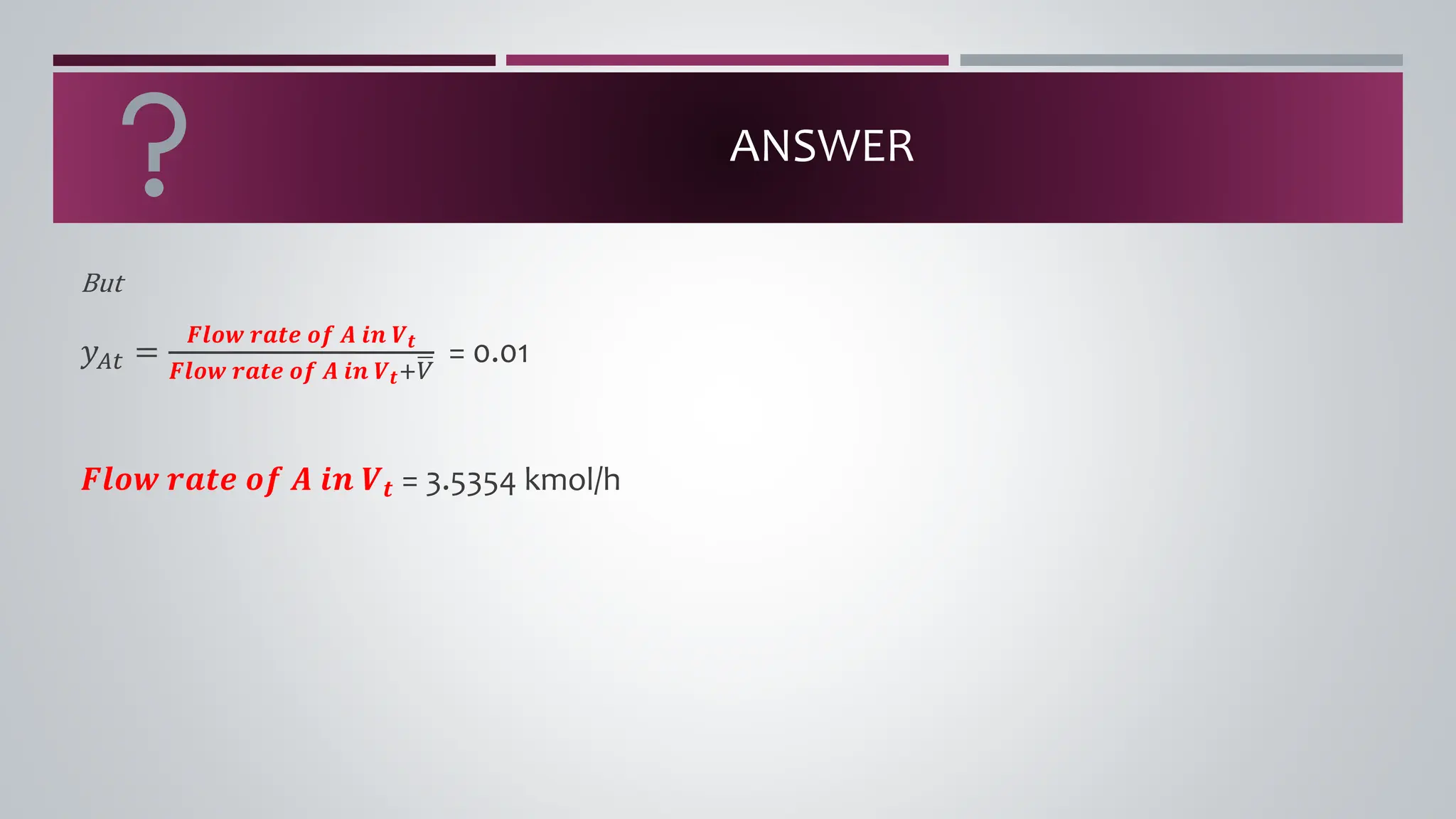
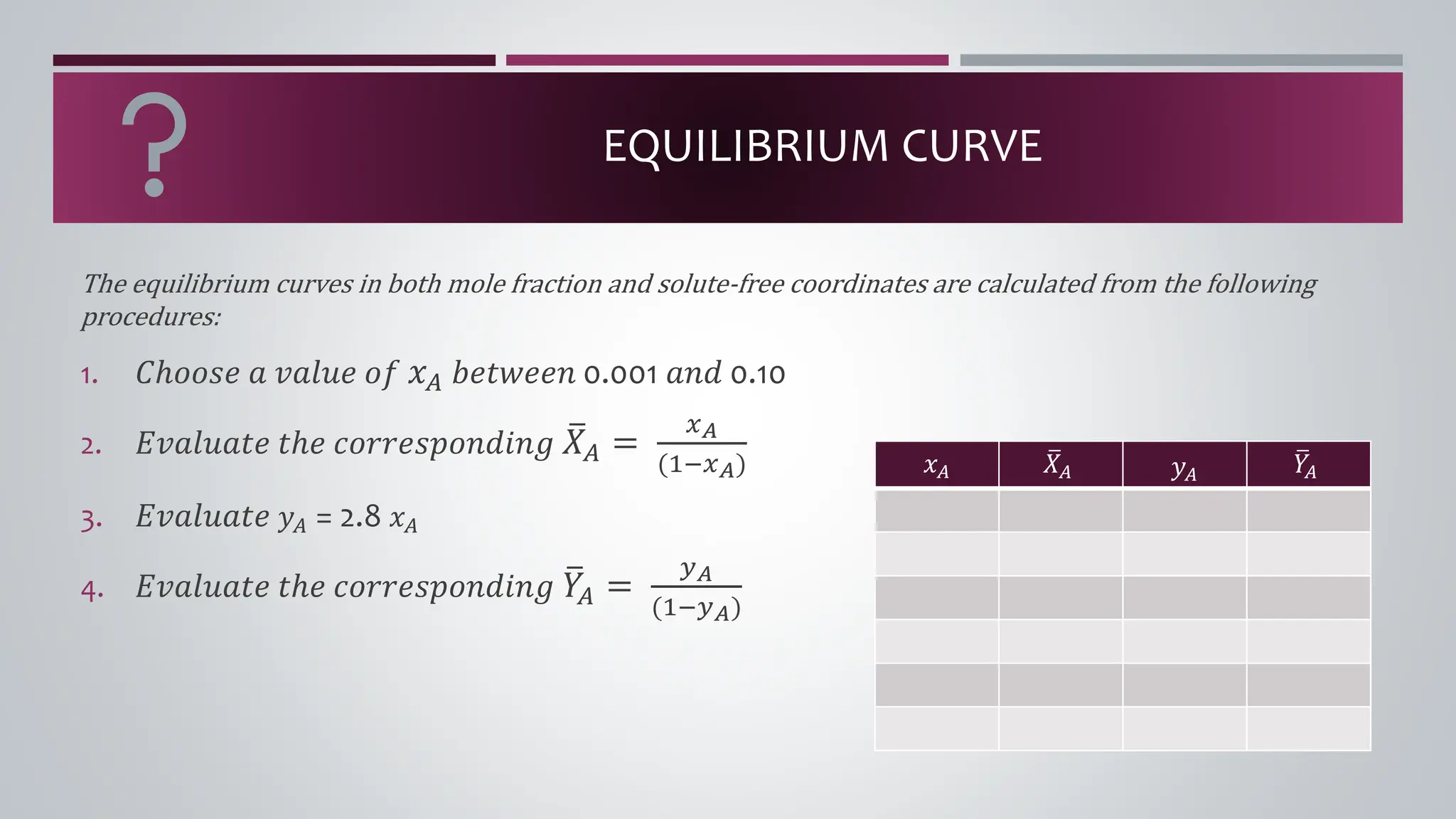
