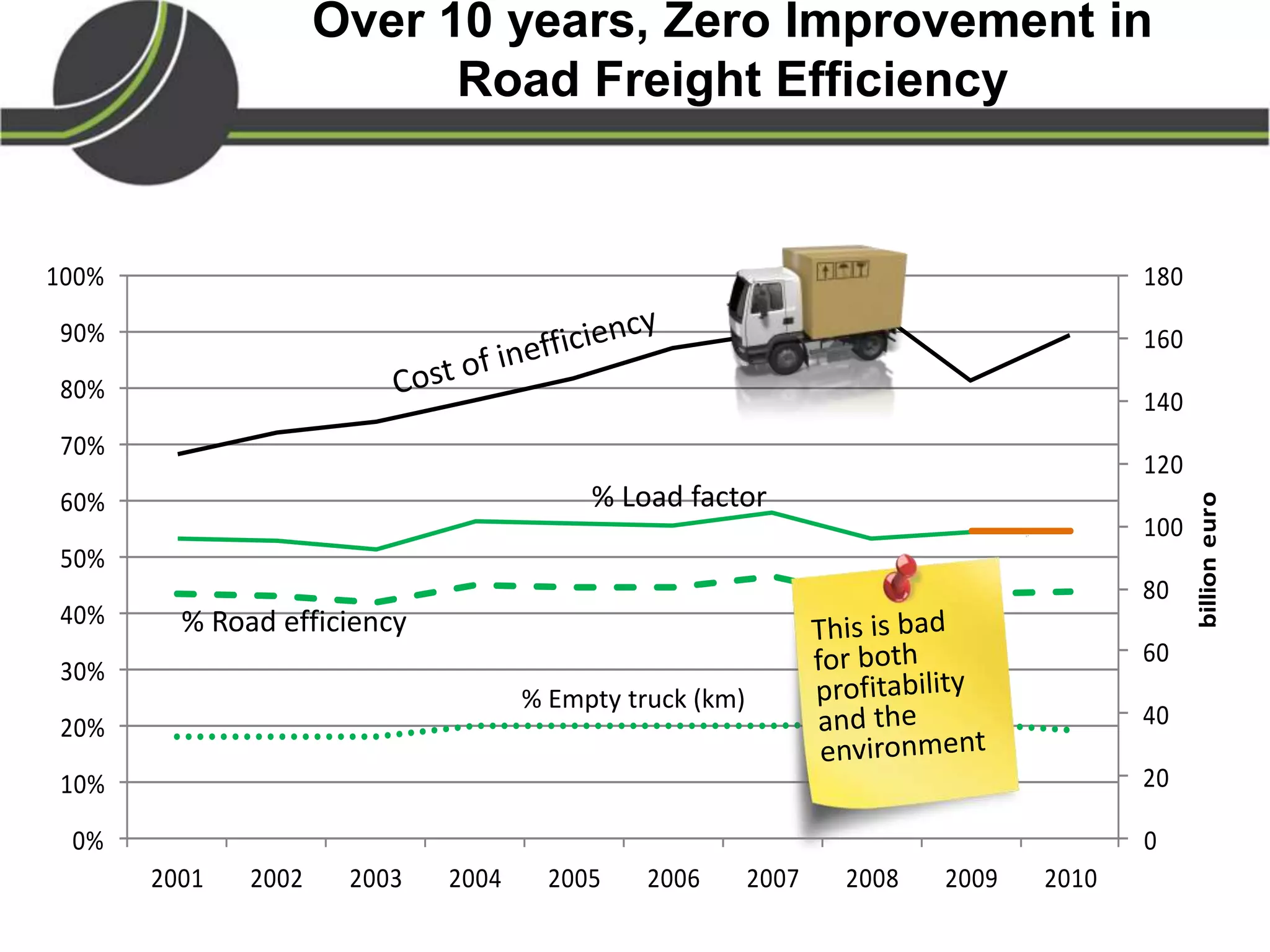
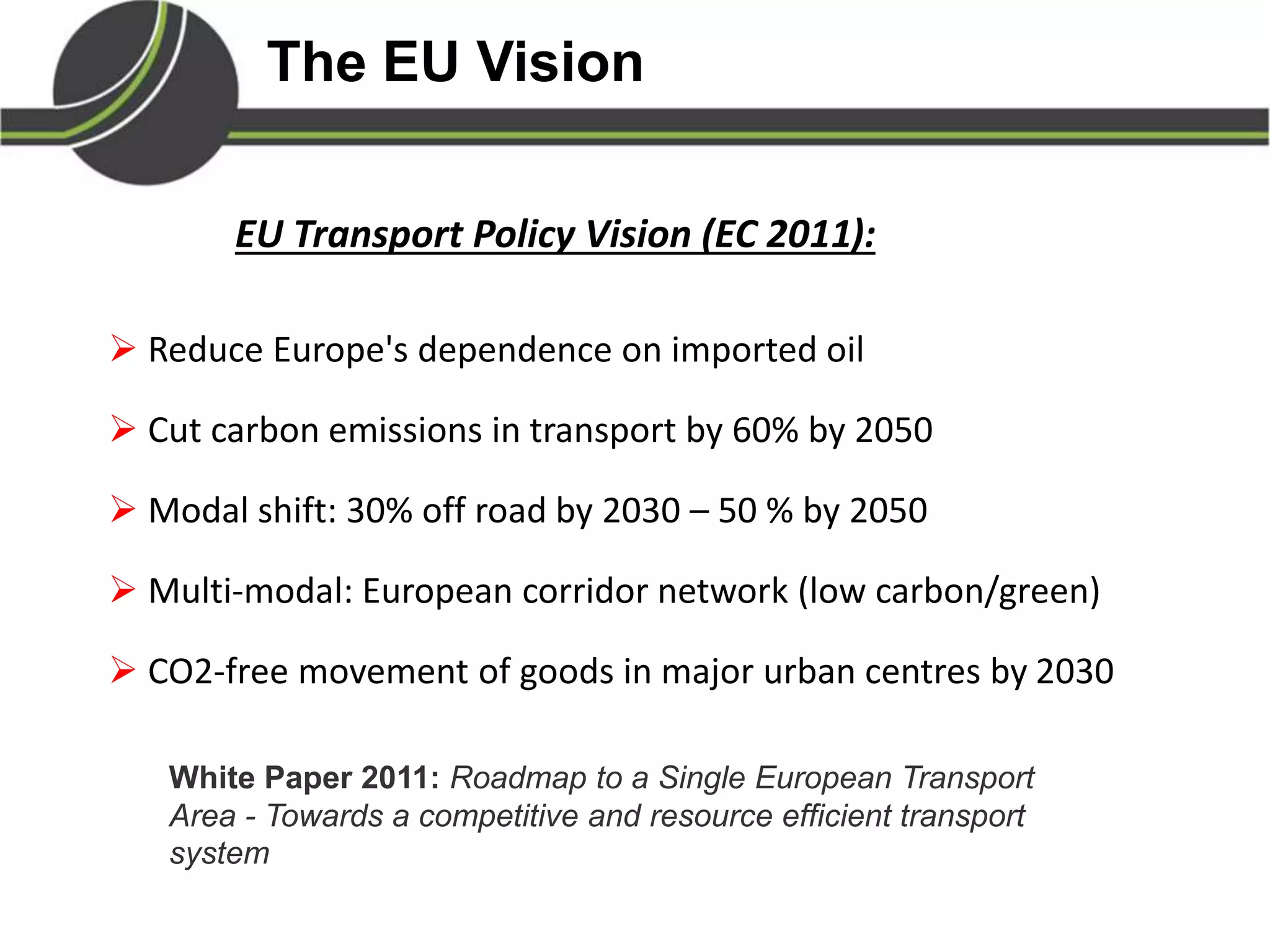
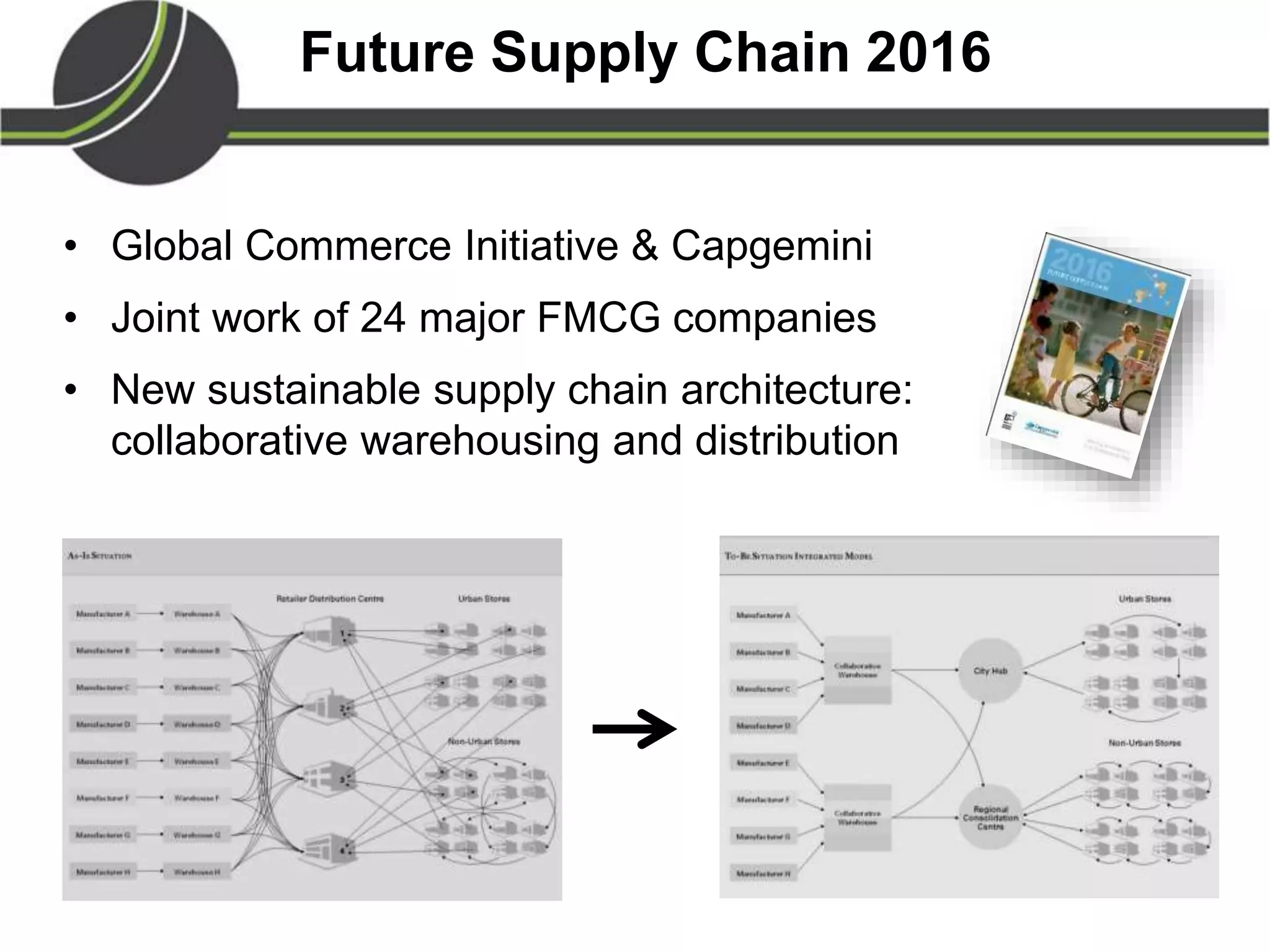
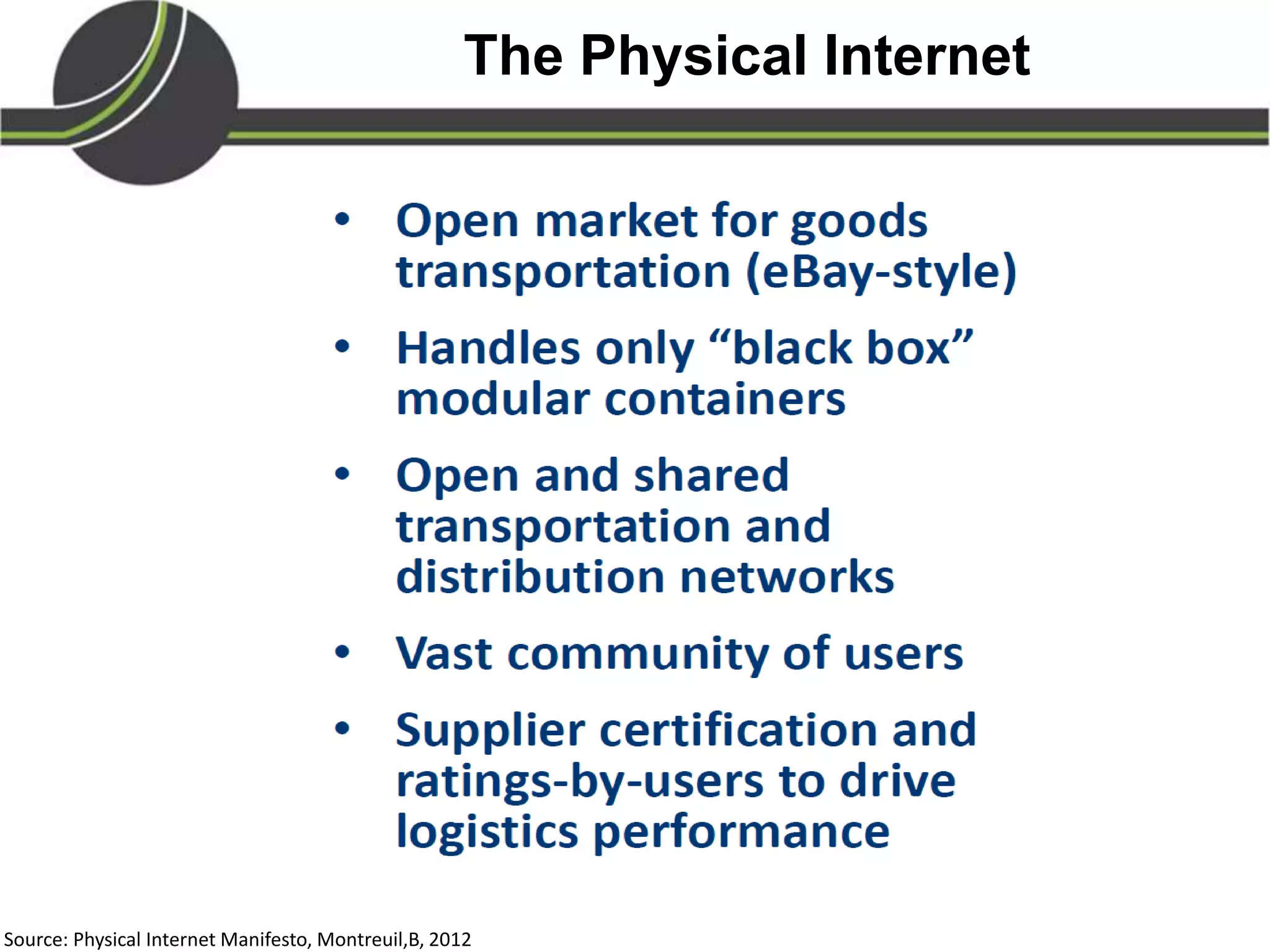
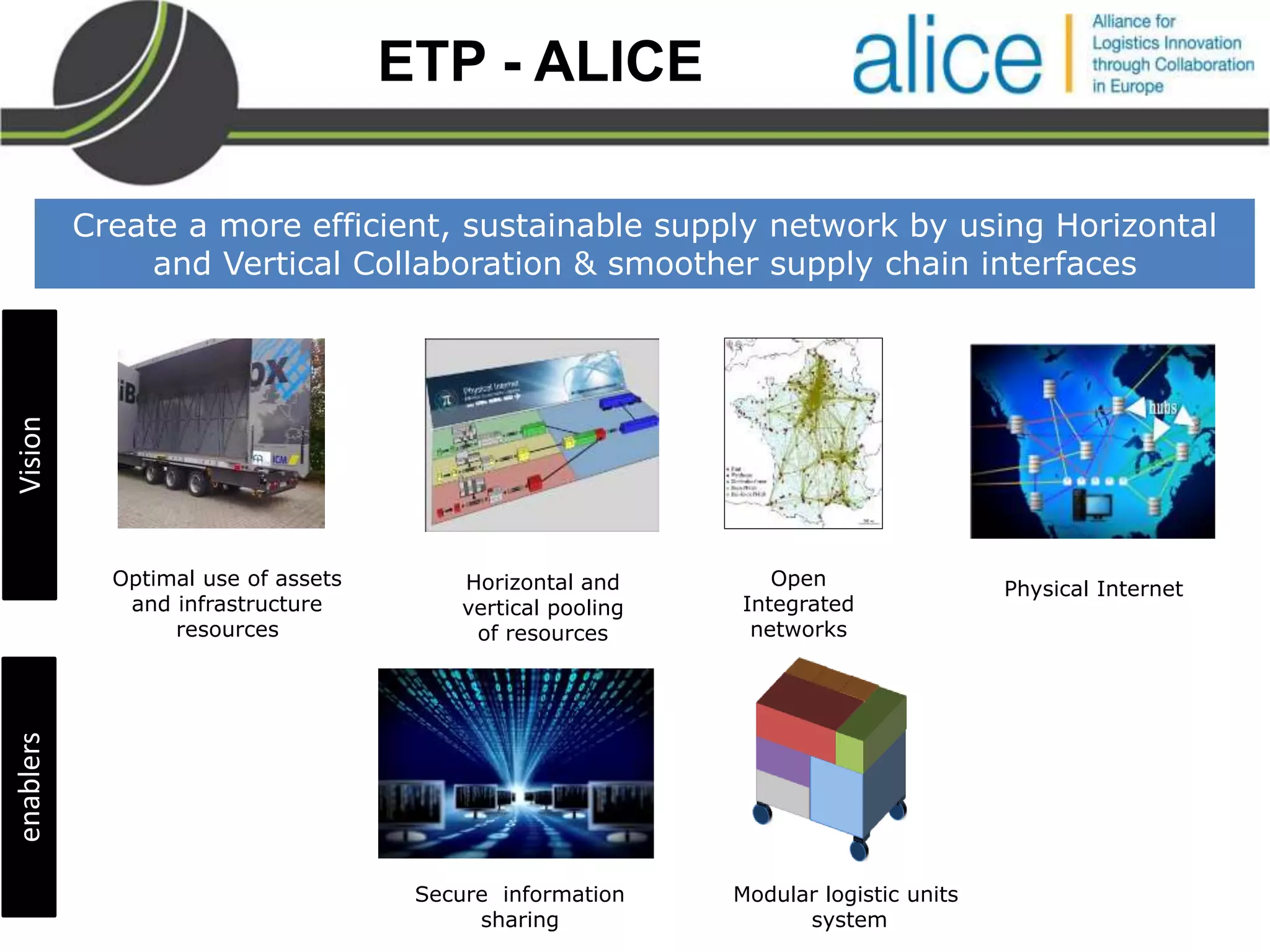
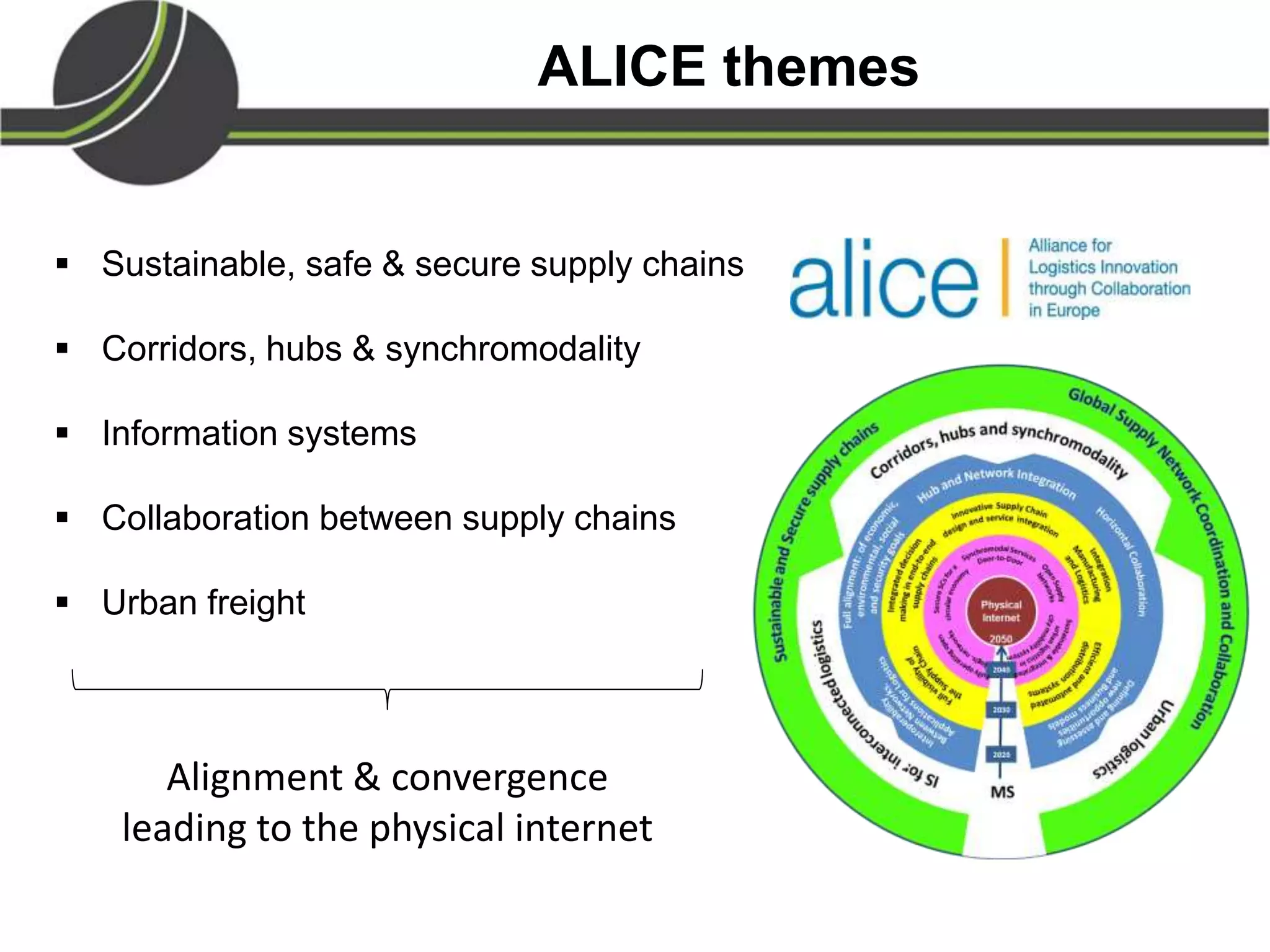
