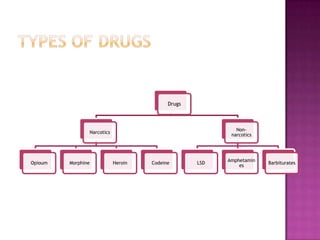
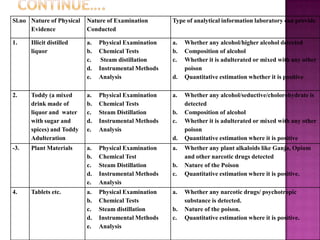
This document discusses different types of drugs including narcotics and non-narcotics. It provides details on opium, morphine, heroin, codeine, barbiturates, cocaine, amphetamines, methamphetamine, marijuana, LSD and other drugs. It explains that narcotics are derived from the Greek word meaning lethargy and includes opium-based drugs and barbiturates. Non-narcotics include LSD, amphetamines and are divided into depressants, stimulants and hallucinogens. The document also outlines the Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances Act of 1985 in India and the role of forensic laboratories in drug identification and analysis