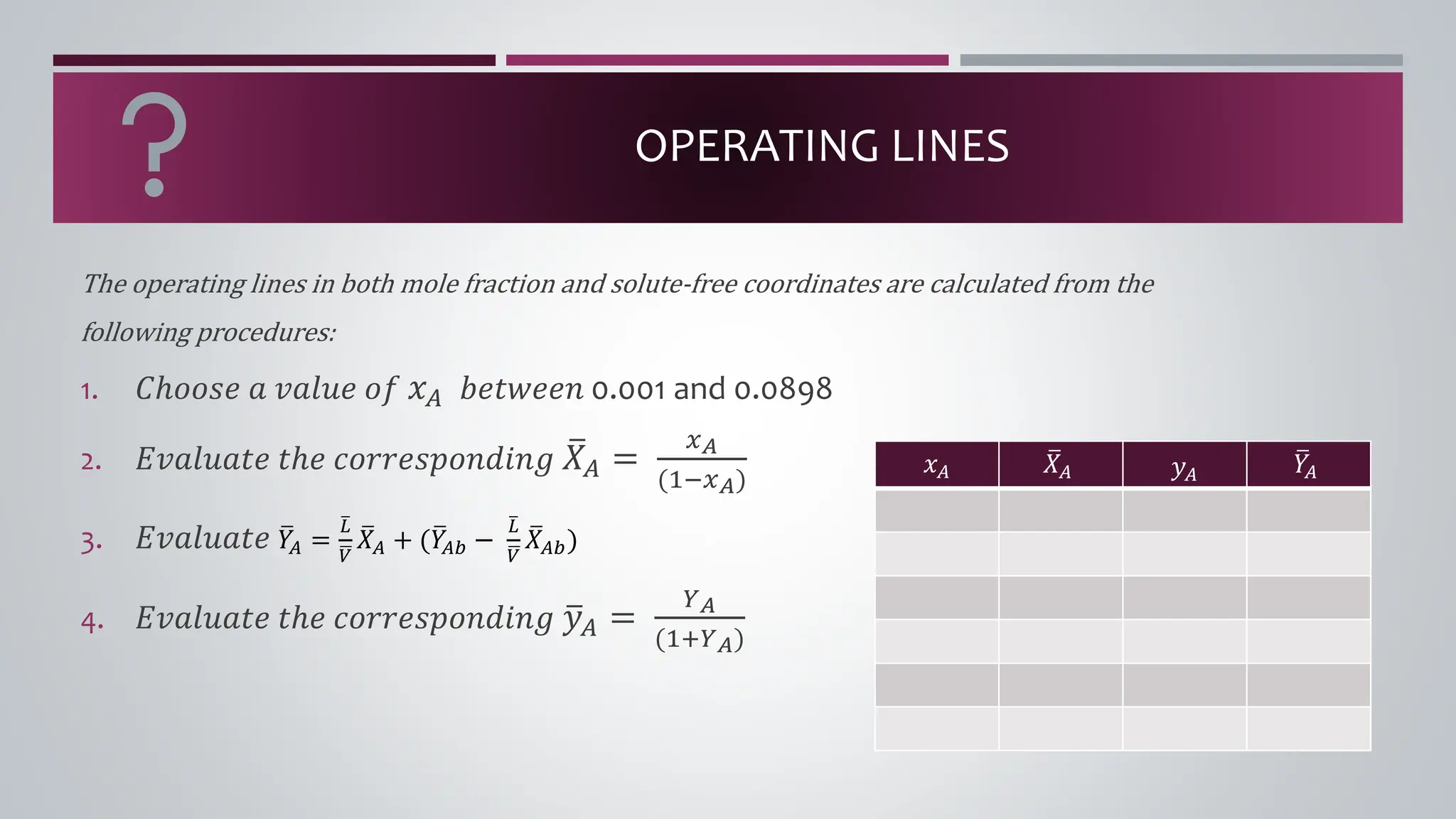
