This document provides an overview of the design of a distillation column. It begins with introducing distillation and its applications. The main design steps are then outlined, including selecting key components, determining operating pressure, specifying separation requirements, calculating minimum reflux ratio, and selecting tower type and sizes. Numerical examples are provided to demonstrate calculating minimum pressure, reflux ratio, and number of theoretical stages. References for further information on process engineering design are also included.










![• Assume Bubble point = 50o C = T = 323K
Antoine Constant for CH3Cl ( Light key Component )
A = 6.9944
B = 902.41
C = 243.61
• Antoine equation :
ln Pv = [ A – (B/T+C) ]
Therefore Pv = 221.794 torr ( CH3Cl)
In the same way ;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/distillation-170926174038/85/Distillation-11-320.jpg)
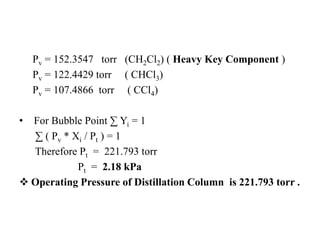



![• Now , for No. of theoretical stages :
lk = light key
hk = heavy key
Nm = log [ {Xlk/Xhk}d * {Xhk/Xlk}b ] / log α lk
Nm = 51.221
The Number of Theoretical stages are 51.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/distillation-170926174038/85/Distillation-16-320.jpg)