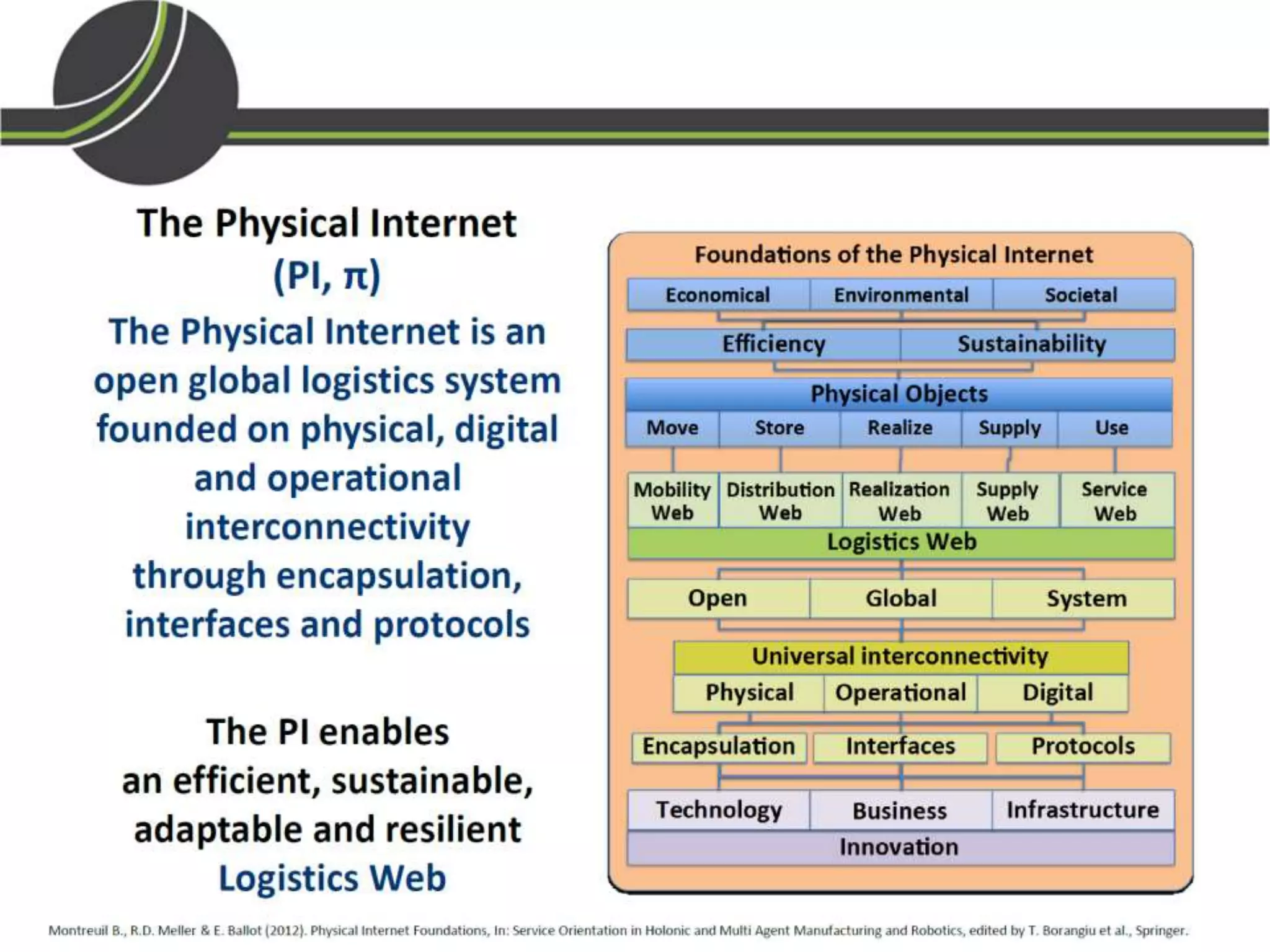
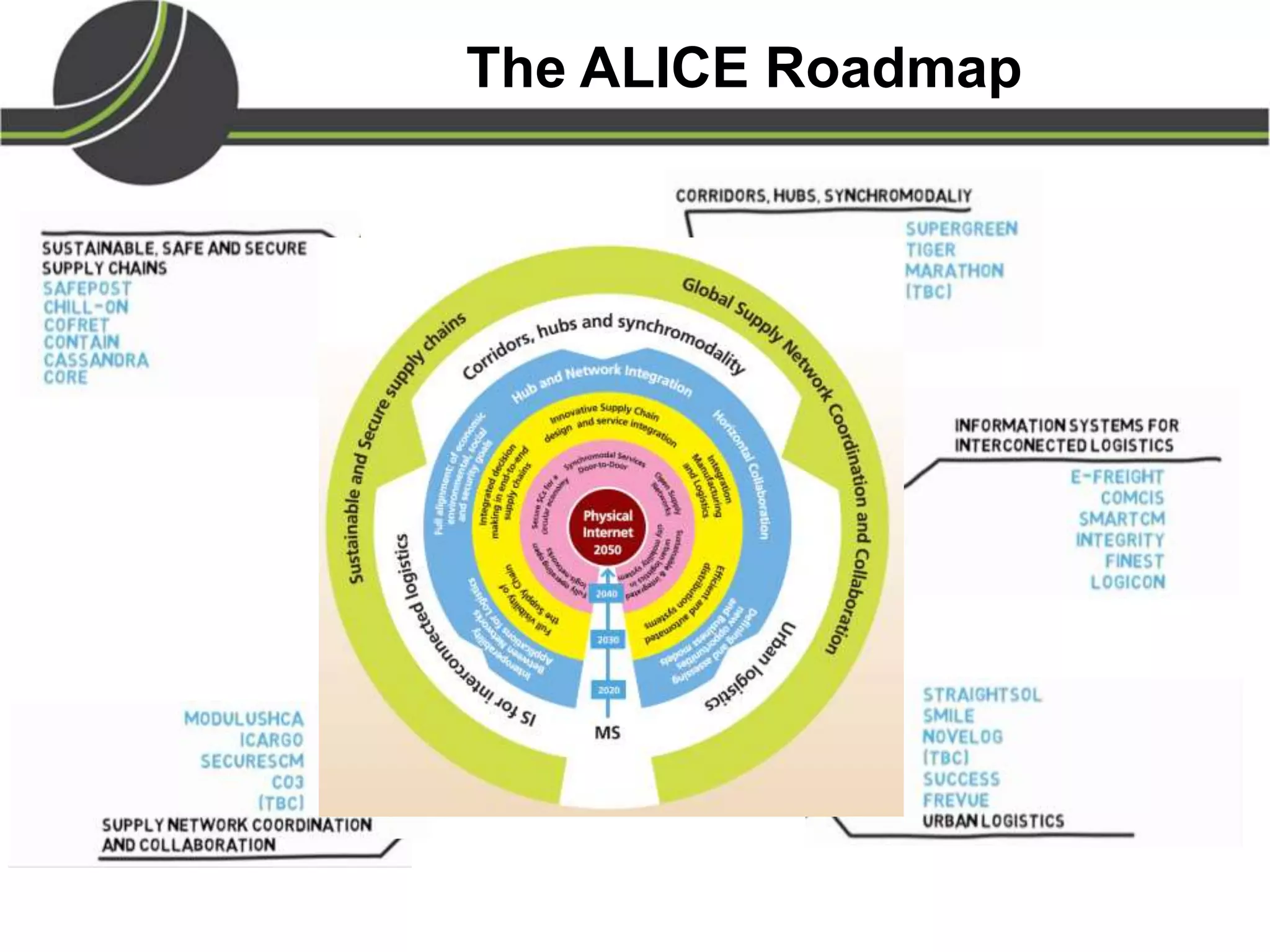
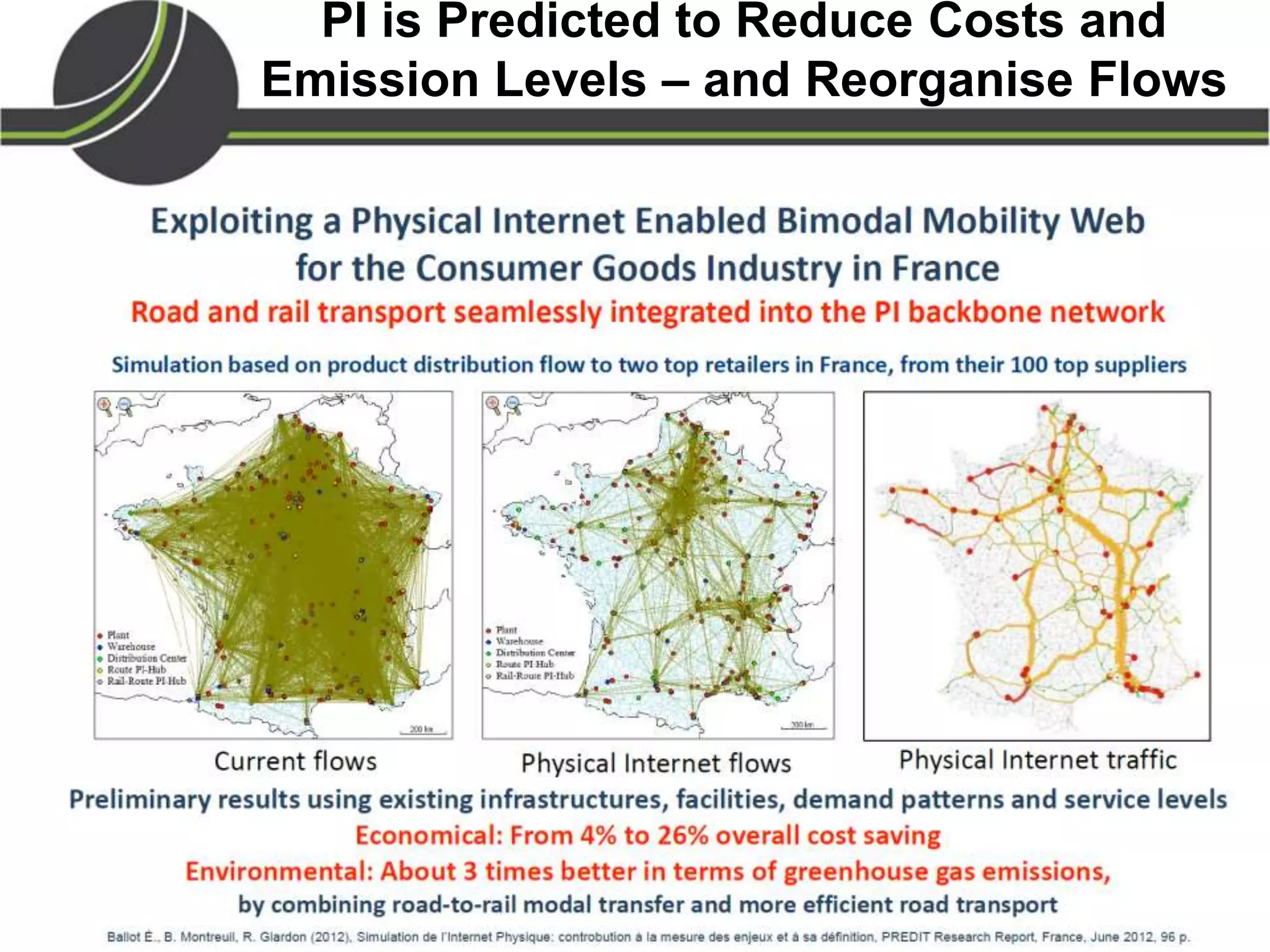
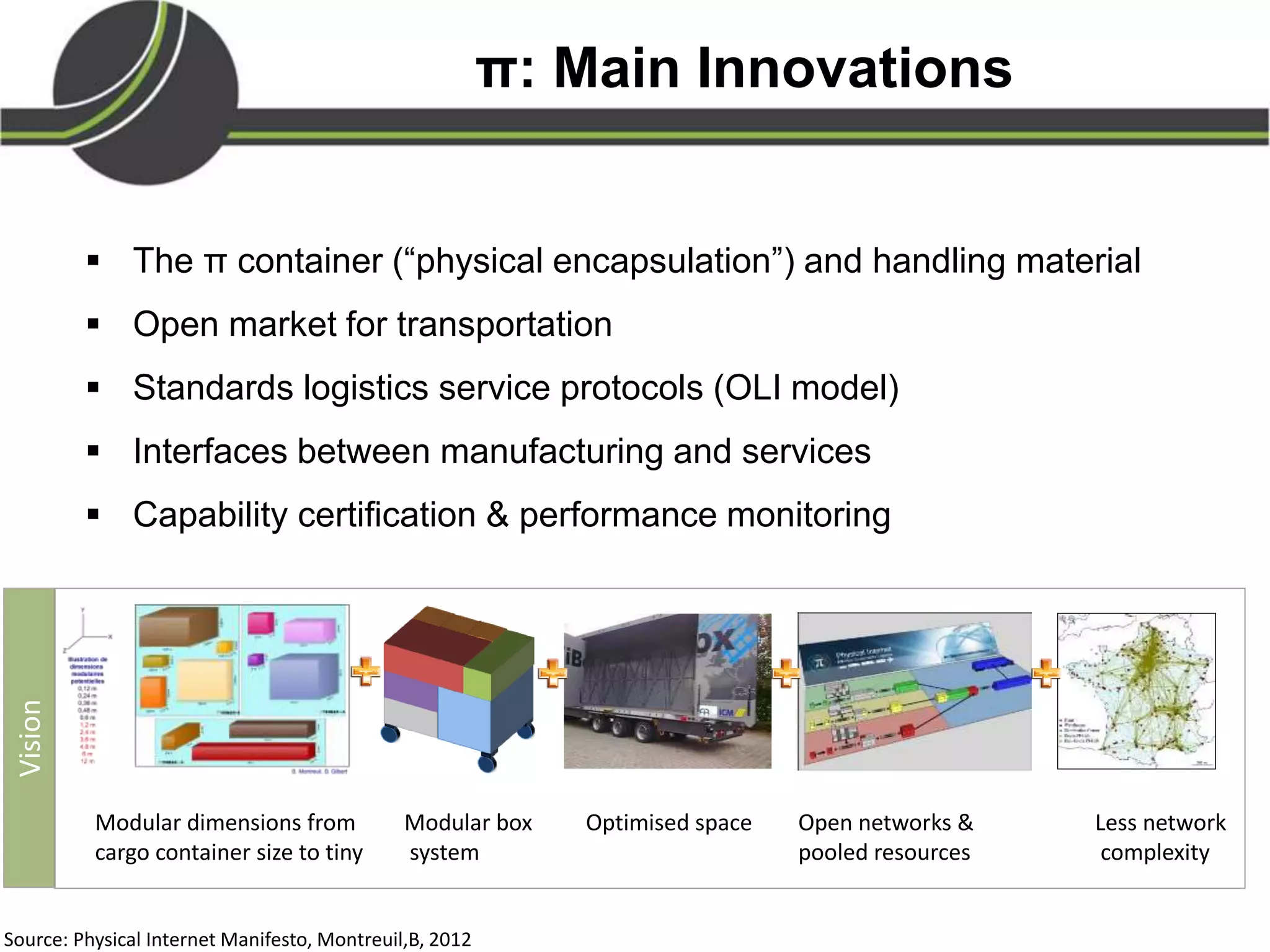
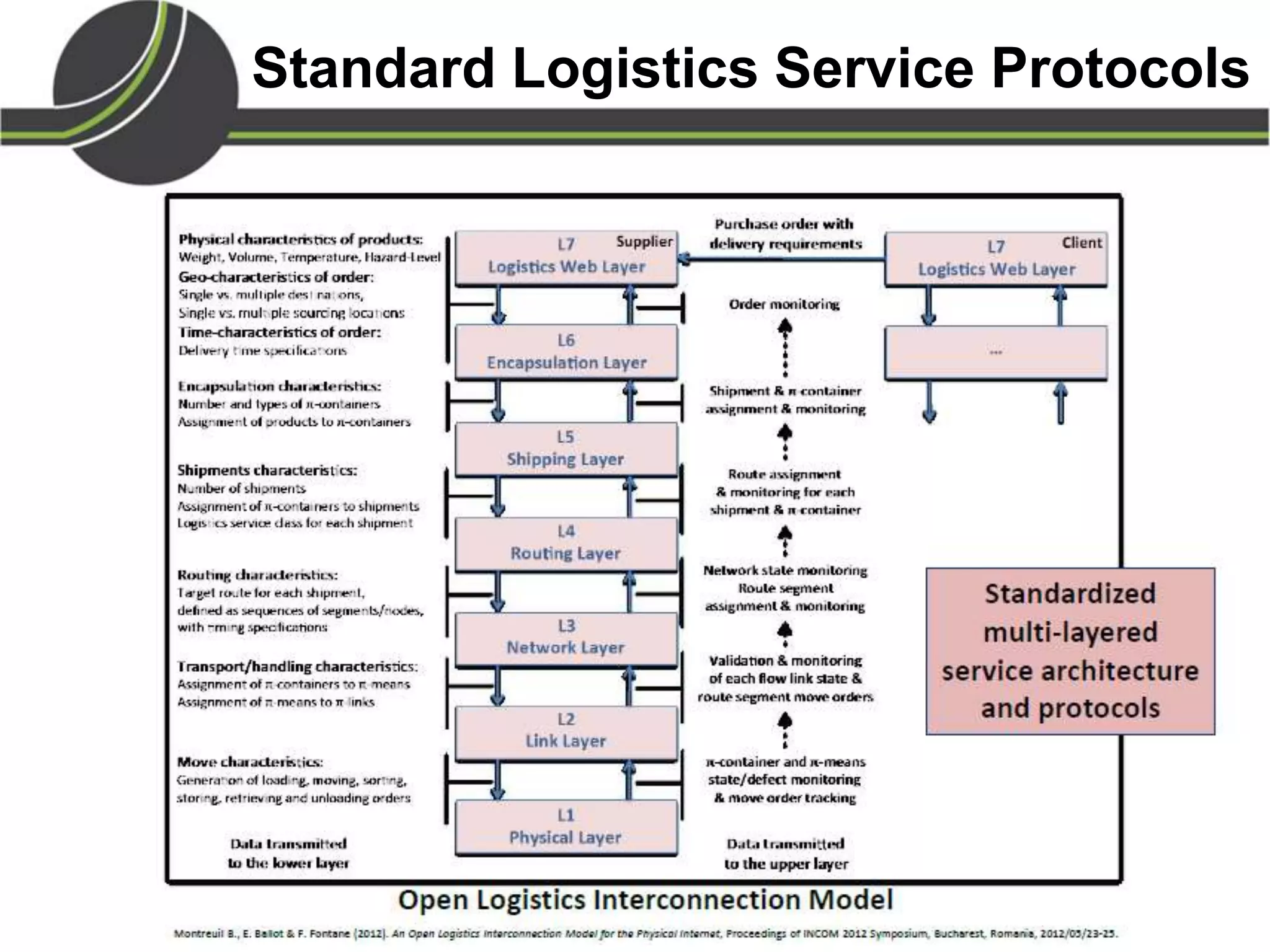