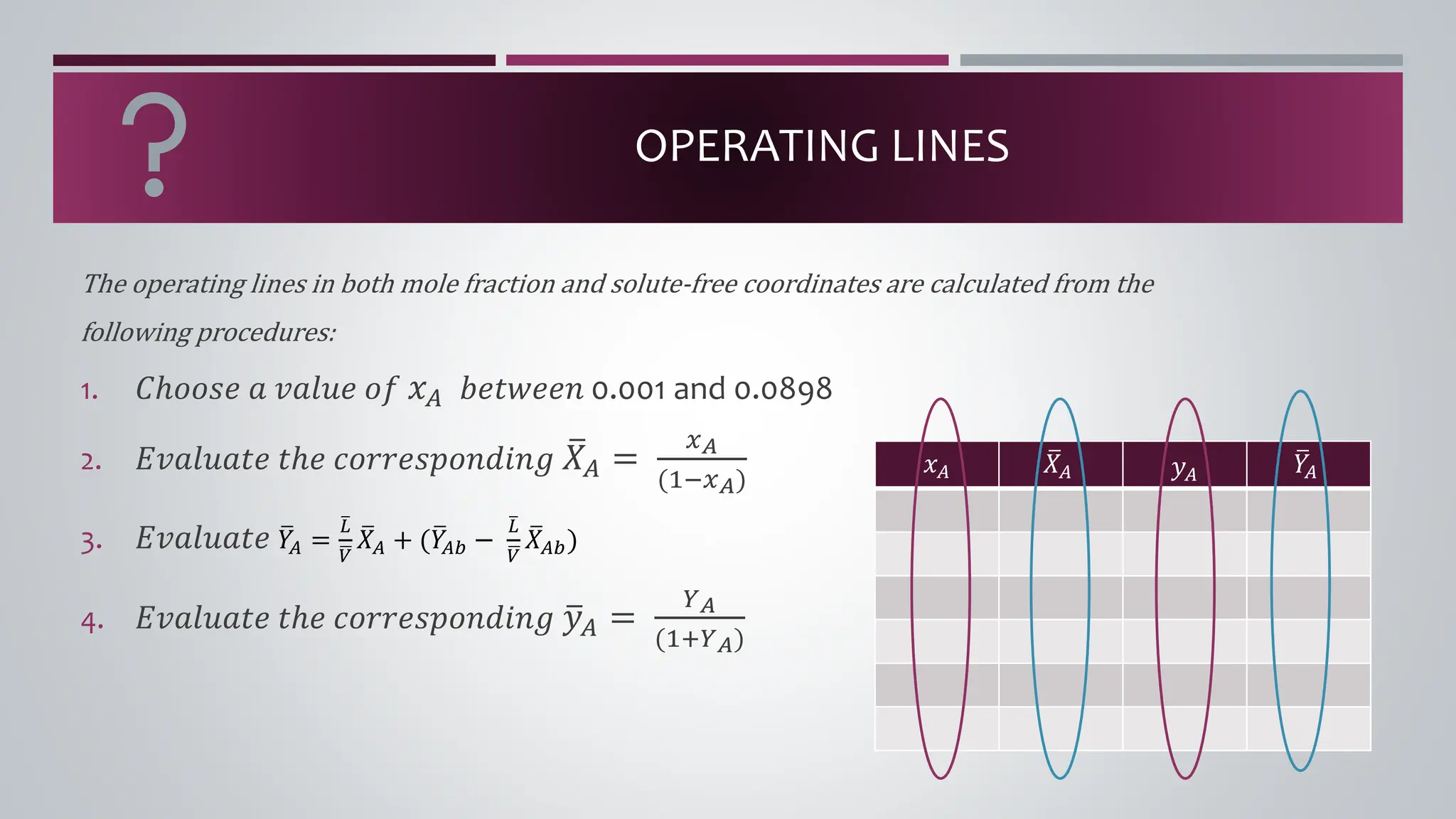
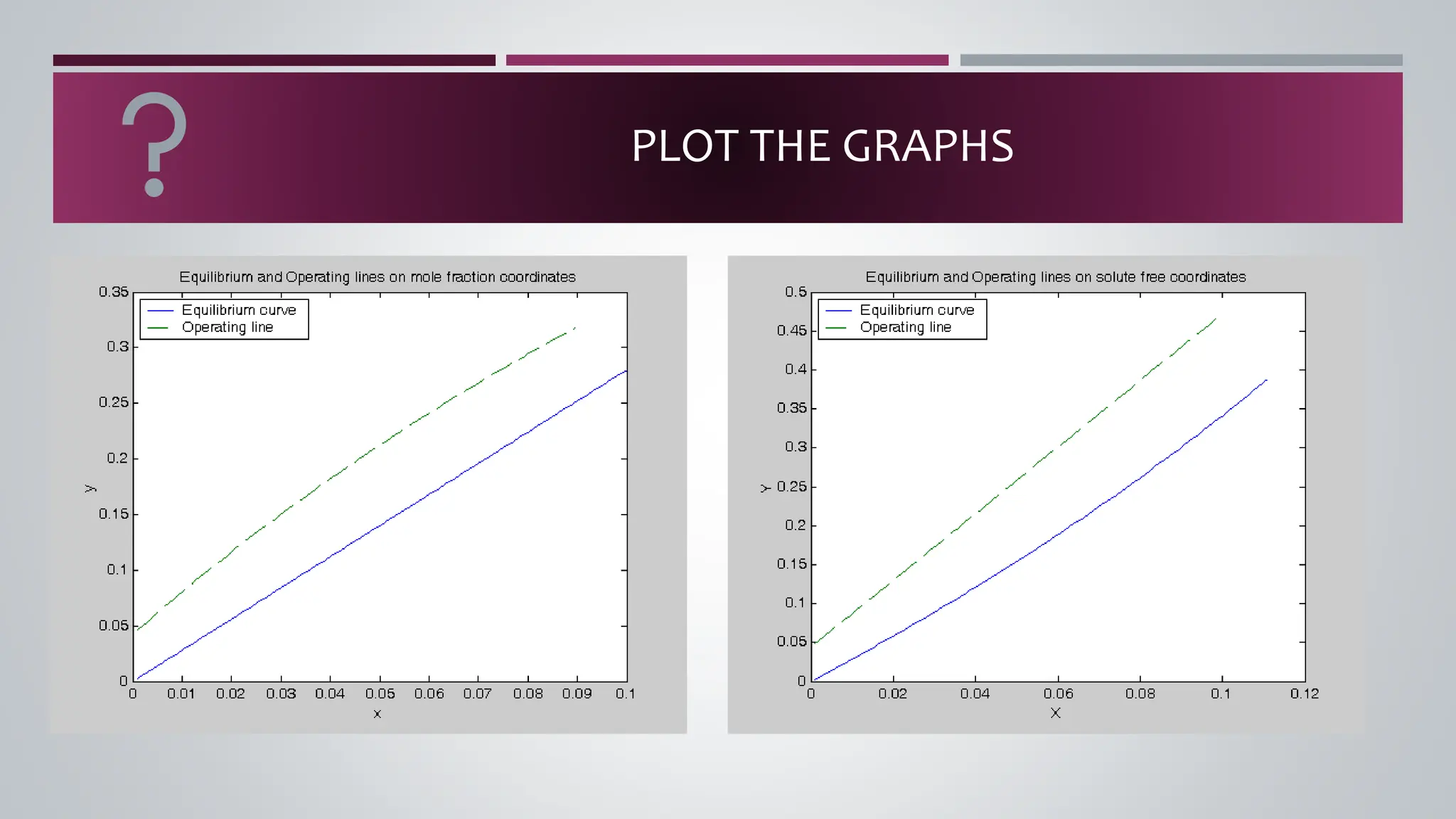
