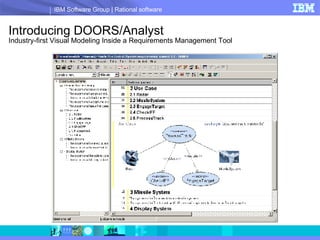
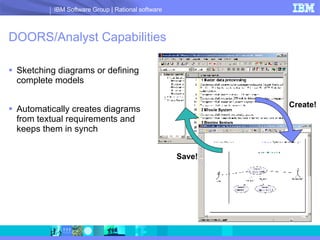
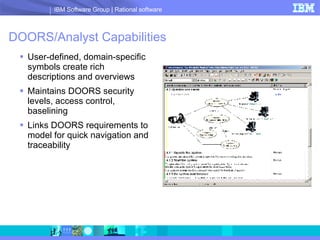
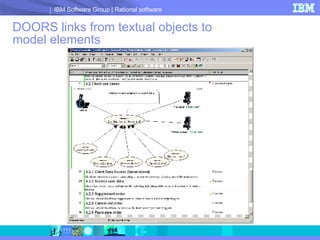
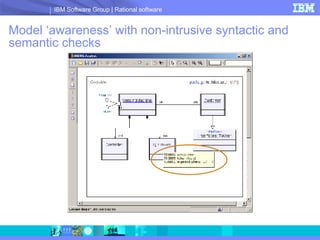
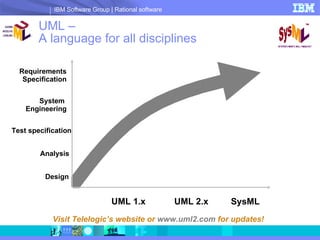
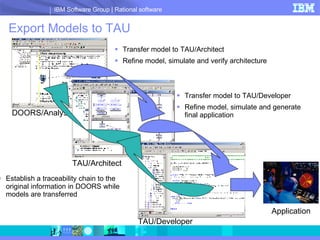
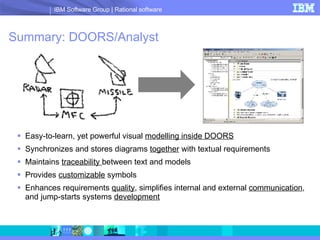
DOORS/Analyst is a visual modeling tool integrated within IBM's DOORS requirements management software. It allows users to create diagrams and models synchronized with textual requirements to facilitate requirements elicitation, communication, and systems development. Key benefits include low learning curve, traceability between visual and textual representations, customizable symbols, and enhanced stakeholder involvement, feedback, and collaboration.