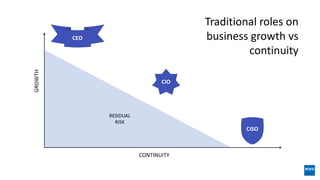
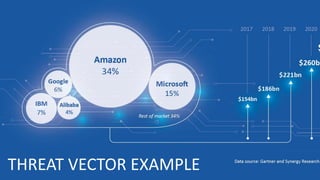
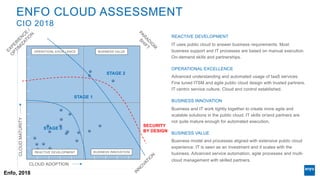
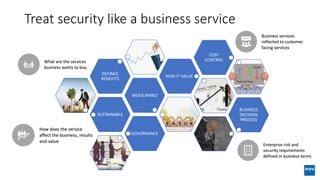
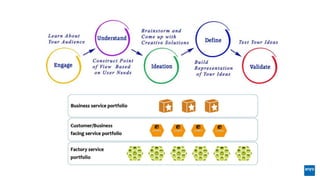
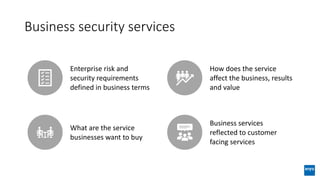
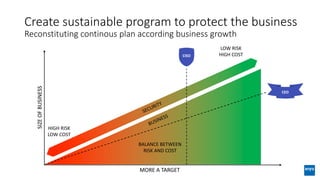
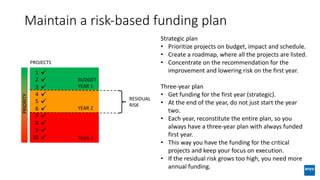
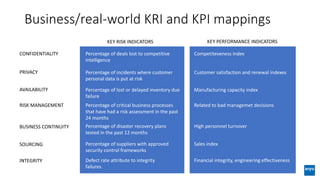
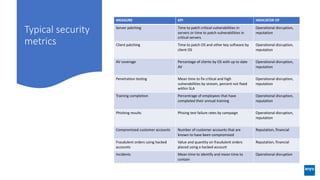
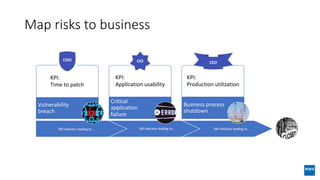
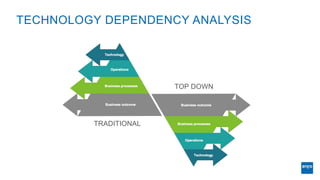
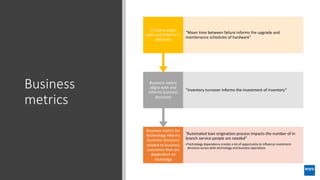
The document discusses corporate governance and responsibilities regarding security management, highlighting varying perspectives among CIOs, CEOs, and CISOs on accountability for security. It emphasizes the need for a business-centric approach to cybersecurity that treats security as a service while integrating it into business outcomes, along with providing a roadmap for sustainable security programs. Key takeaways include understanding roles and goals, creating clear responsibilities, and adopting risk-based funding plans to align security with business strategies.