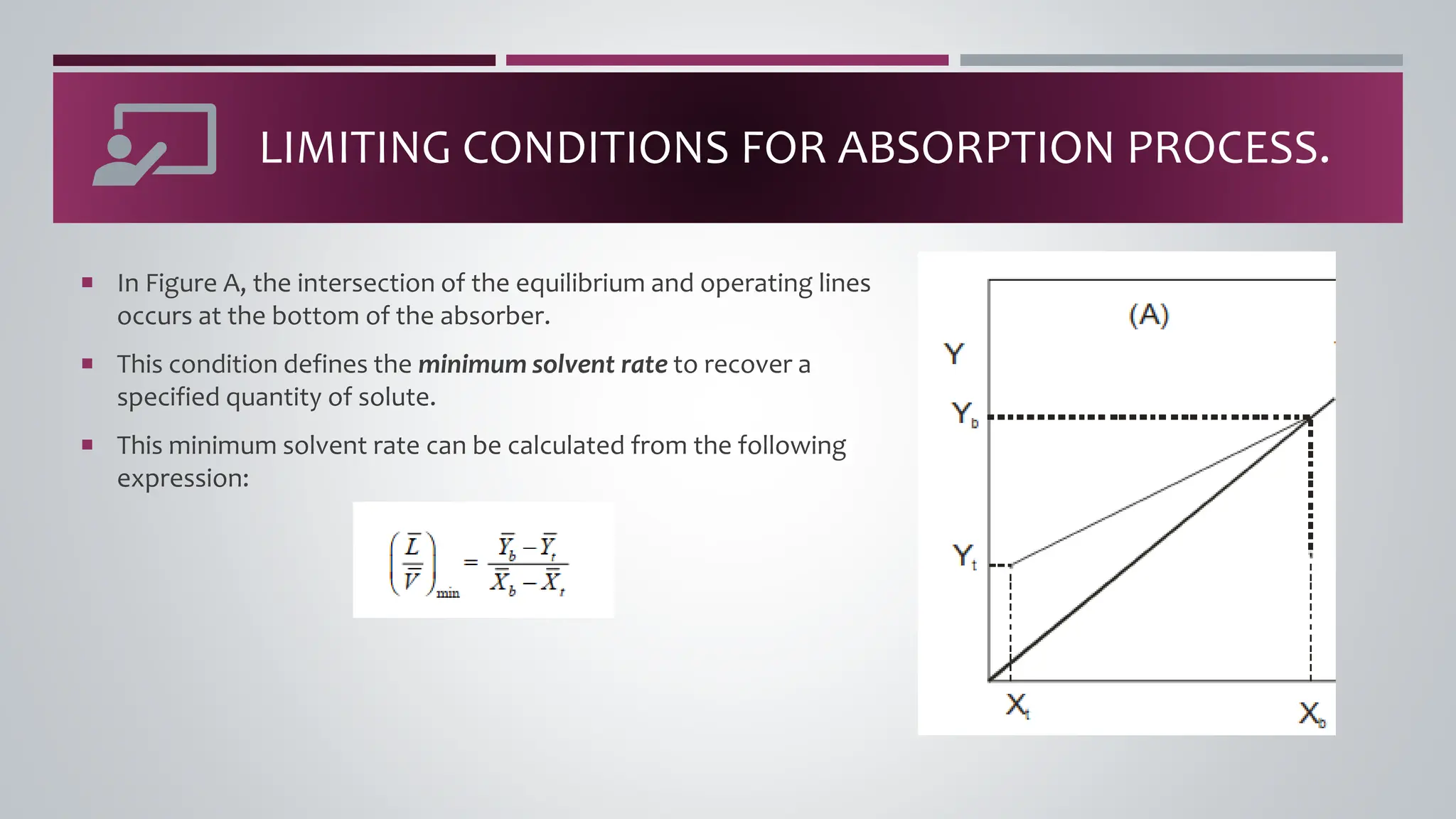
