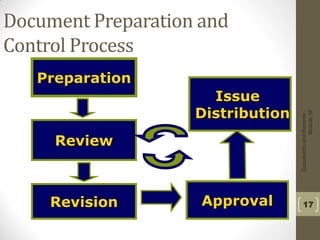
This document discusses the difference between documents and records and why organizations need to manage them. Documents communicate information through policies, processes, and procedures and need updating, while records provide evidence of activities and do not change. Properly managing documents and records helps organizations ensure consistent quality activities, facilitate monitoring and audits, and minimize miscommunication. It also allows historical information to be evaluated for current use. Documents include policies that state general intentions, processes that describe activity steps, and procedures with detailed instructions. Records capture specific activity information like worksheets and forms.