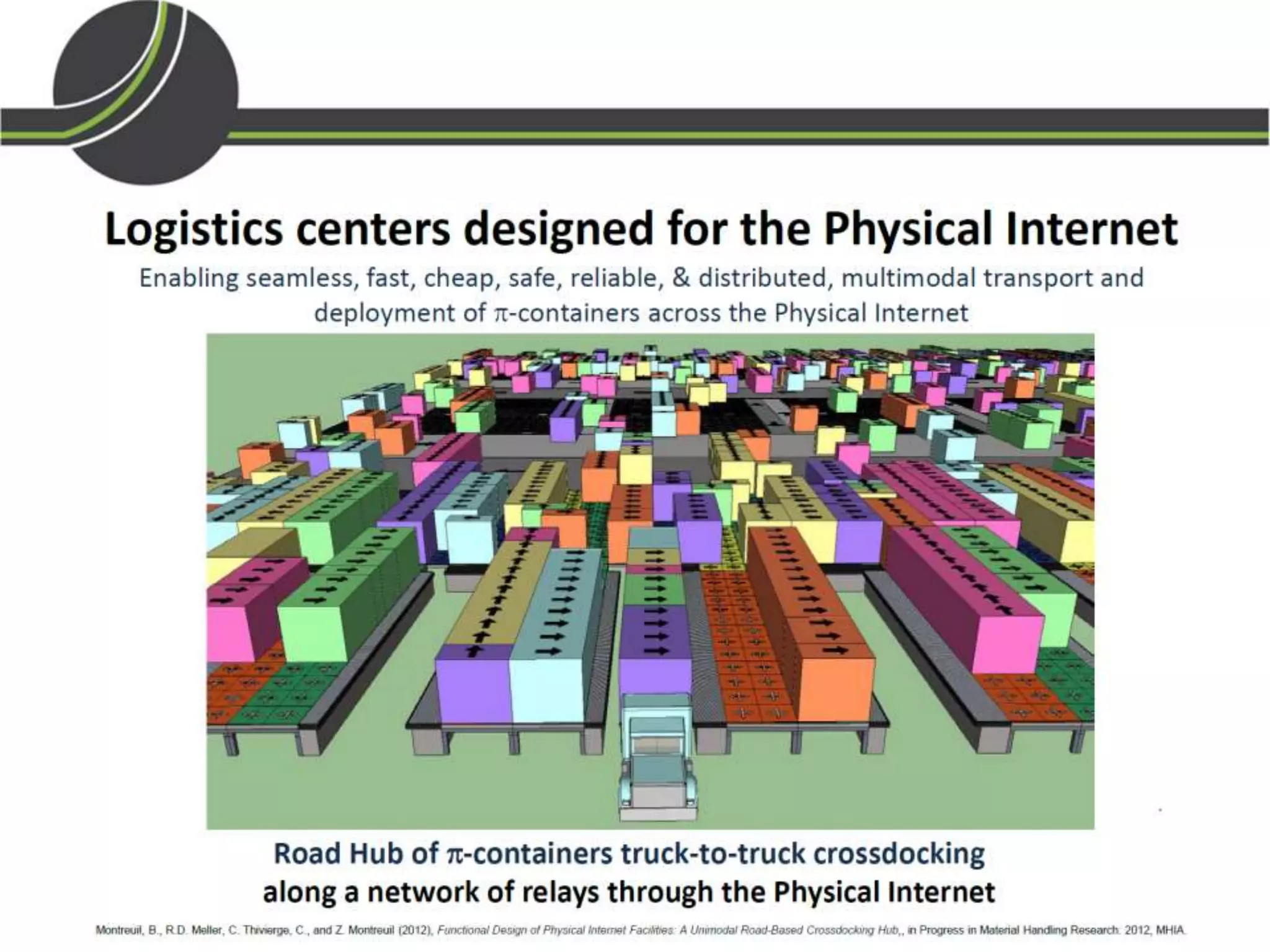
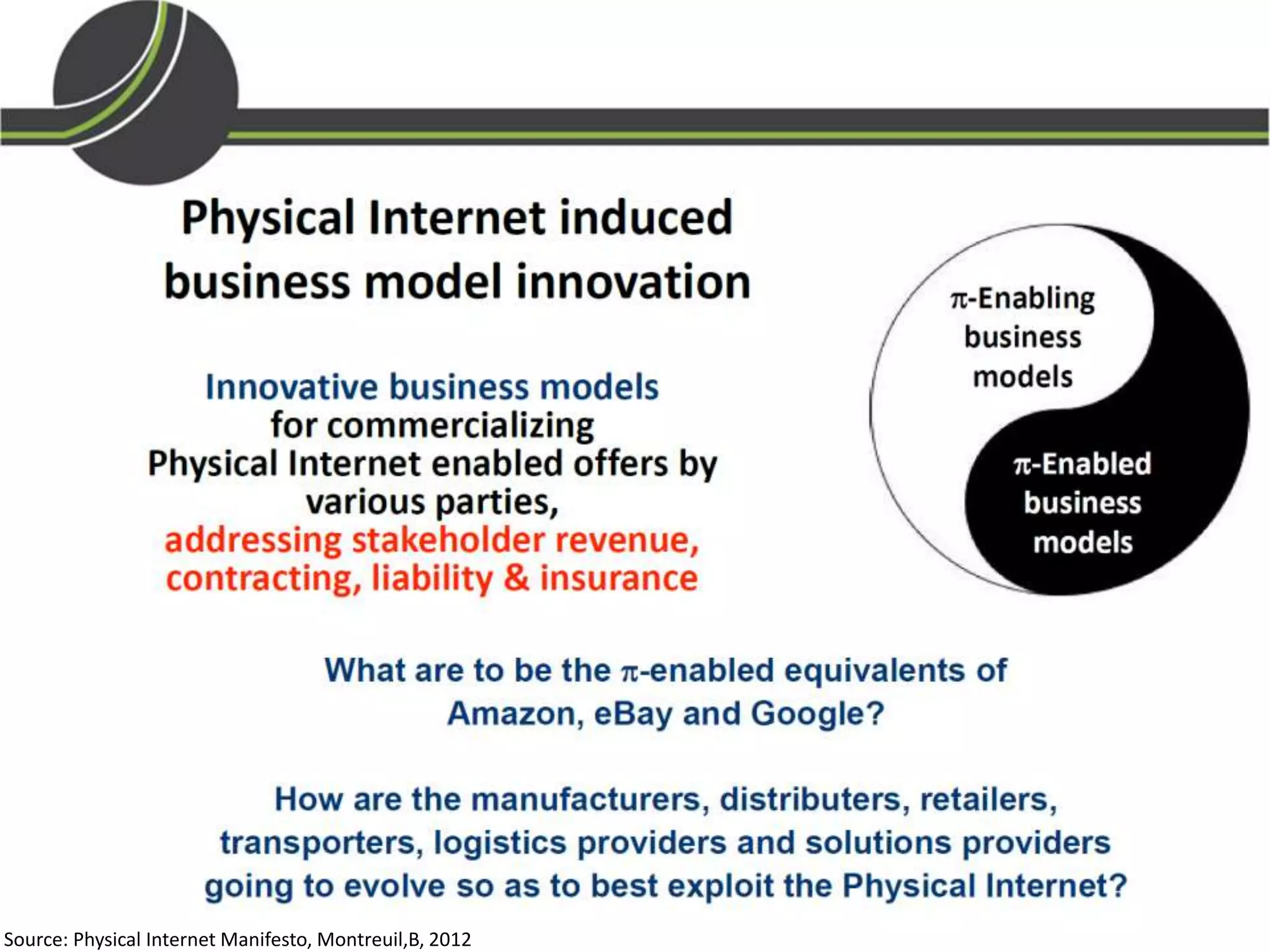
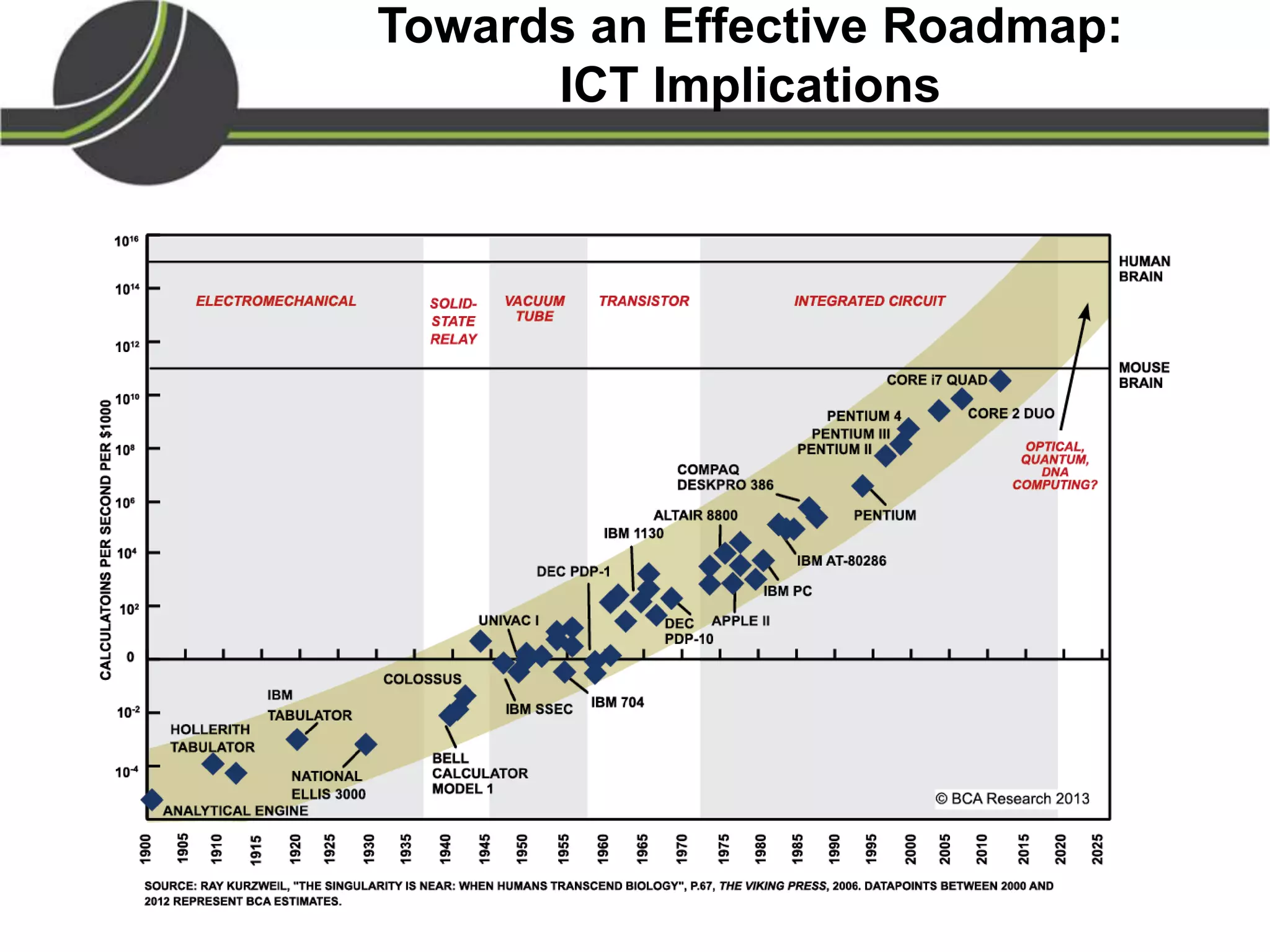
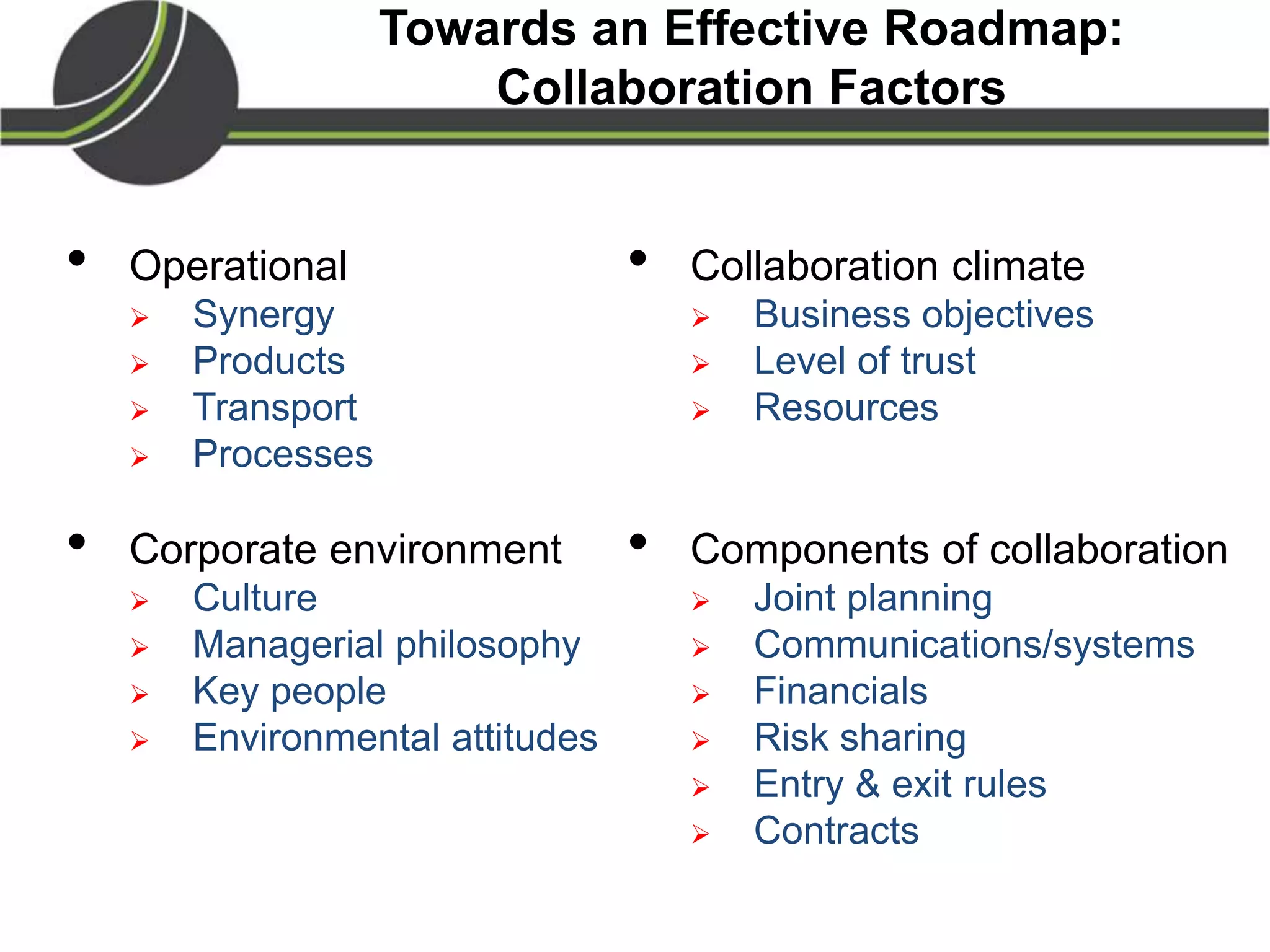
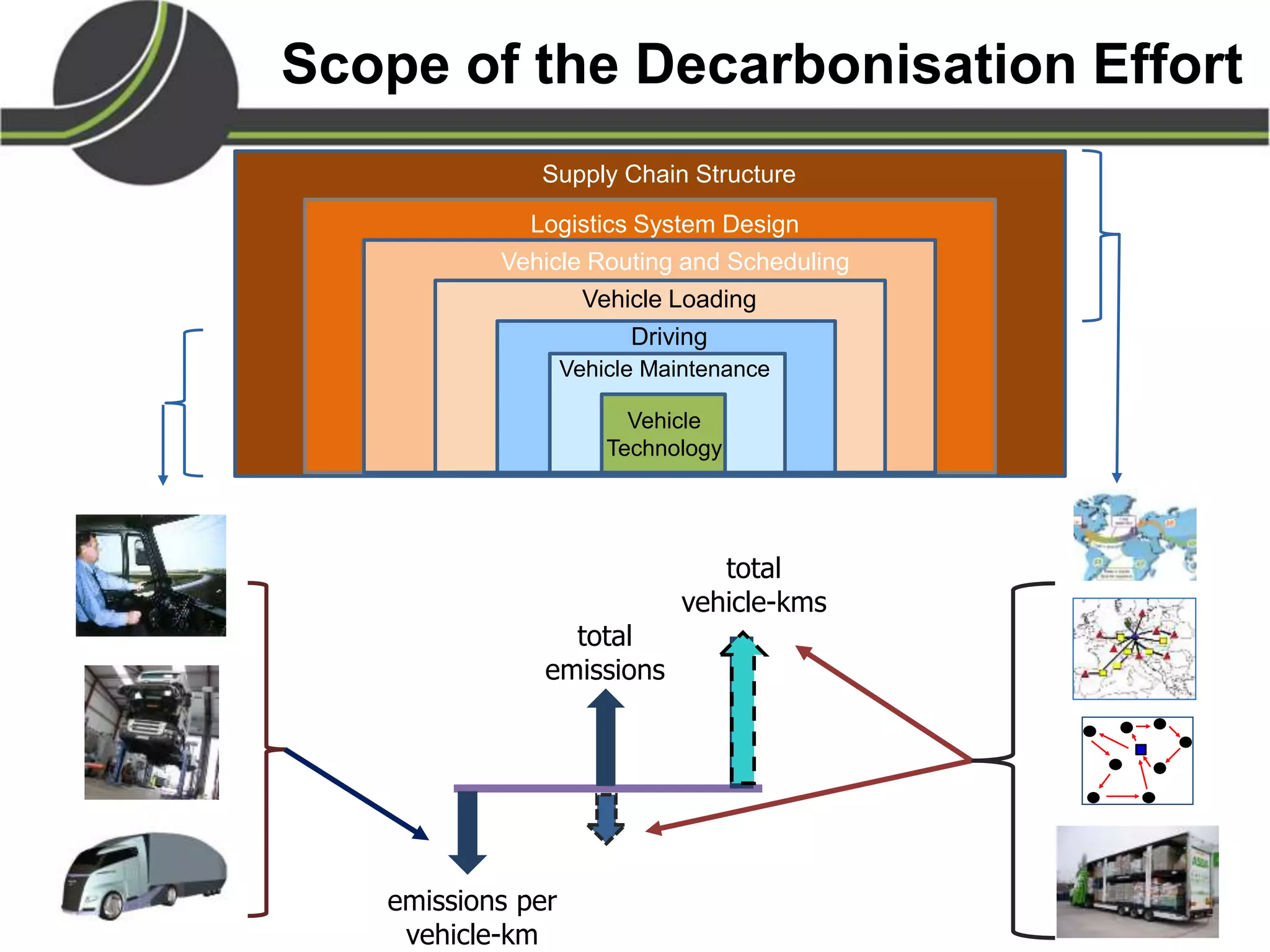
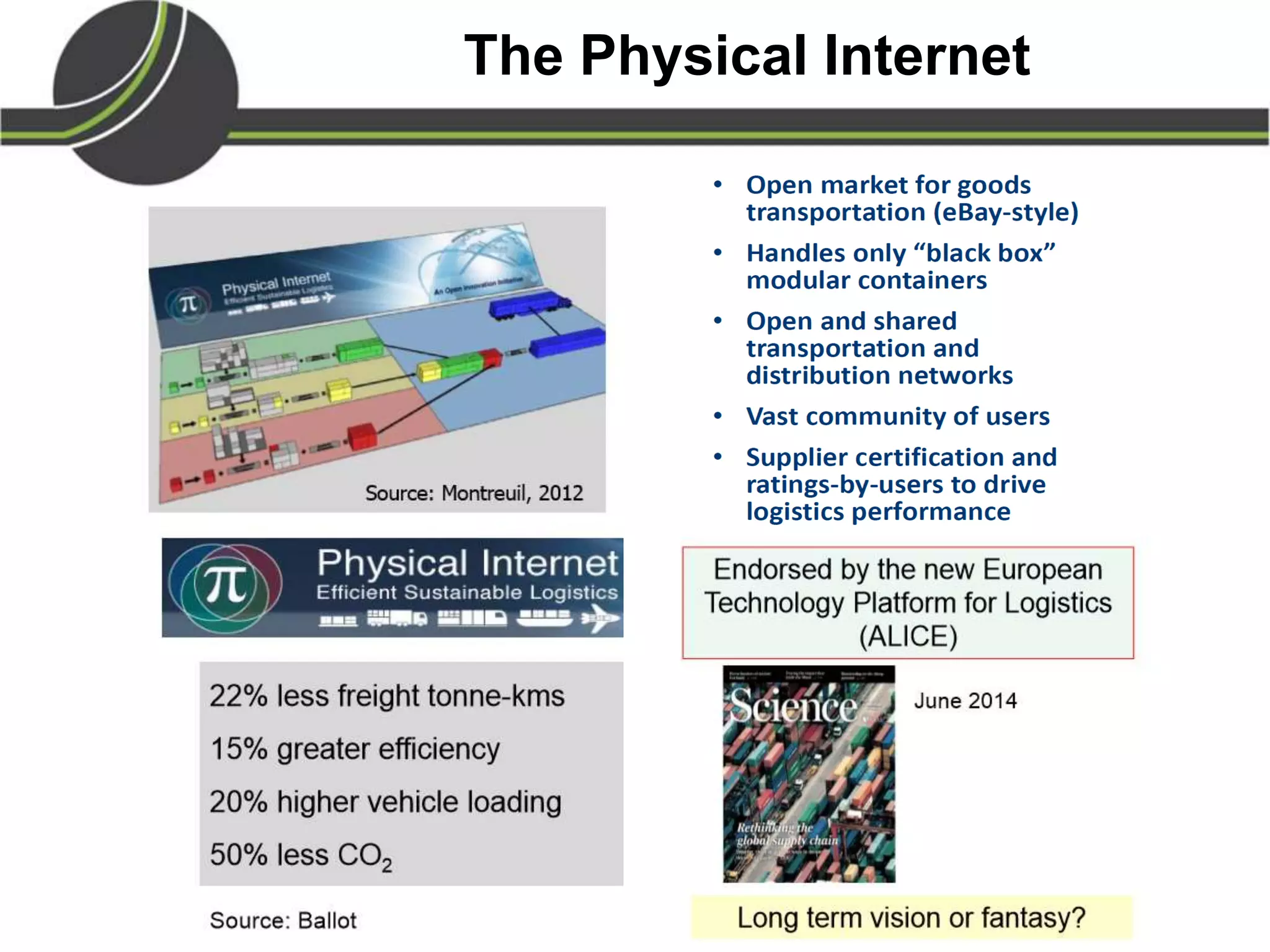