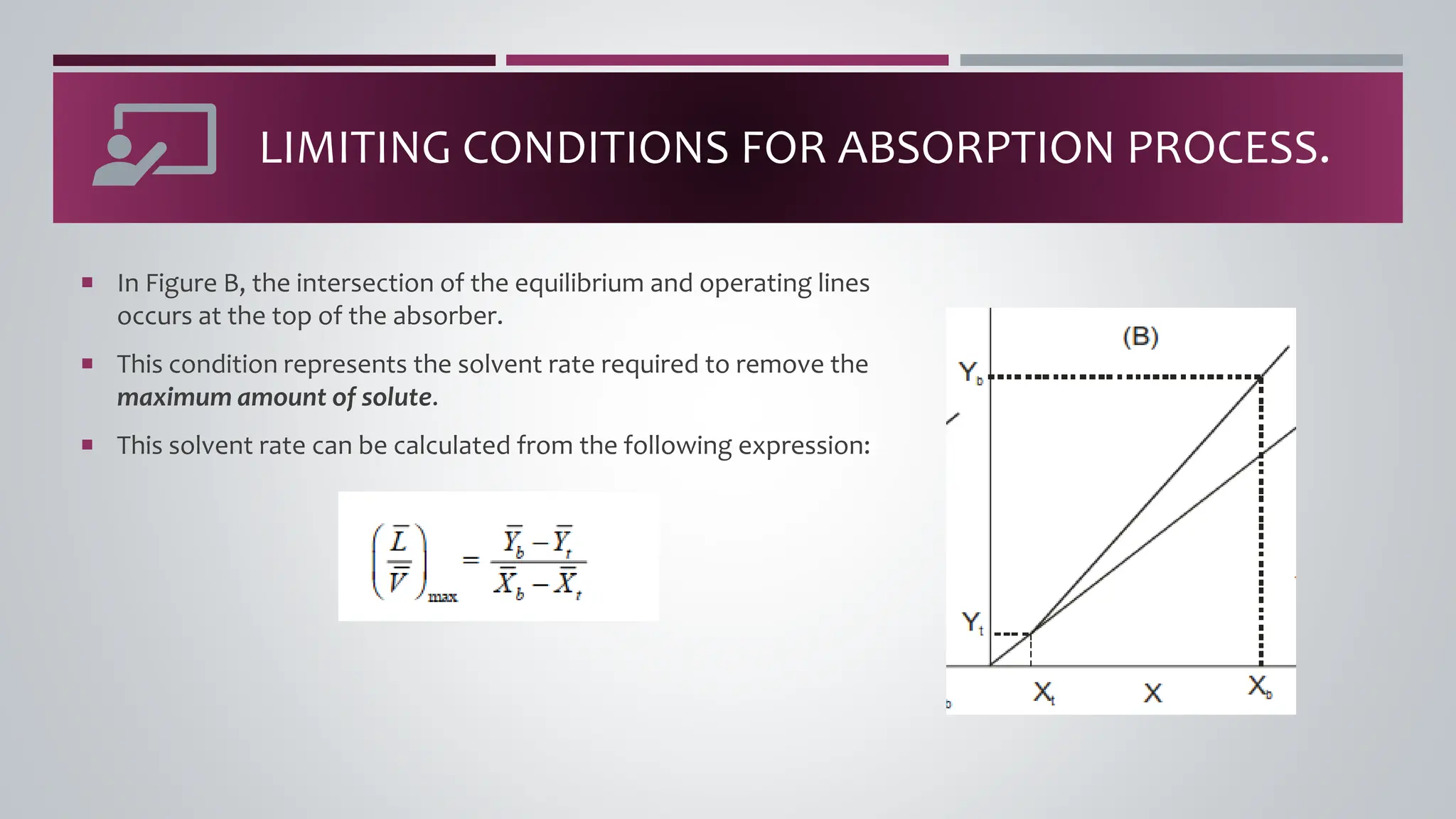
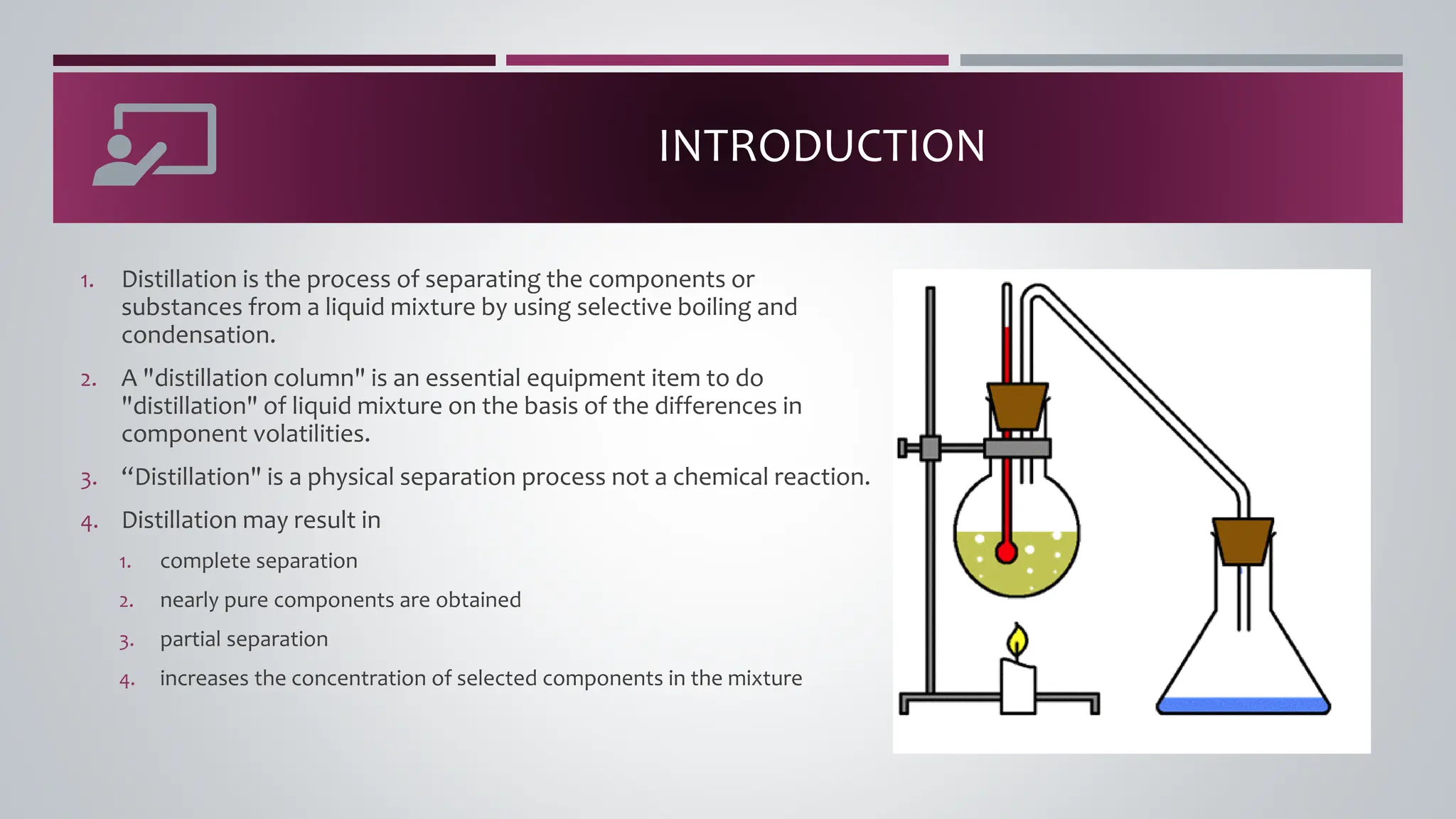
