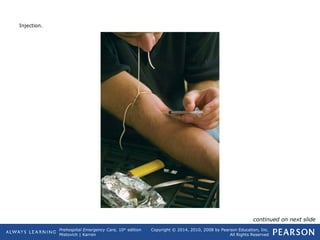
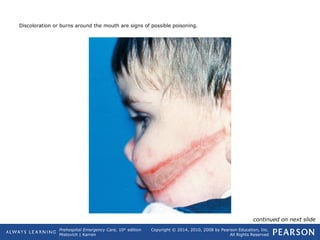
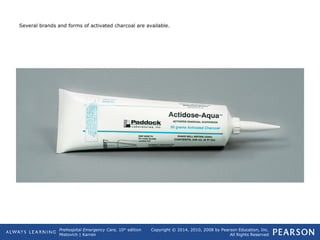
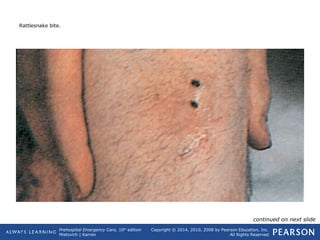
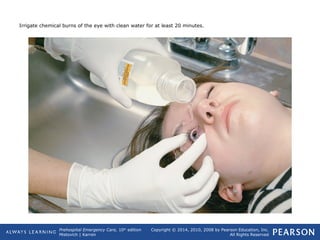
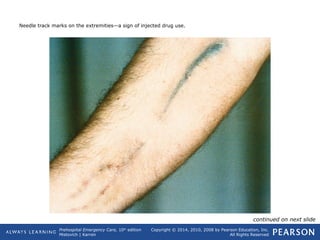
This document provides an overview of toxicologic emergencies and poisonings from a prehospital emergency care textbook. It defines poisons and poisoning, and describes the four main routes poisons can enter the body (ingestion, inhalation, injection, absorption). It focuses on ingested poisons, noting they are a common cause of accidental poisoning, especially in children. For patients with suspected ingestion, EMTs are instructed to assess airway, breathing, circulation, and mental status, obtain a history, and monitor for signs and symptoms of poisoning. Supportive care like oxygen and activated charcoal (if approved) are emphasized, along with consulting medical direction or a poison control center.