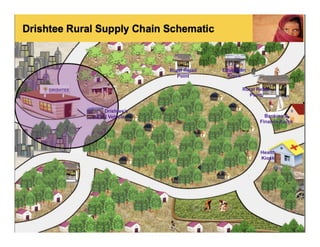
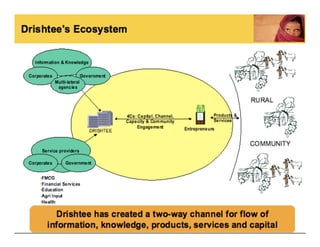
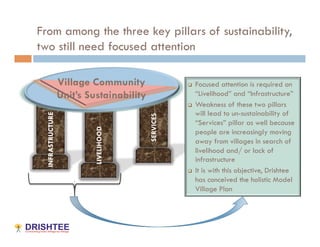
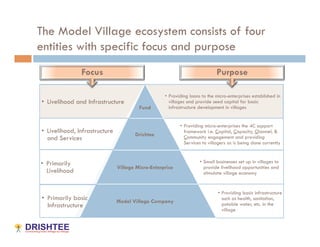
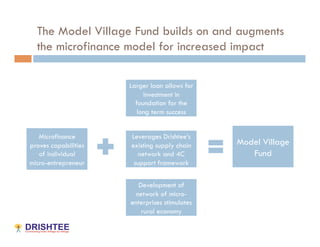
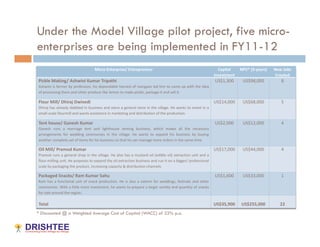
The Model Village Plan aims to promote sustainability in rural India by addressing key challenges faced by villages through a comprehensive approach focusing on livelihood, infrastructure, and services. Drishtee has established a rural supply chain network, supporting micro-enterprises and enhancing community resources, with the goal of scaling up the successful model from one pilot village to 500 by 2016. Participation is encouraged for critical evaluation, development of new business models, and funding support for the initiative.