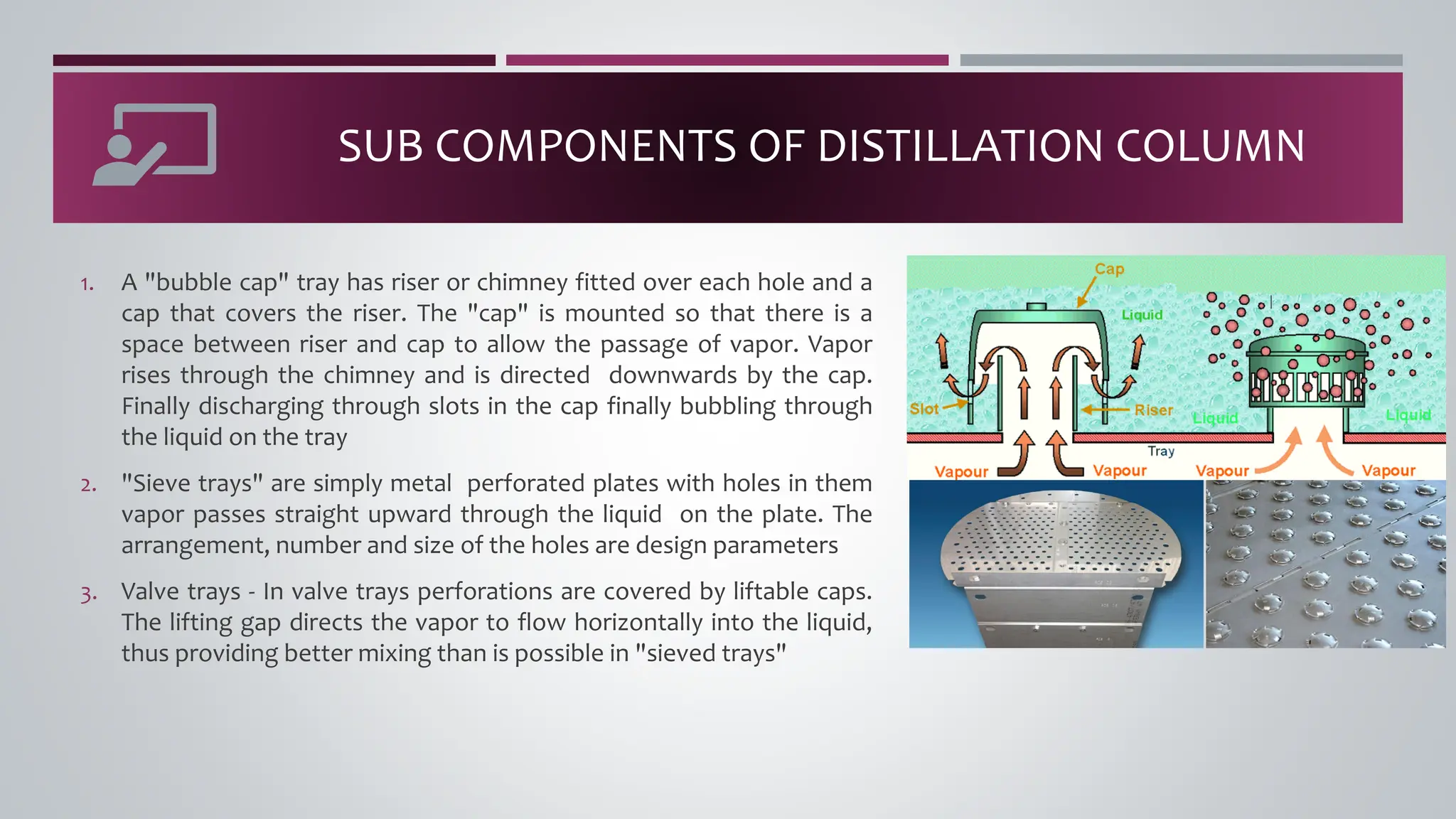
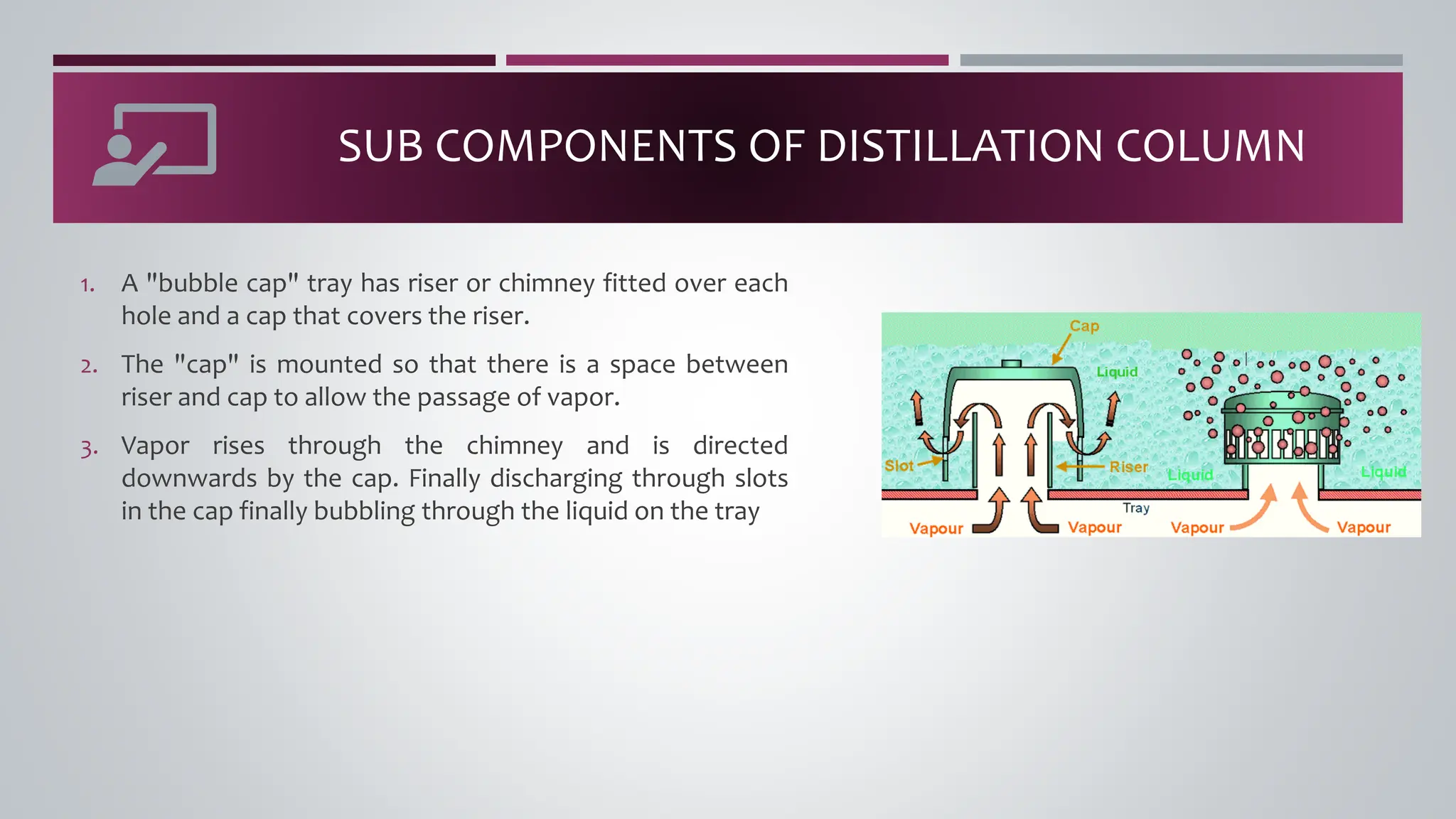
