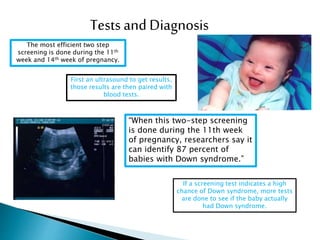
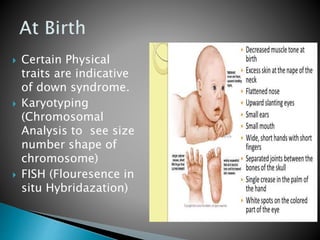
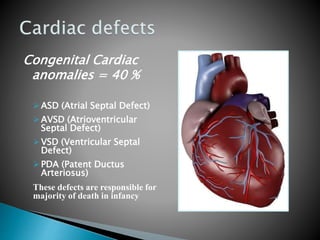
Down syndrome is a genetic condition caused by the presence of an extra chromosome 21, either fully or partially. It causes developmental delays and cognitive impairment. The majority (95%) of Down syndrome cases are caused by trisomy 21, where there are three copies of chromosome 21 instead of the usual two. Risk increases with the age of the mother. Screening tests during pregnancy can identify 87% of cases, and diagnostic tests like amniocentesis or CVS can confirm the diagnosis. Common physical traits include a flattened face and small stature. Individuals with Down syndrome also have an increased risk of health issues like congenital heart defects, leukemia, and early-onset Alzheimer's disease.