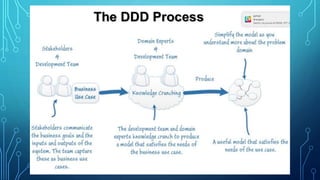
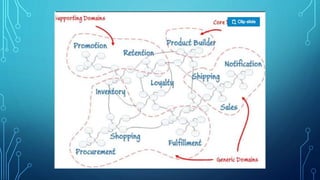
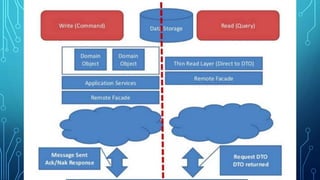
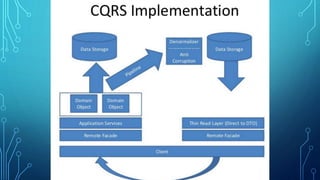
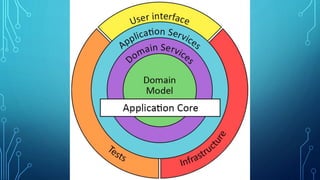
This document provides an overview of domain-driven design (DDD). It defines key DDD concepts like domain, model, ubiquitous language, bounded context, entities, value objects, aggregates, and services. The document explains that DDD is a software design approach for complex domains that models the domain and represents it in code. It focuses on exploring models collaboratively with domain experts and keeping the implementation tightly bound to the model.