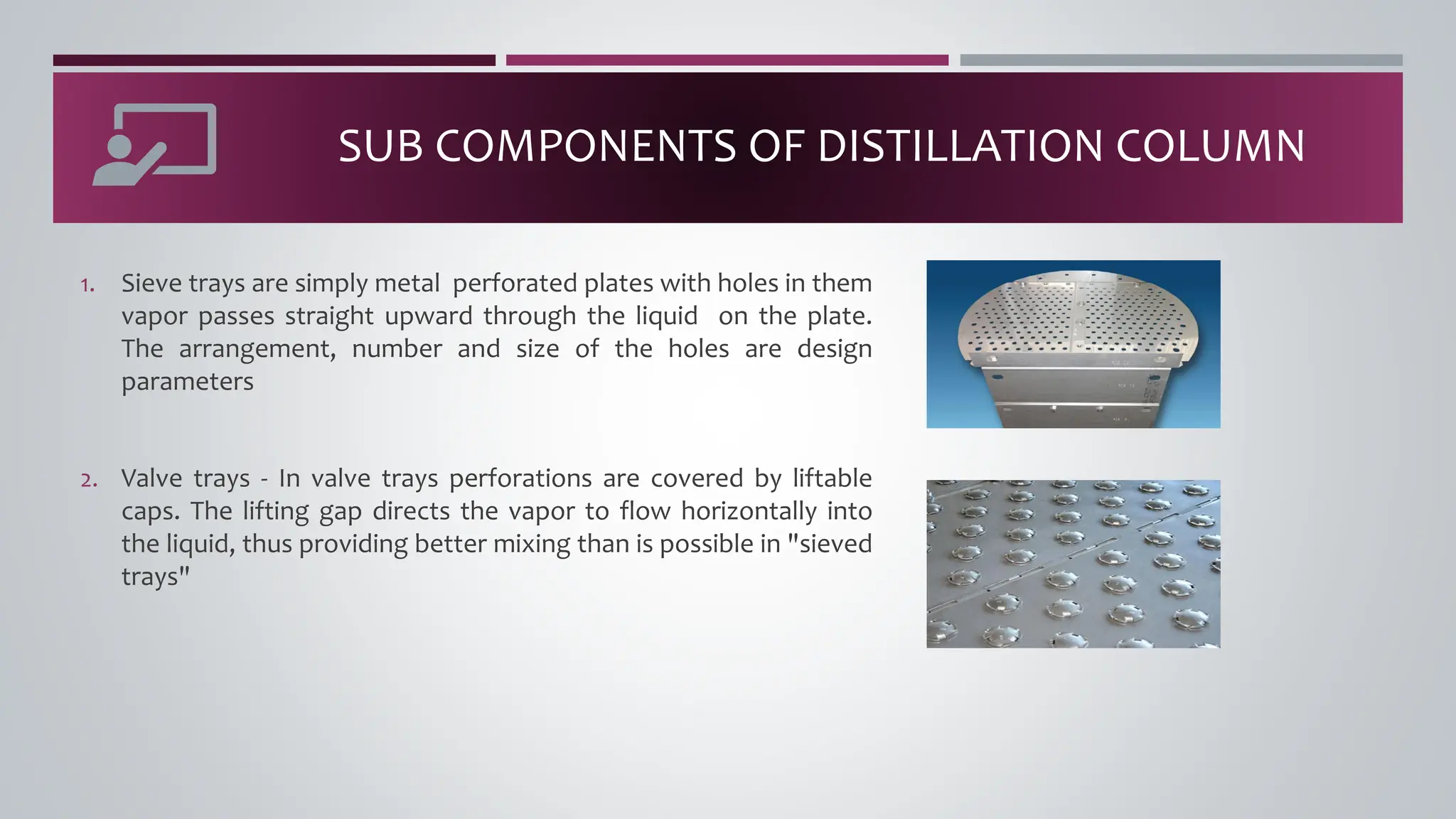
