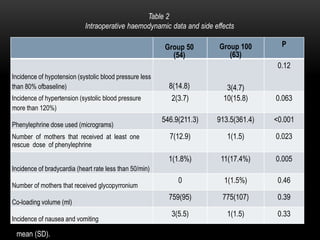
This document summarizes a study that compared two different phenylephrine (PE) infusion rates for preventing hypotension during spinal anesthesia for elective cesarean sections. The study randomized 117 patients to receive either a PE infusion of 50 mcg/min (Group 50) or 100 mcg/min (Group 100). The results found that a PE rate of 50 mcg/min was as effective as 100 mcg/min at maintaining blood pressure within normal ranges. Group 50 also had significantly less maternal bradycardia (1.8% vs 17.4%) compared to Group 100. Neonatal outcomes were similar between the two groups, including Apgar scores, umbilical cord blood gases, and acid-