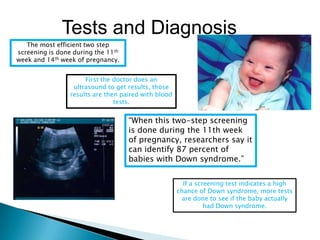
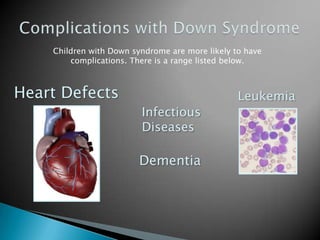
Down syndrome is a genetic condition where a person has three copies of chromosome 21 instead of the usual two. This extra genetic material causes developmental delays and other issues. Down syndrome can range from mild to severe depending on the individual. The majority of Down syndrome cases are not inherited and are caused by random errors during cell division. Common physical signs include a flattened face, small ears and mouth, upward slanting eyes, and decreased muscle tone at birth. The risk of having a child with Down syndrome increases with the mother's age. Screening tests during pregnancy can detect 87% of Down syndrome cases. Diagnostic tests like amniocentesis or CVS can confirm a Down syndrome diagnosis. Individuals with Down syndrome may experience health