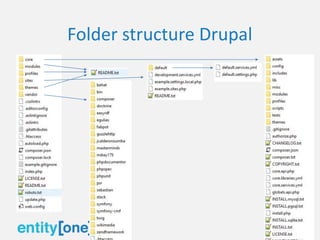
The document provides an overview of Drupal 8, highlighting its features, installation requirements, and core concepts such as nodes, entities, and modules. It introduces the administration areas of content, structure, appearance, configuration, and user management, along with multilingual capabilities in Drupal. Additionally, it emphasizes the community aspect of Drupal and its history, including the background of its creator.