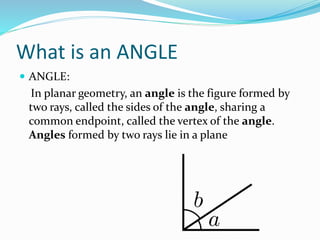
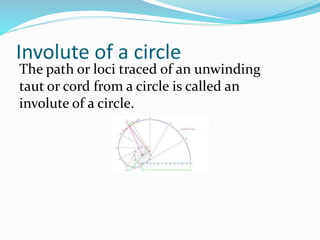
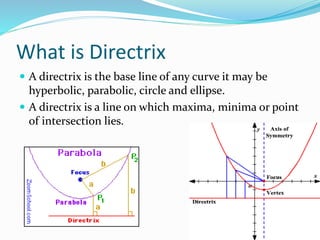
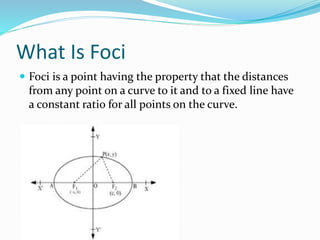
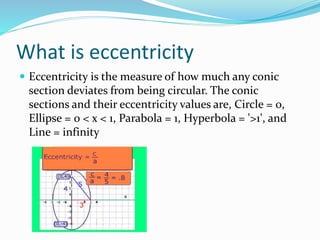
This document discusses various geometric shapes and concepts. It defines angles, polygons, involutes, ellipses, hyperbolas, parabolas, directrix, foci, and eccentricity. Some key points covered include: angles are formed by two rays with a common endpoint; there are four types of angles; polygons are plane figures formed by straight line segments that form a closed chain; involutes are curves traced by unwinding a thread from a circle or polygon; ellipses and hyperbolas are conic sections formed by intersecting a plane with a cone; parabolas are curves formed when a plane is parallel to a cone's side; directrix is the base line of different curves; foci are points related