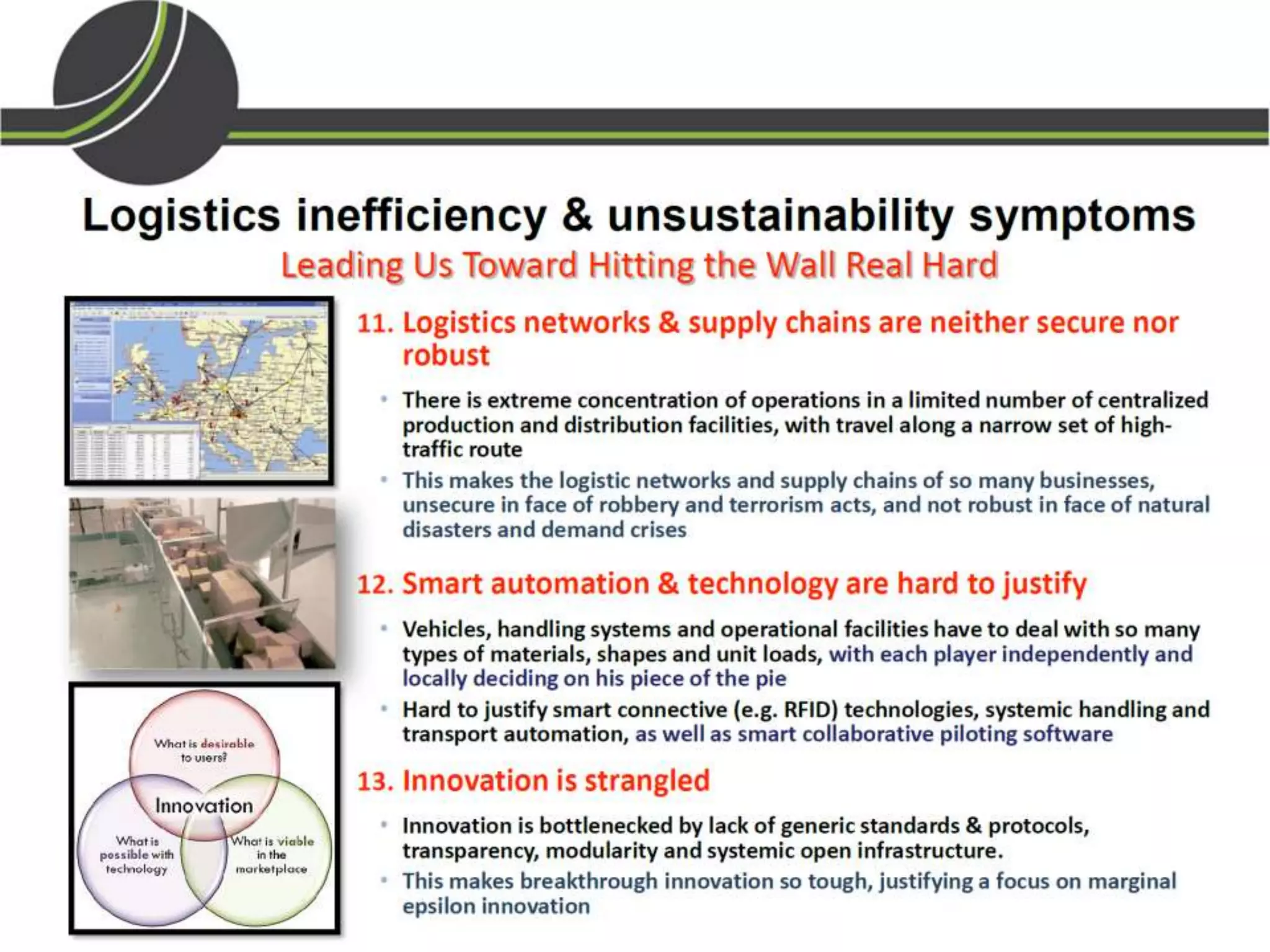
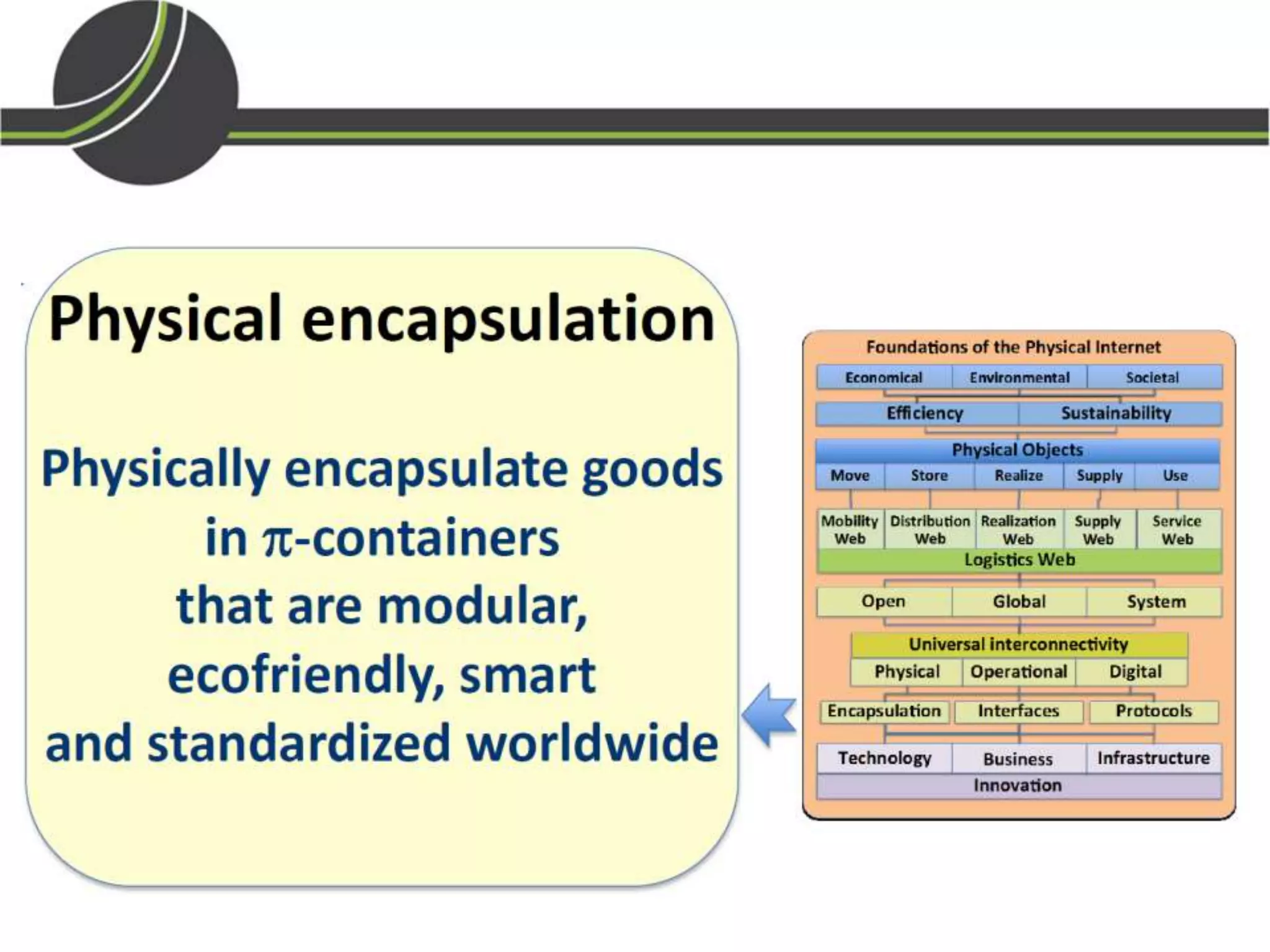
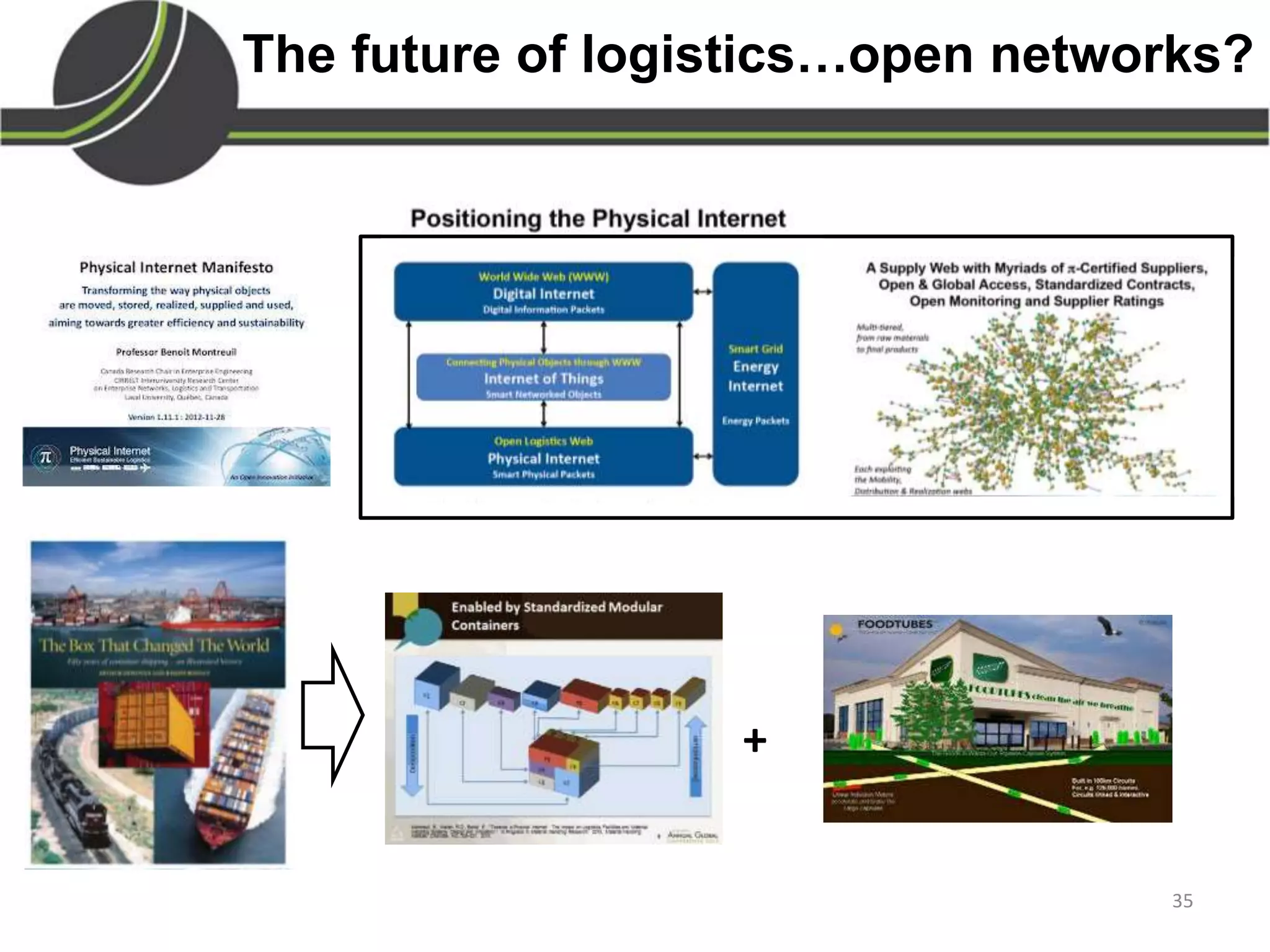
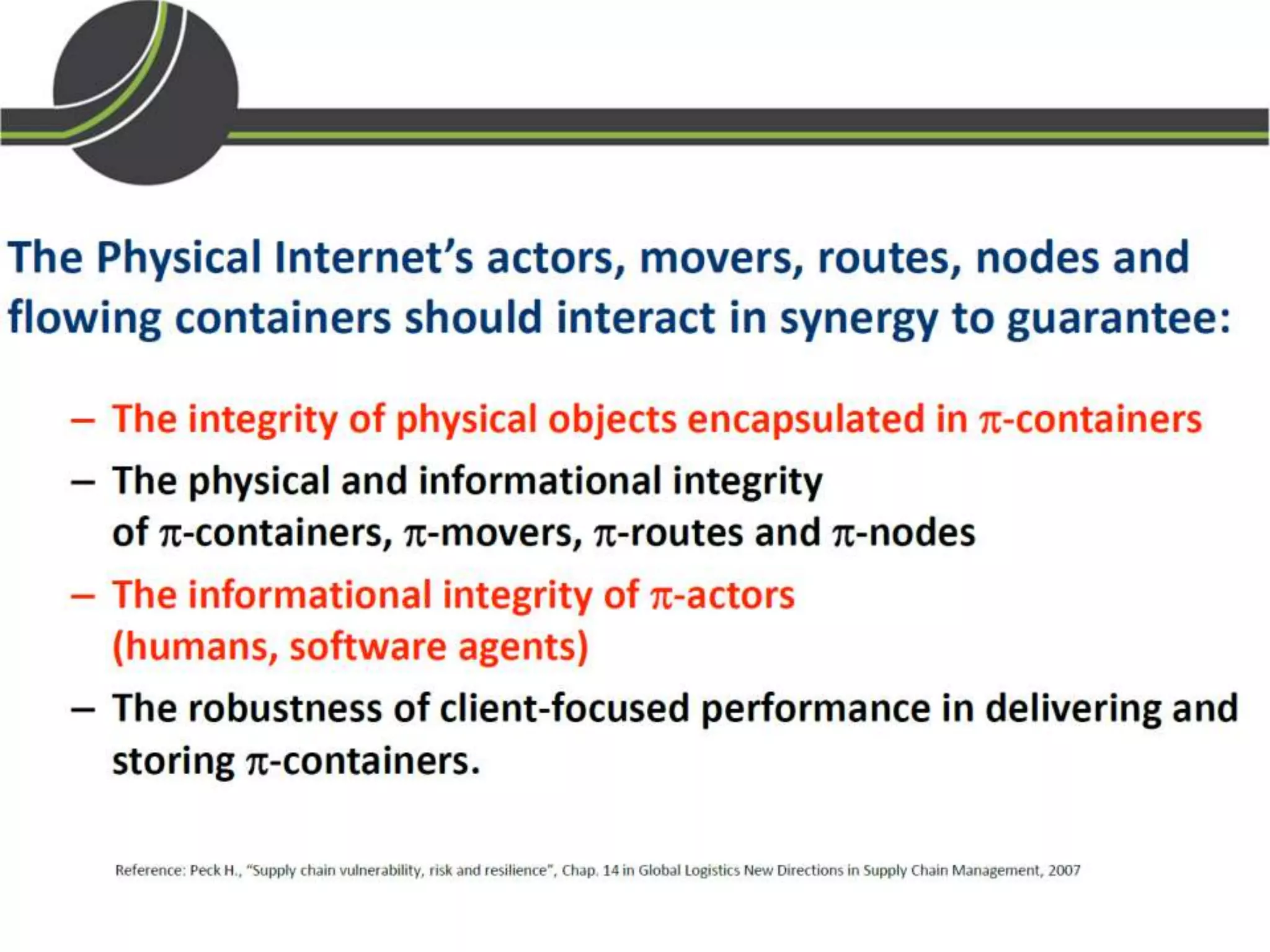
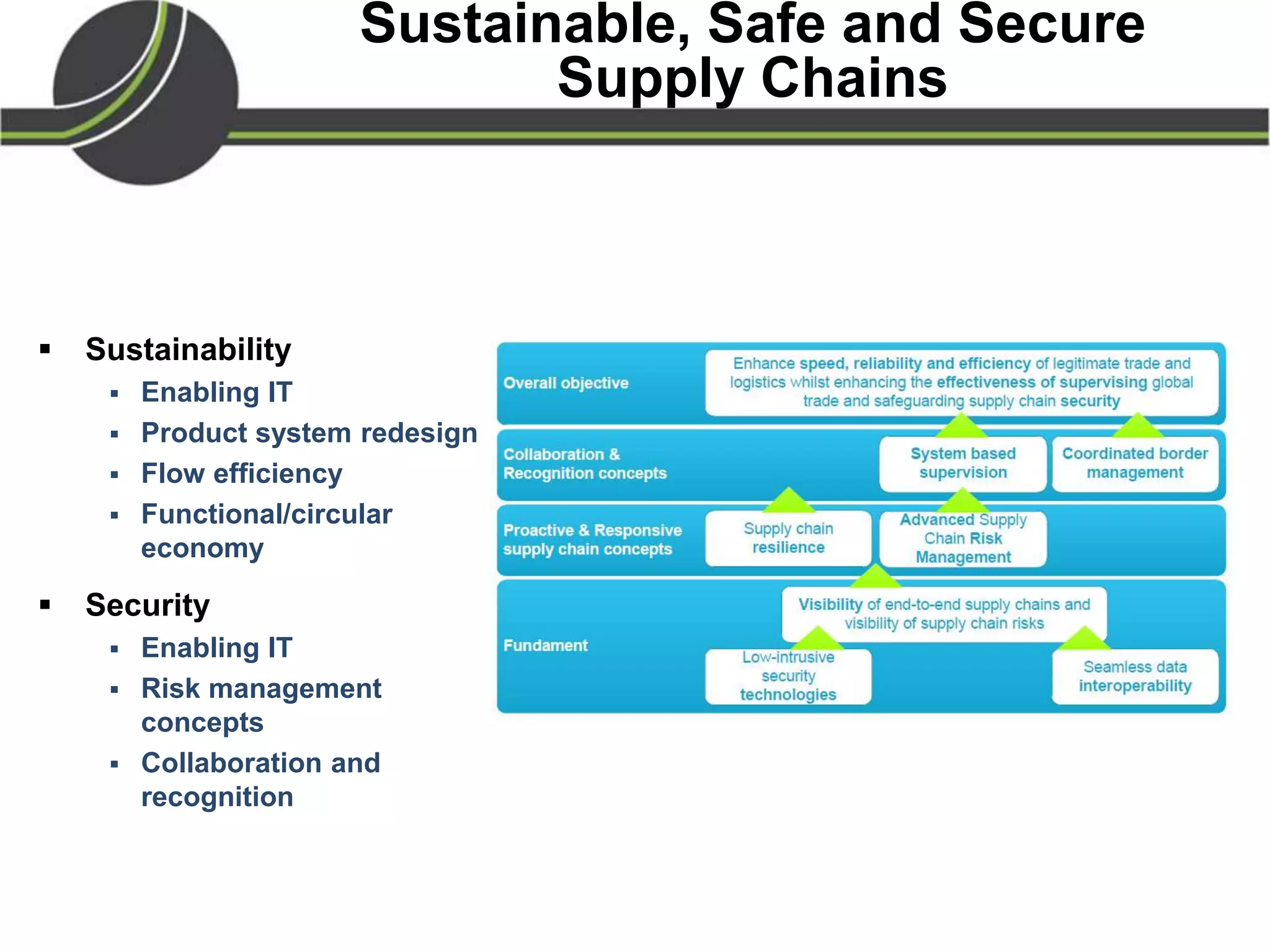
