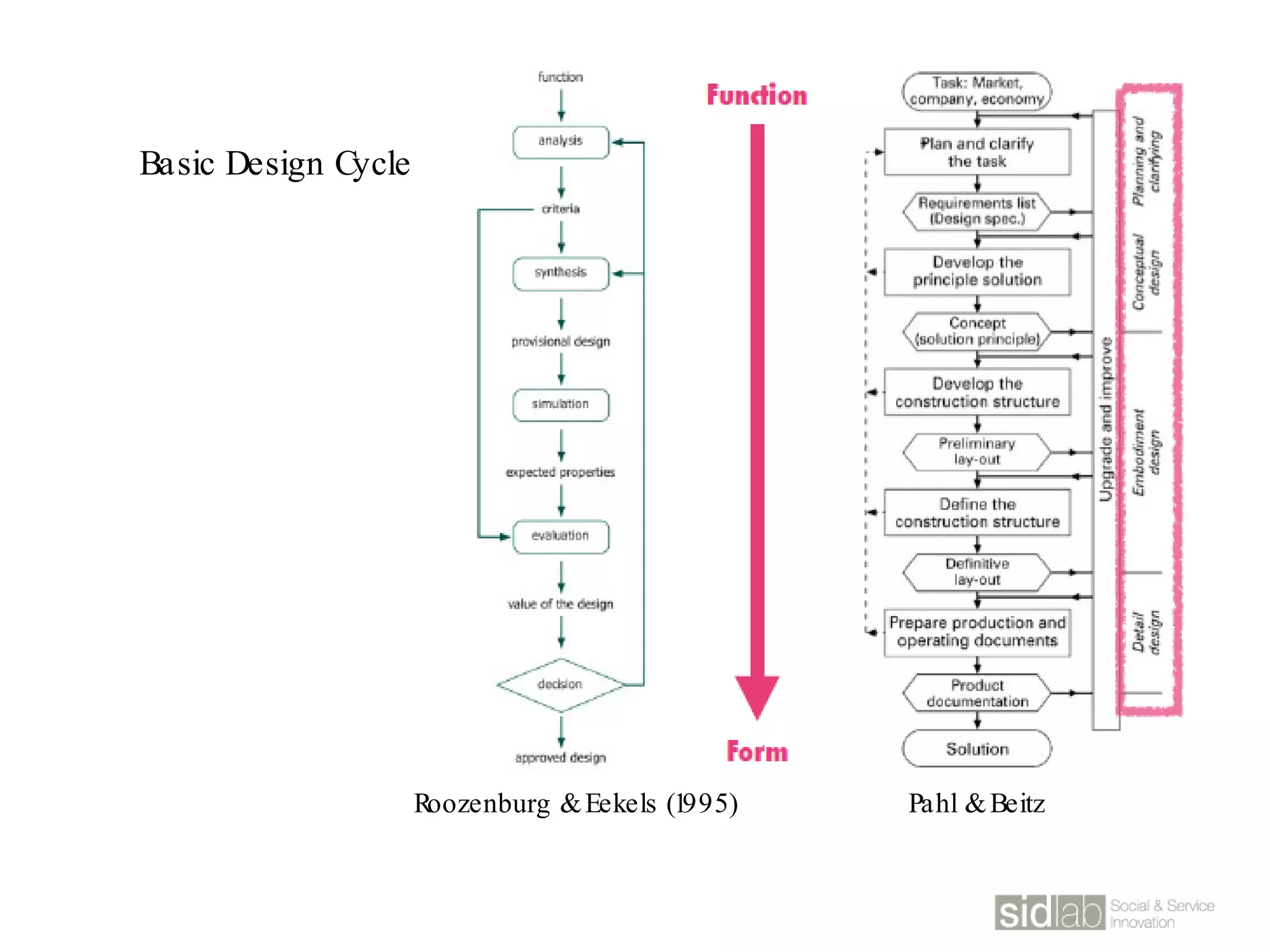
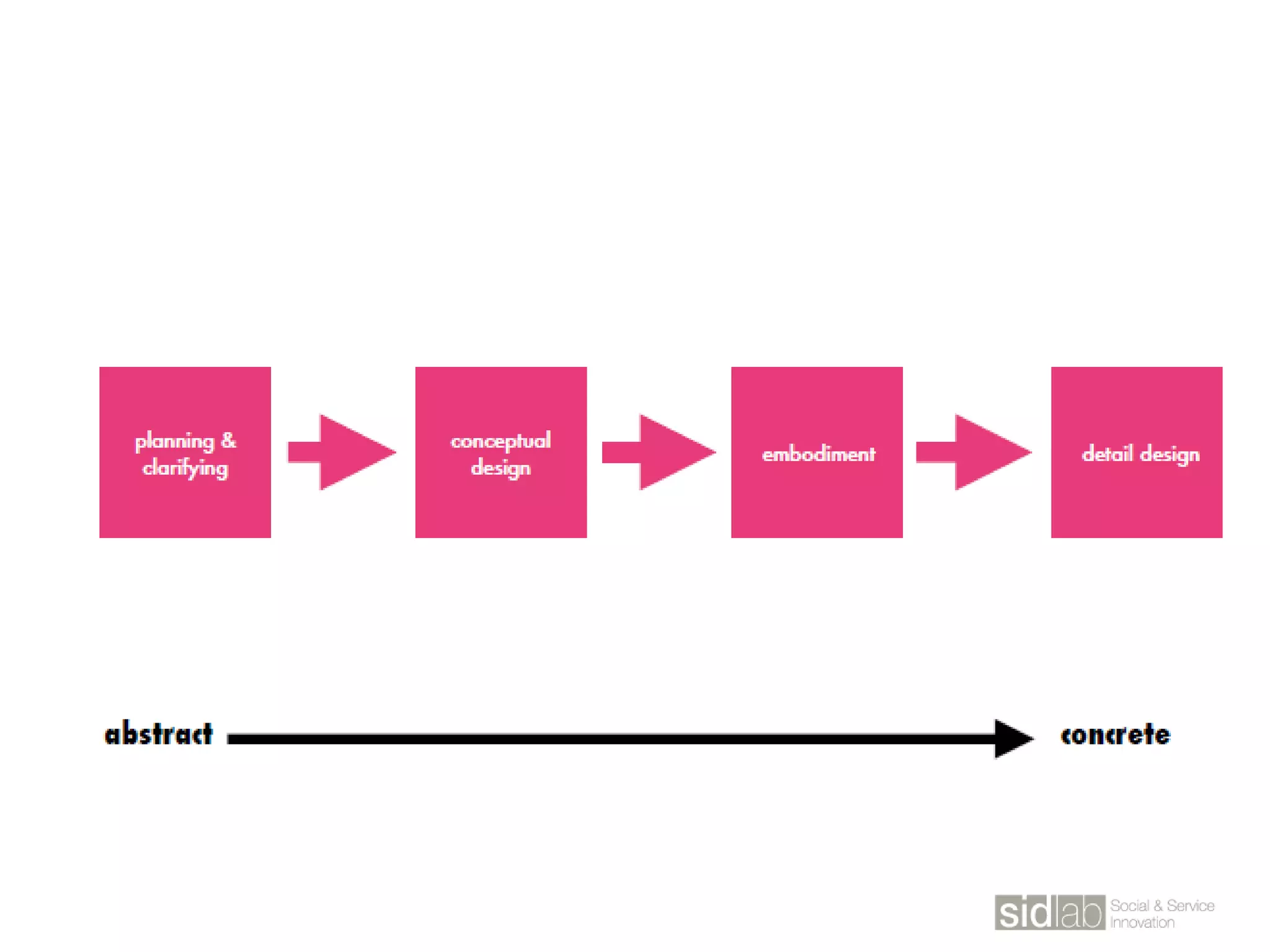
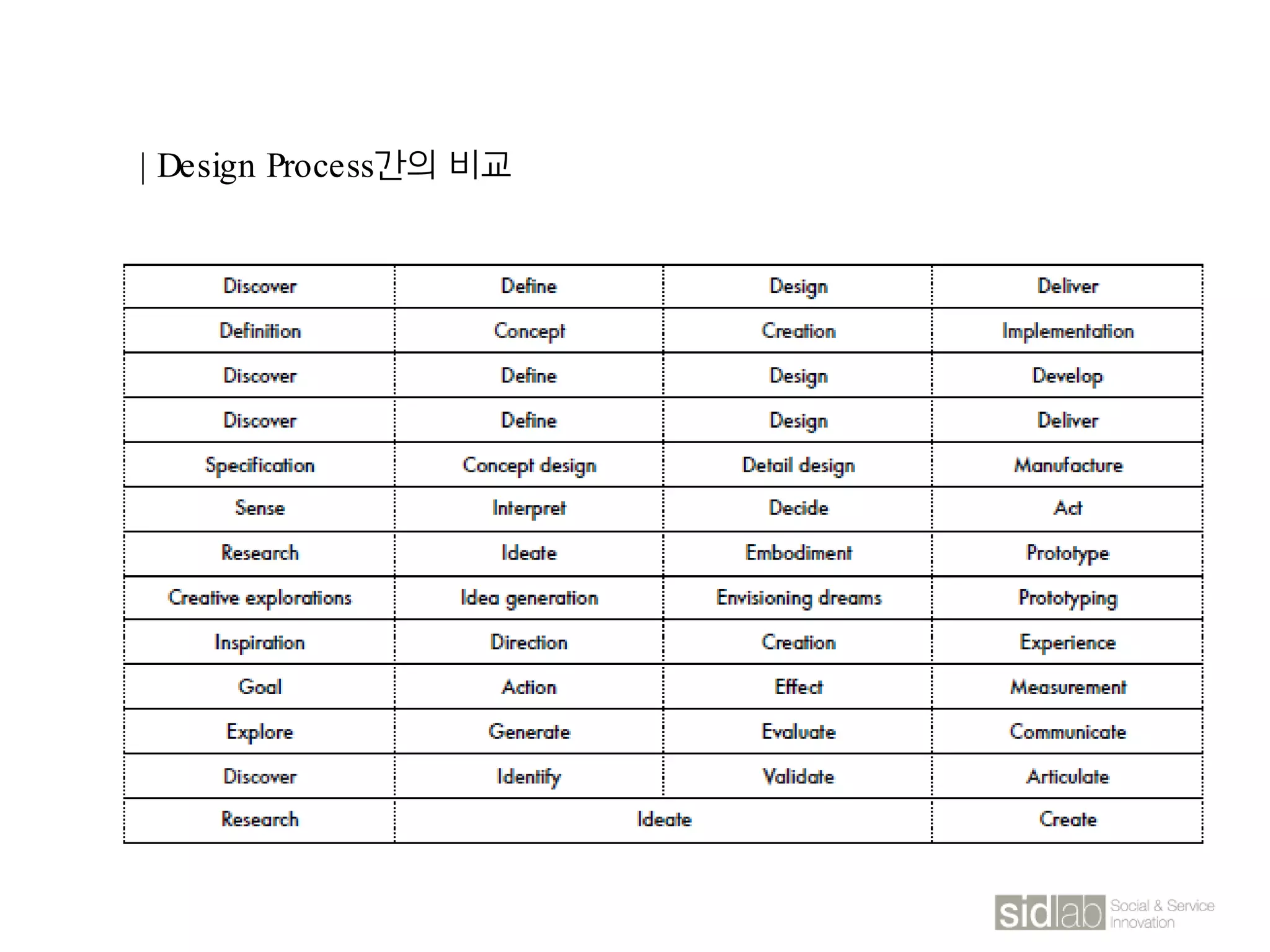
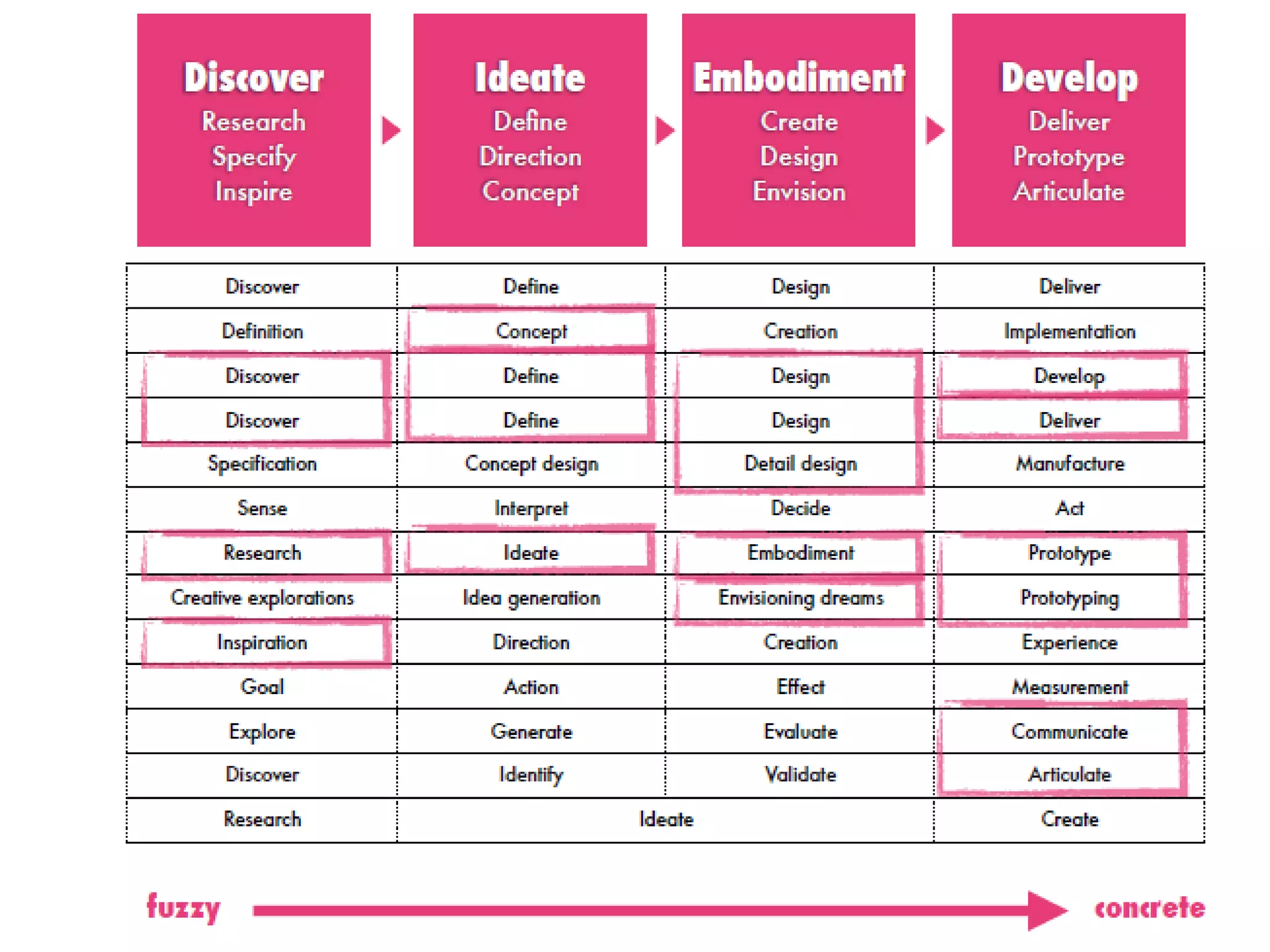
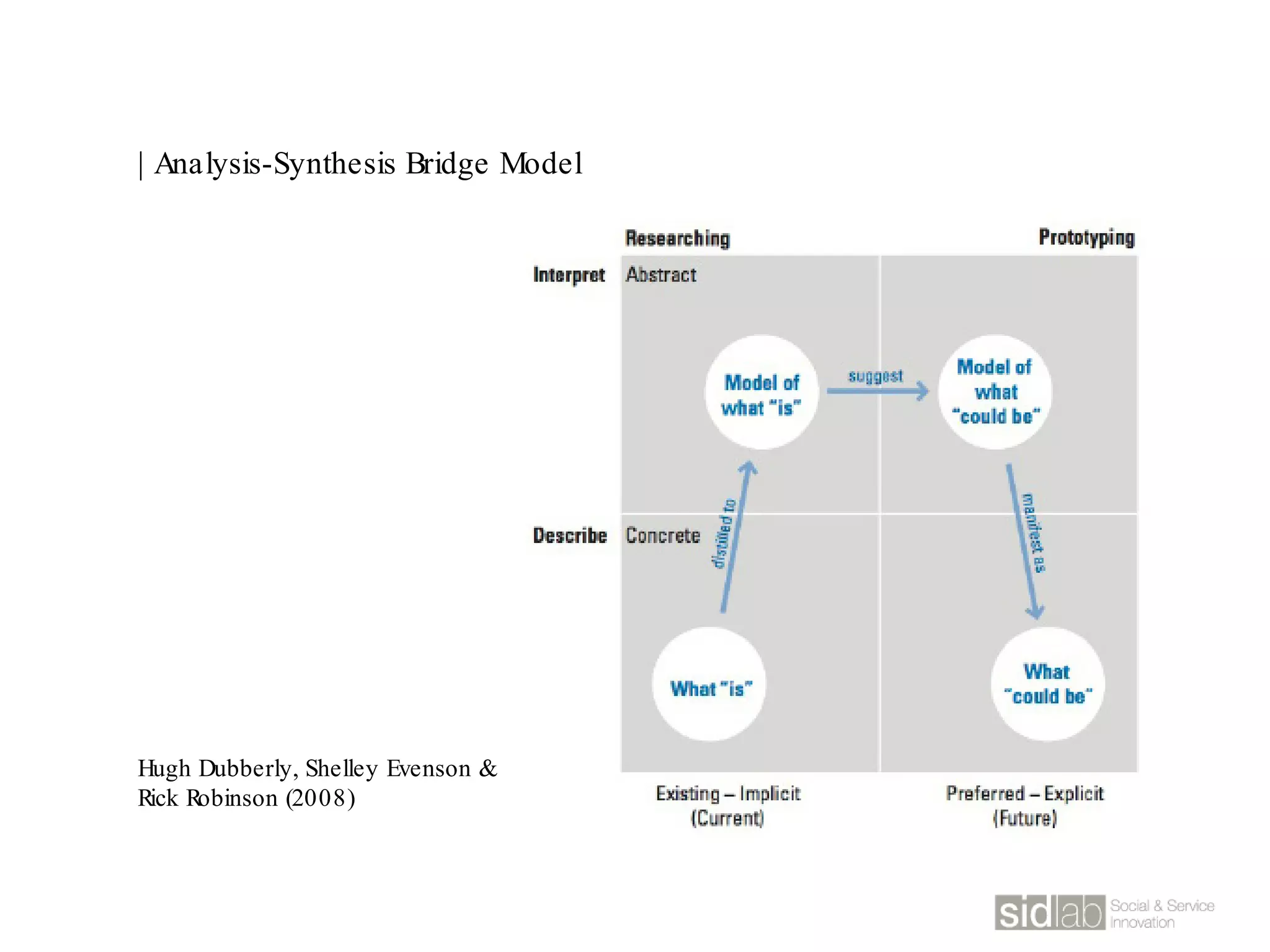
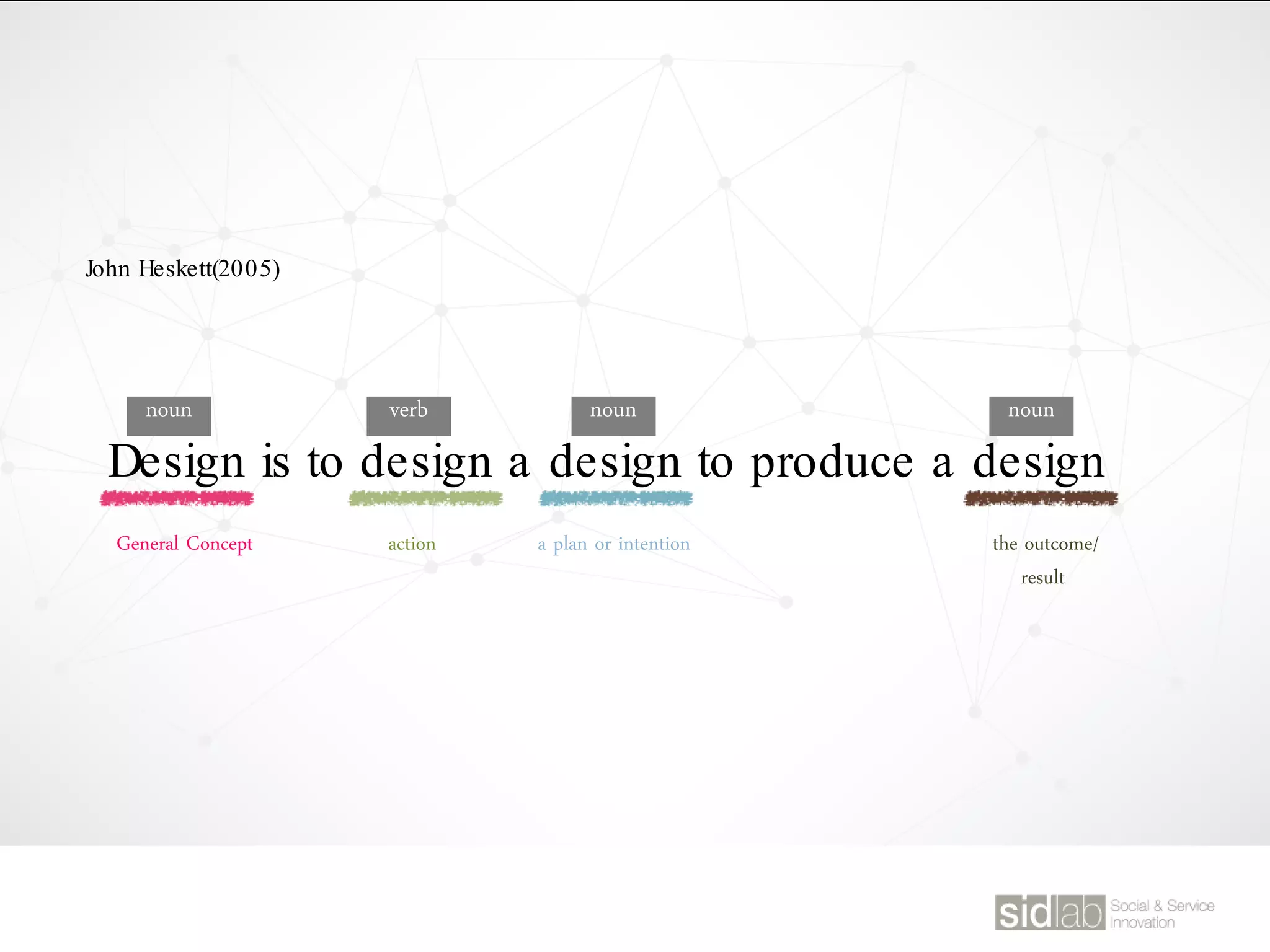
The document provides an overview of design thinking basics. It defines design using keywords like general concept, action, and plan/intention. Design is described as creating products, systems, or services that satisfy human needs and improve lives while respecting the environment. Designers are paid to envision better futures and make them happen. Design involves imagining what does not yet exist and making it real. It is about making decisions with uncertainty. The document also discusses what design processes are, how they involve steps to achieve goals, and how they are not always linear. It explores the positions of design between art and science.























!["Everyone can – and does – design.
We all design when we plan for
something new to happen, whether
that might be a new version of a recipe,
a new arrangement of the living
room furniture, or a new lay tour of a
personal web page. […] So design
thinking is something inherent within
human cognition; it is a key part of
what makes us human.” (p. 3)
Nigel Cross (2011)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/02classdefinition-150913082002-lva1-app6891/75/DT2015-CLASS02-29-2048.jpg)