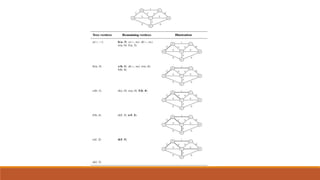
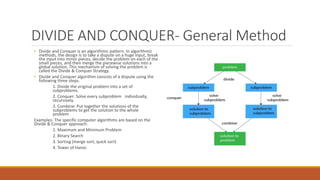
Divide and conquer is an algorithm design paradigm where a problem is broken into smaller subproblems, those subproblems are solved independently, and then their results are combined to solve the original problem. Some examples of algorithms that use this approach are merge sort, quicksort, and matrix multiplication algorithms like Strassen's algorithm. The greedy method works in stages, making locally optimal choices at each step in the hope of finding a global optimum. It is used for problems like job sequencing with deadlines and the knapsack problem. Minimum cost spanning trees find subgraphs of connected graphs that include all vertices using a minimum number of edges.


![The Merge Sort Algorithm
• The Merge Sort function repeatedly divides the array into two halves until we reach a stage where we try
to perform Merge Sort on a sub array of size 1 i.e. p == r.
• After that, the merge function comes into play and combines the sorted arrays into larger arrays until the
whole array is merged.
• Mergesort is a perfect example of a successful application of the divide-andconquer technique. It sorts a
given array A[0..n − 1] by dividing it into two halves A[0..n/2 − 1] and A[n/2..n − 1], sorting each of them
recursively, and then merging the two smaller sorted arrays into a single sorted one](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit2ppt-230313112734-b301122f/85/Divide-and-Conquer-Greedy-Techniques-4-320.jpg)


![Quicksort
• Quicksort is the other important sorting algorithm that is based on the divide-andconquer approach.
Unlike mergesort, which divides its input elements according to their position in the array, quicksort
divides them according to their value.
• A partition is an arrangement of the array’s elements so that all the elements to the left of some
element A[s] are less than or equal to A[s], and all the elements to the right of A[s] are greater than or
equal to it:
• Obviously, after a partition is achieved, A[s] will be in its final position in the sorted array, and we can
continue sorting the two subarrays to the left and to the right of A[s] independently
• Note the difference with mergesort: there, the division of the problem into two subproblems is
immediate and the entire work happens in combining their solutions; here, the entire work happens in
the division stage, with no work required to combine the solutions to the subproblems.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit2ppt-230313112734-b301122f/85/Divide-and-Conquer-Greedy-Techniques-7-320.jpg)

![Quicksort…
If all the splits happen in the middle of corresponding subarrays, we will have the best case. The number of key
comparisons in the best case satisfies the recurrence
In the worst case, all the splits will be skewed to the extreme: one of the two sub arrays will be empty, and the
size of the other will be just 1 less than the size of the sub array being partitioned. This unfortunate situation will
happen, in particular, for increasing arrays, i.e., for inputs for which the problem is already solved! Indeed, if
A[0..n − 1] is a strictly increasing array and we use A[0] as the pivot, the left-to-right scan will stop on A[1] while
the right-to-left scan will go all the way to reach A[0], indicating the split at position 0.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit2ppt-230313112734-b301122f/85/Divide-and-Conquer-Greedy-Techniques-9-320.jpg)

![Strassen’s Matrix Multiplication…
Pseudocode of Strassen’s multiplication
Divide matrix A and matrix B in 4 sub-matrices of size N/2 x N/2 as shown in the above diagram.
Calculate the 7 matrix multiplications recursively.
Compute the submatrices of C.
Combine these submatricies into our new matrix C
In this algorithm, the statement “C[i][j] += A[i][k] * B[k][j]” executes n³ times as evident from the
three nested for loops and is the most costly operation in the algorithm. So, the time complexity of
the naive algorithm is O(n³).
Now let’s take a look at Strassen algorithm. Strassen algorithm is a recursive method for matrix
multiplication where we divide the matrix into 4 sub-matrices of dimensions n/2 x n/2 in each
recursive step.
For example, consider two 4 x 4 matrices A and B that we need to multiply. A 4 x 4 can be divided into
four 2 x 2 matrices](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit2ppt-230313112734-b301122f/85/Divide-and-Conquer-Greedy-Techniques-11-320.jpg)