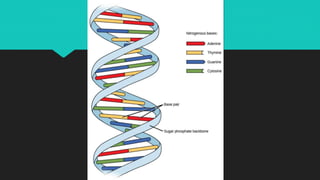
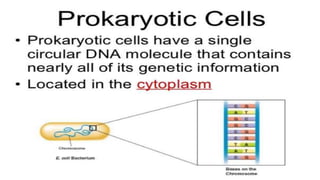
DNA contains the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms. It is a nucleic acid located in the cell nucleus that contains the sugar deoxyribose. DNA replicates itself with high accuracy before cell division due to the specific base pairing of adenine with thymine and cytosine with guanine. RNA plays an important role in protein synthesis by carrying instructions from DNA in the nucleus to the cytoplasm. There are three main types of RNA: messenger RNA, ribosomal RNA, and transfer RNA.