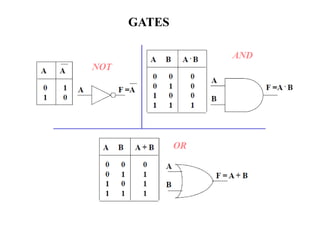
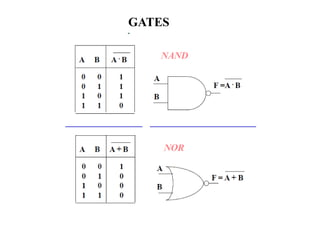
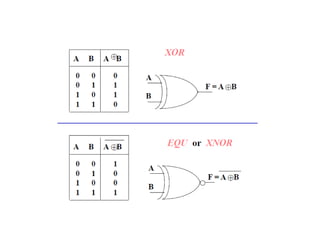
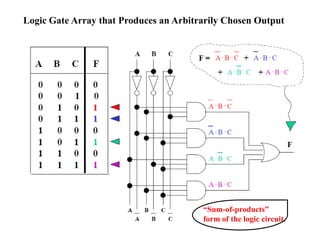
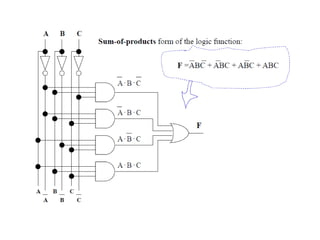
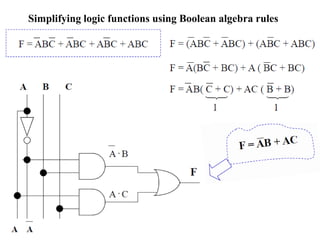
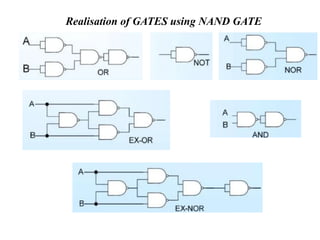
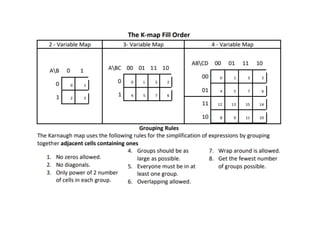
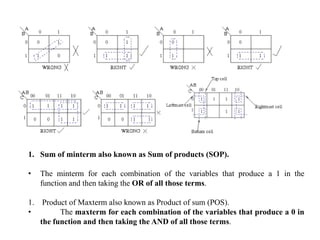
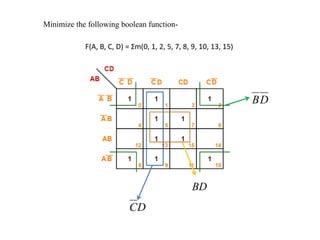
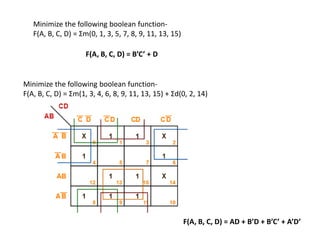
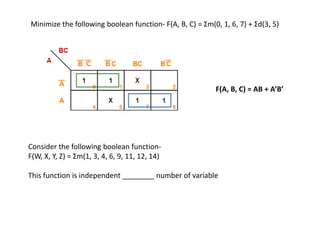
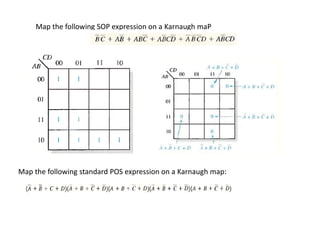
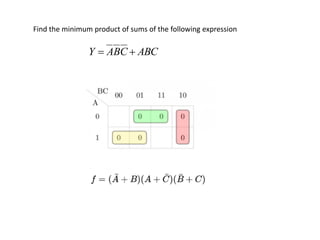
1. The document discusses digital logic circuits and their use of binary logic with 0 representing false and 1 representing true.
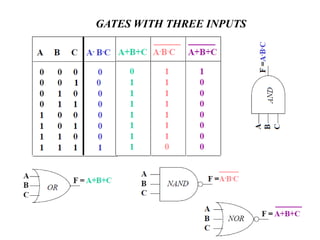
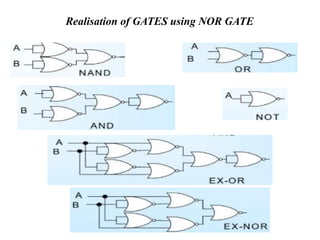
2. It explains that complex digital logic circuits like computers can be built using basic logic gates that perform operations like NOT, AND, OR, etc.
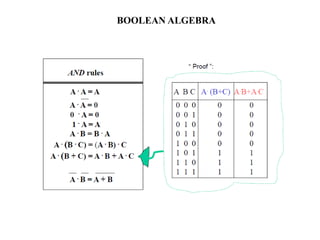
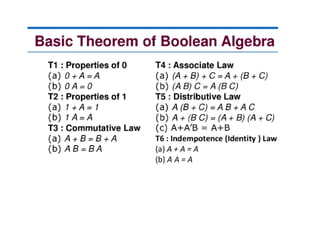
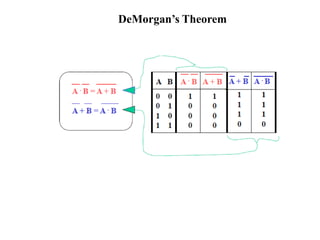
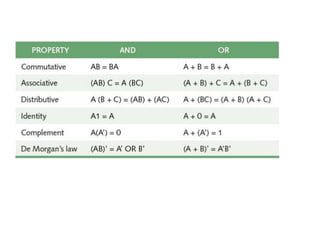
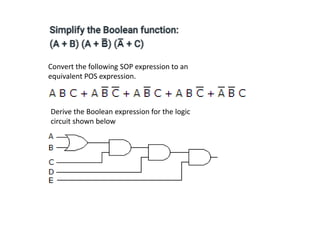
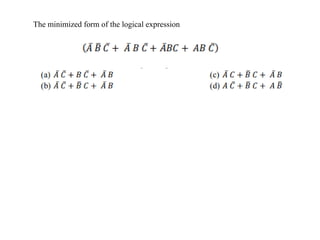
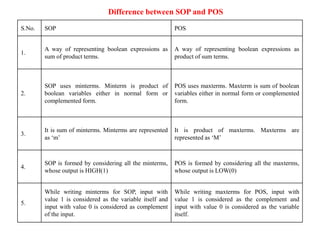
3. Boolean algebra is used as a formal tool to describe and design complex binary logic circuits using gates.