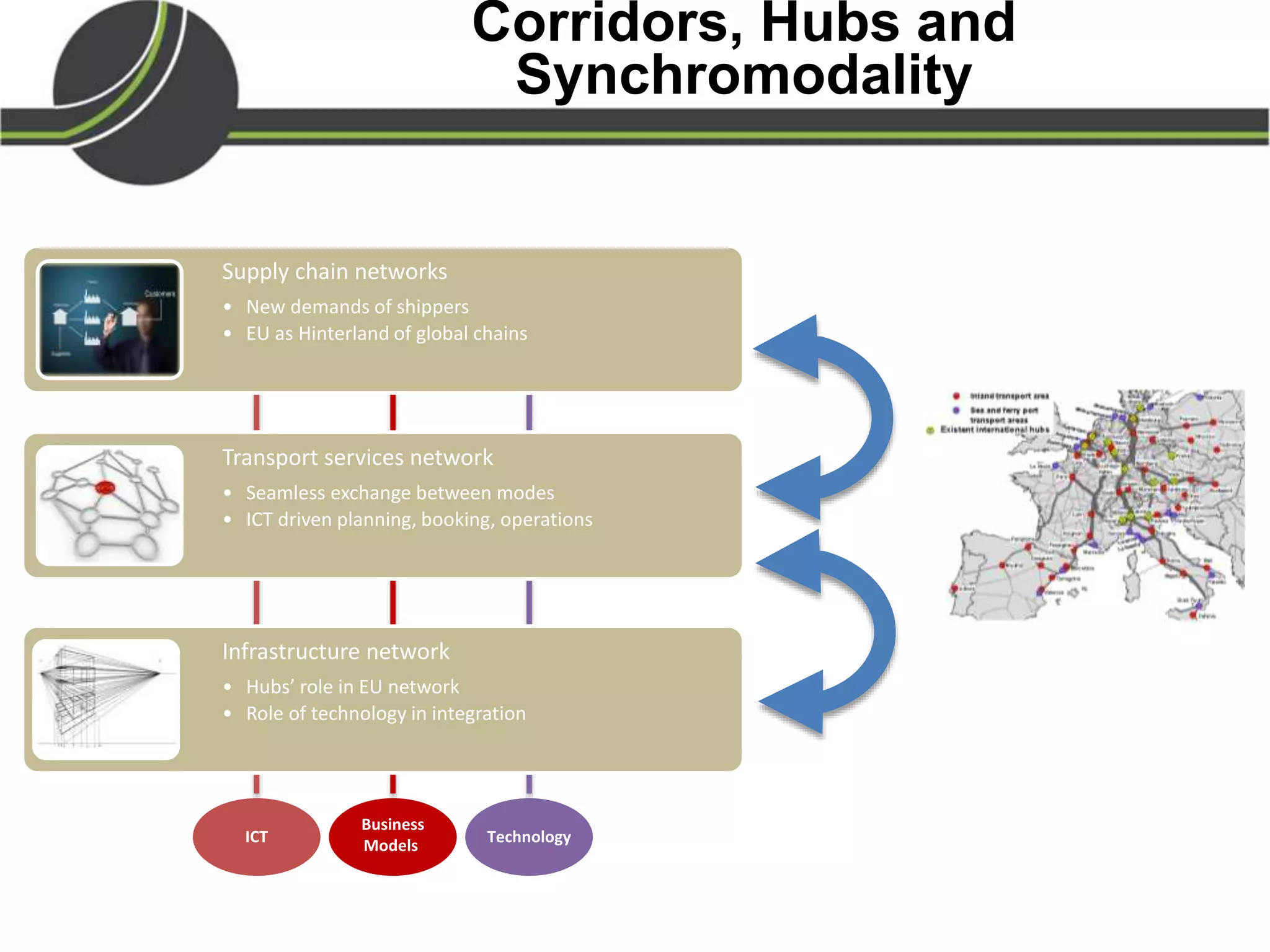
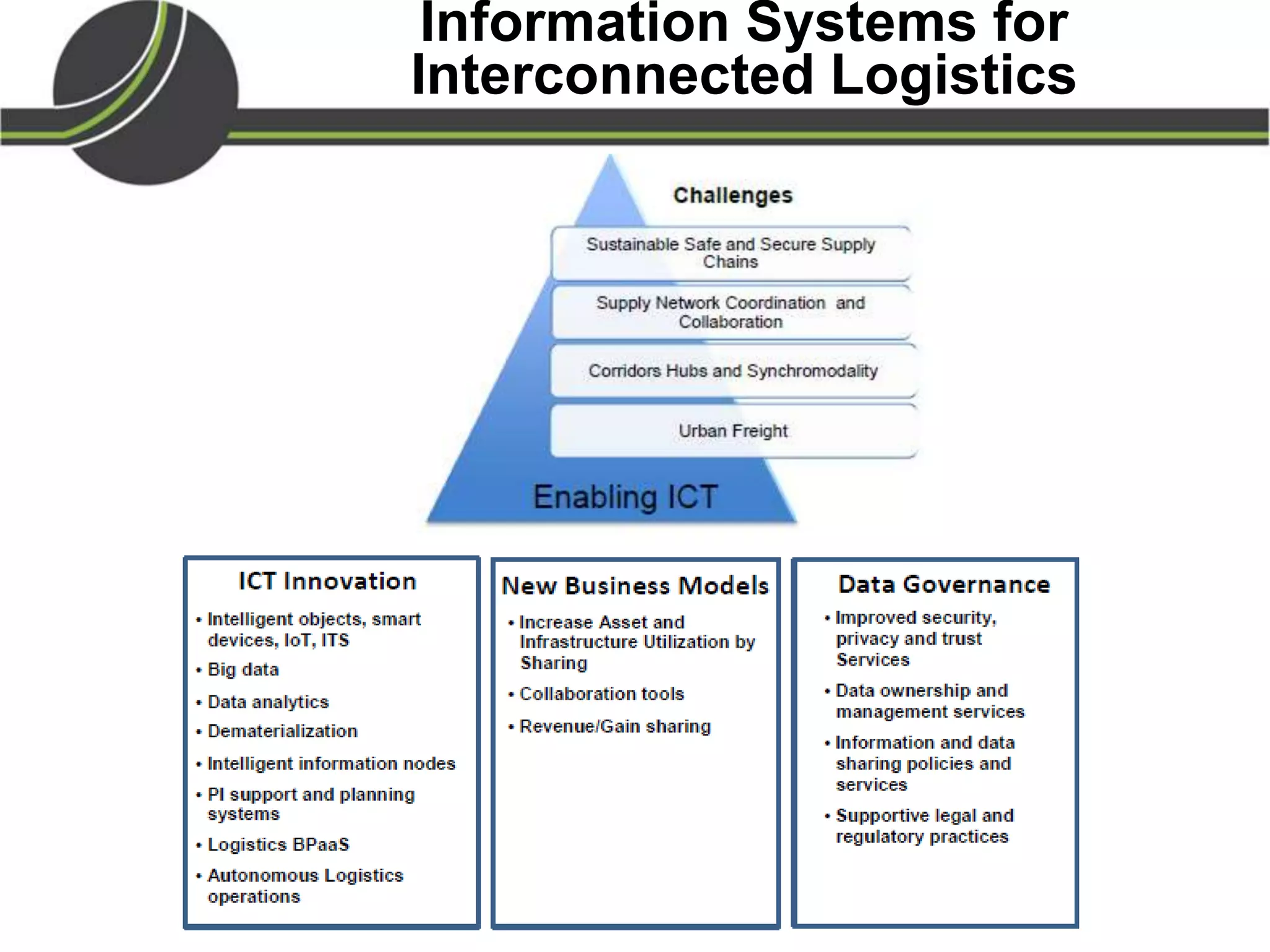
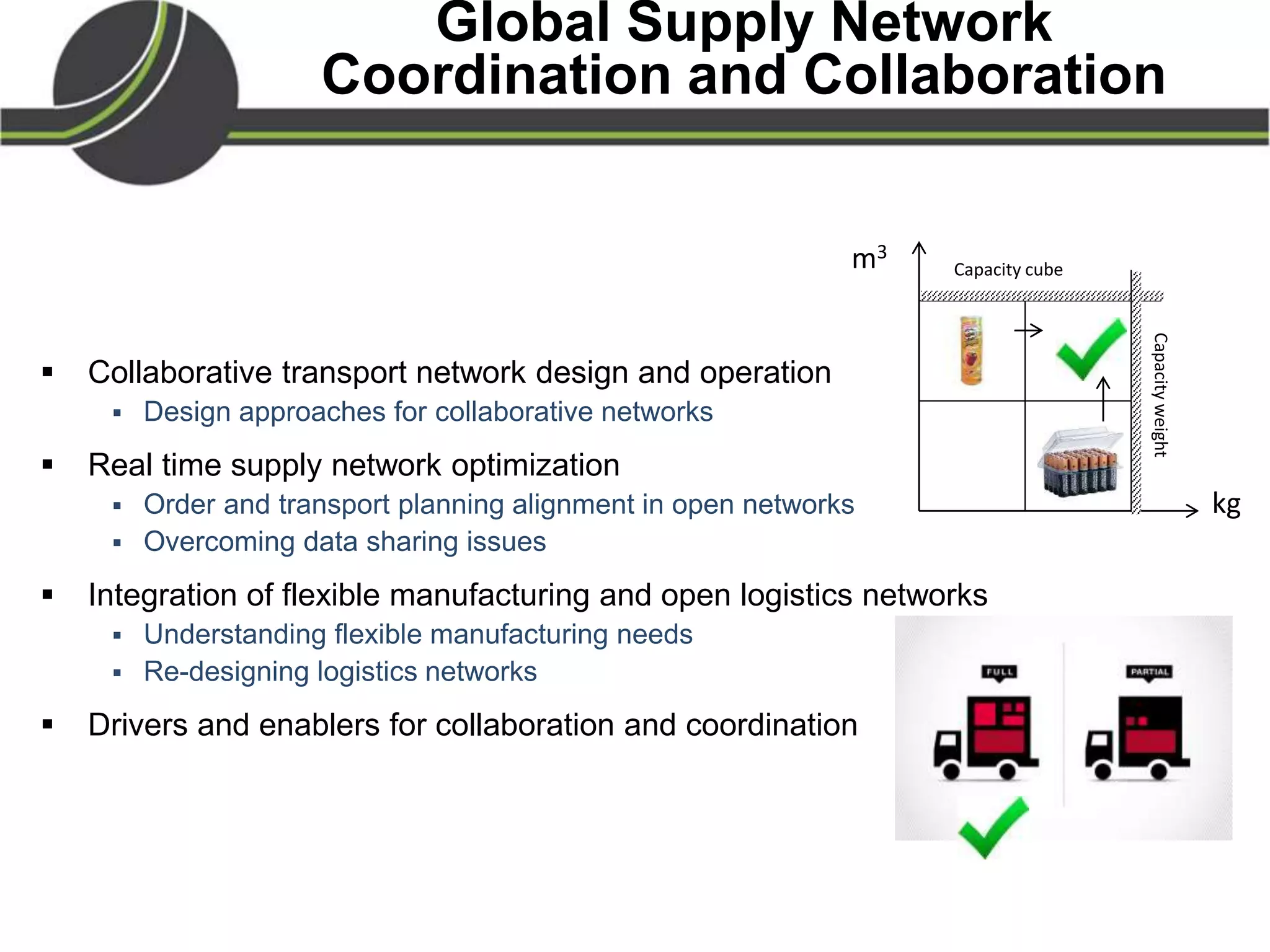
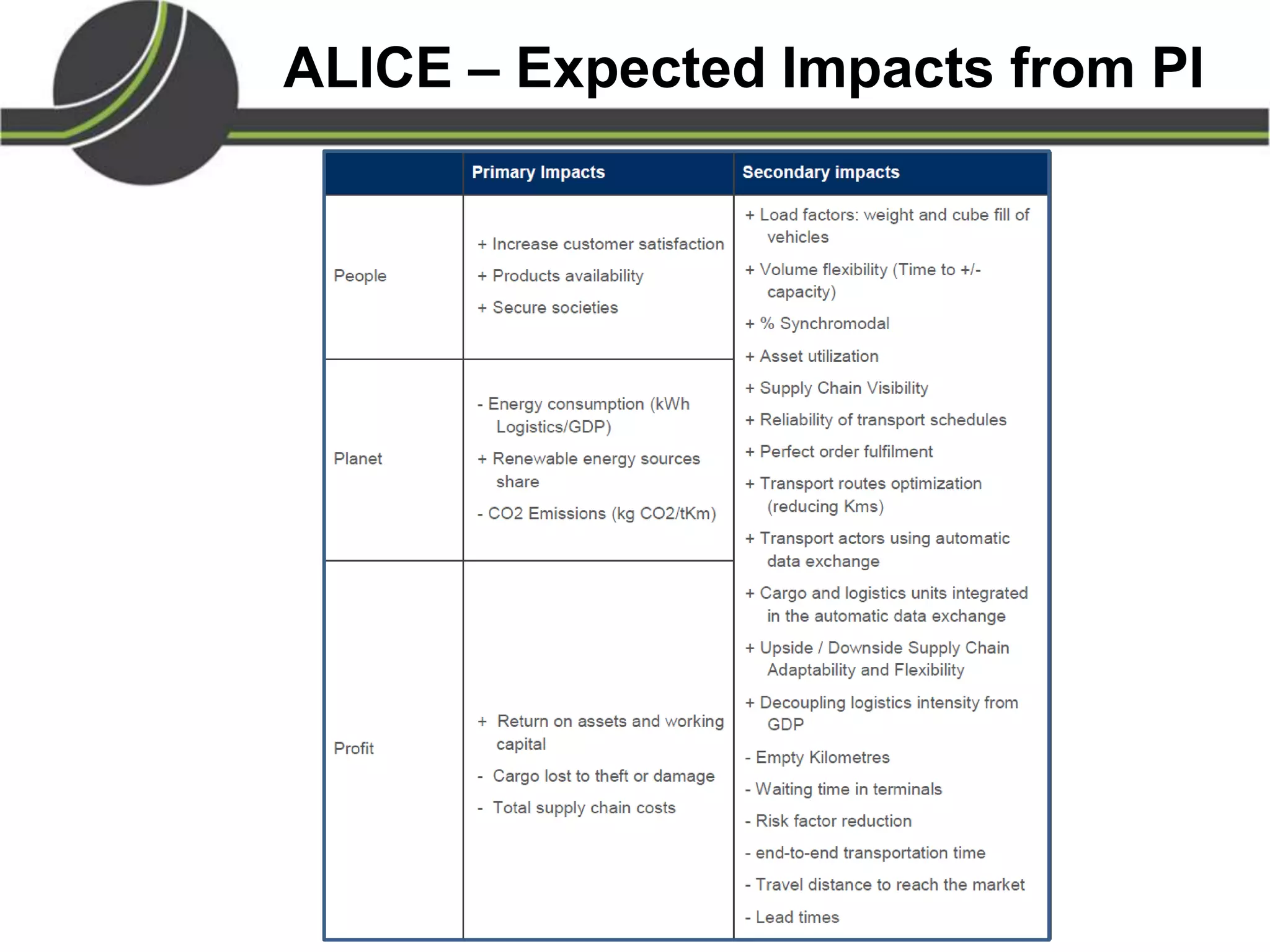
This document summarizes a presentation on the Physical Internet concept. It discusses how current freight transport is inefficient, with little improvement in load factors and road efficiency over 10 years. It then outlines the EU vision for more sustainable freight by 2050, including reducing oil dependence and carbon emissions. The Physical Internet concept is presented as a way to improve efficiency by using standardized containers and open logistics networks, with potential to reduce costs and emissions through pooled resources. Key enablers include IT systems, collaboration between organizations, and standardized protocols. Overall the Physical Internet is framed as a way to optimize freight transport networks rather than a single solution.