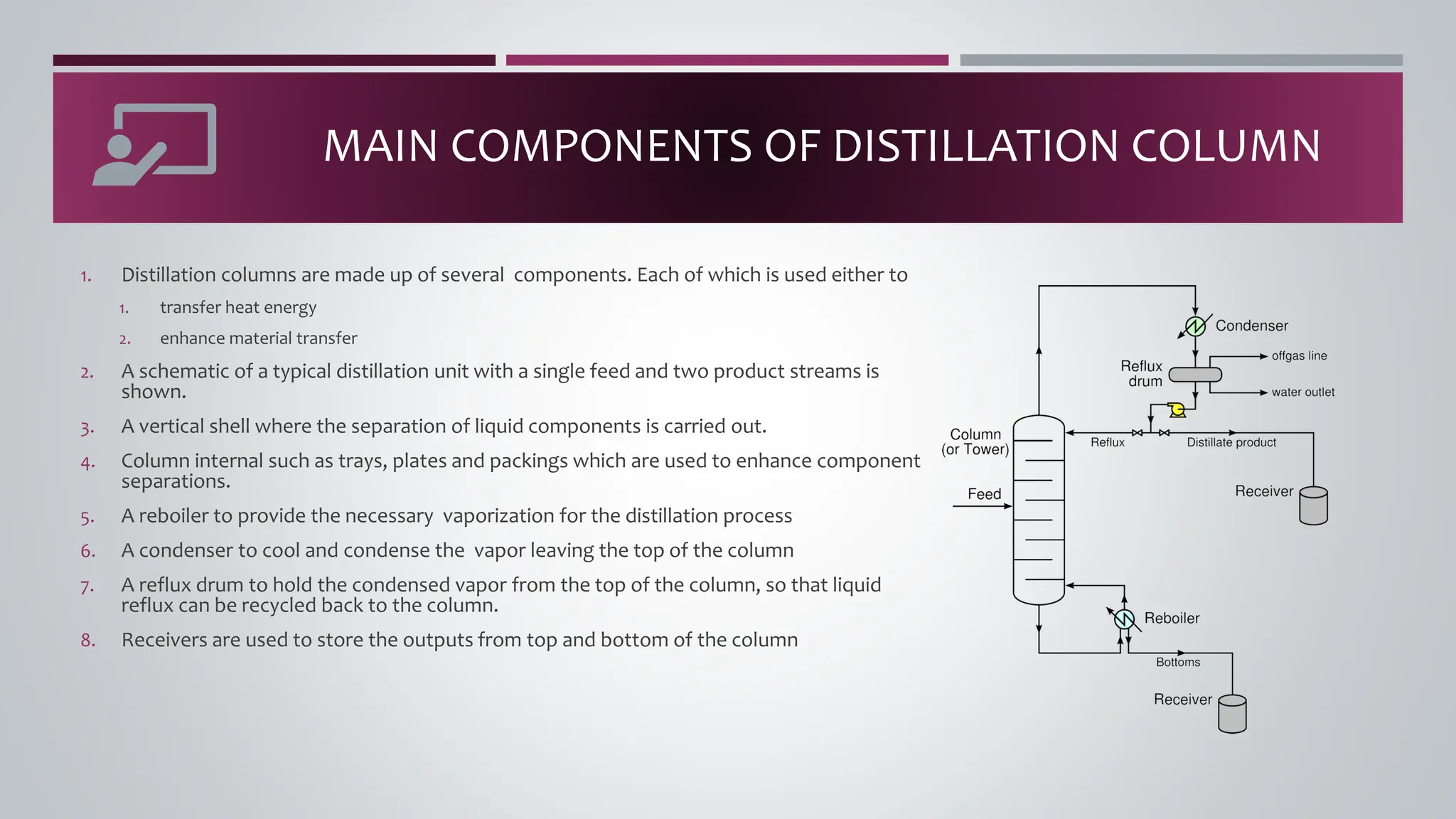
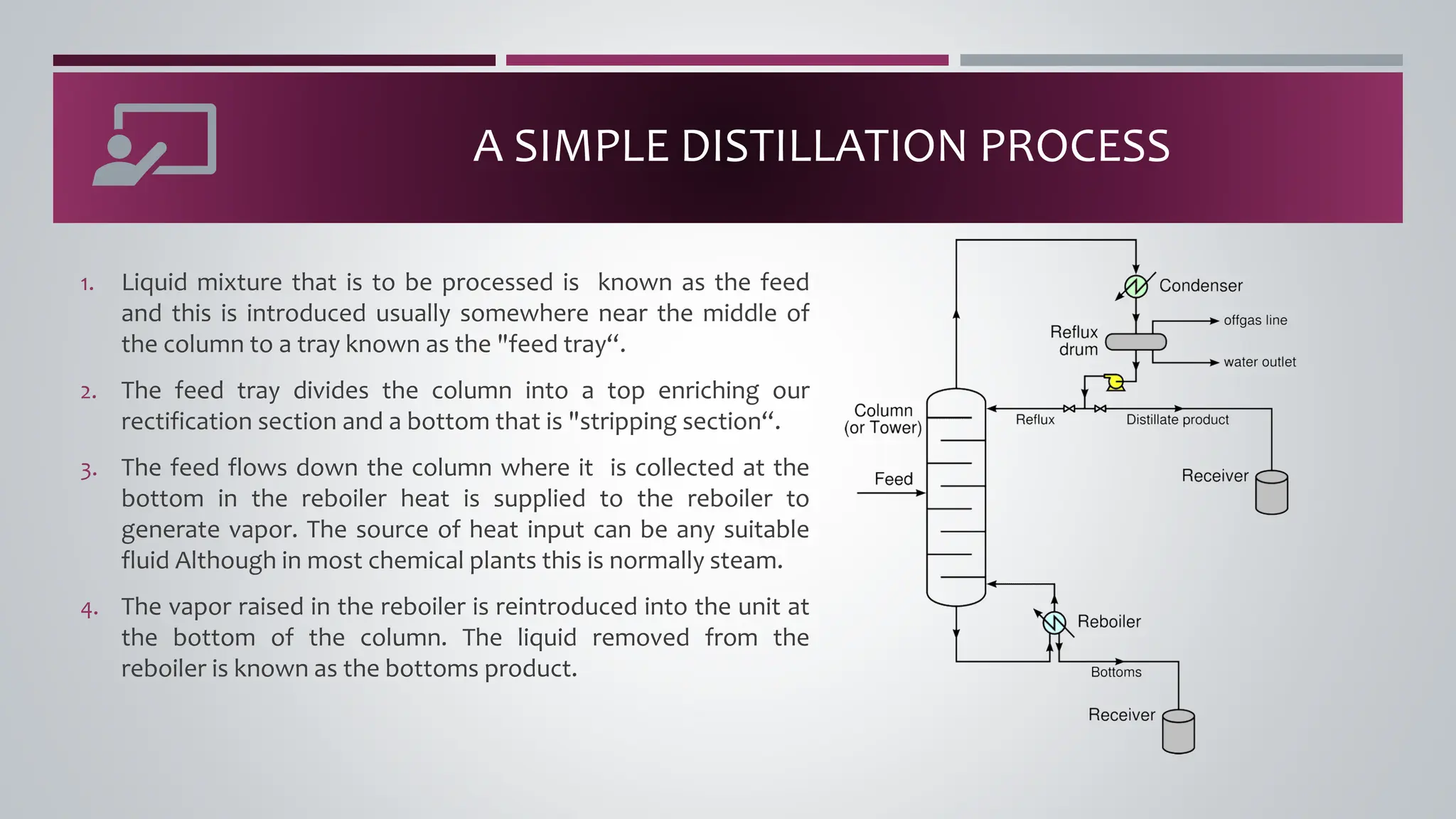
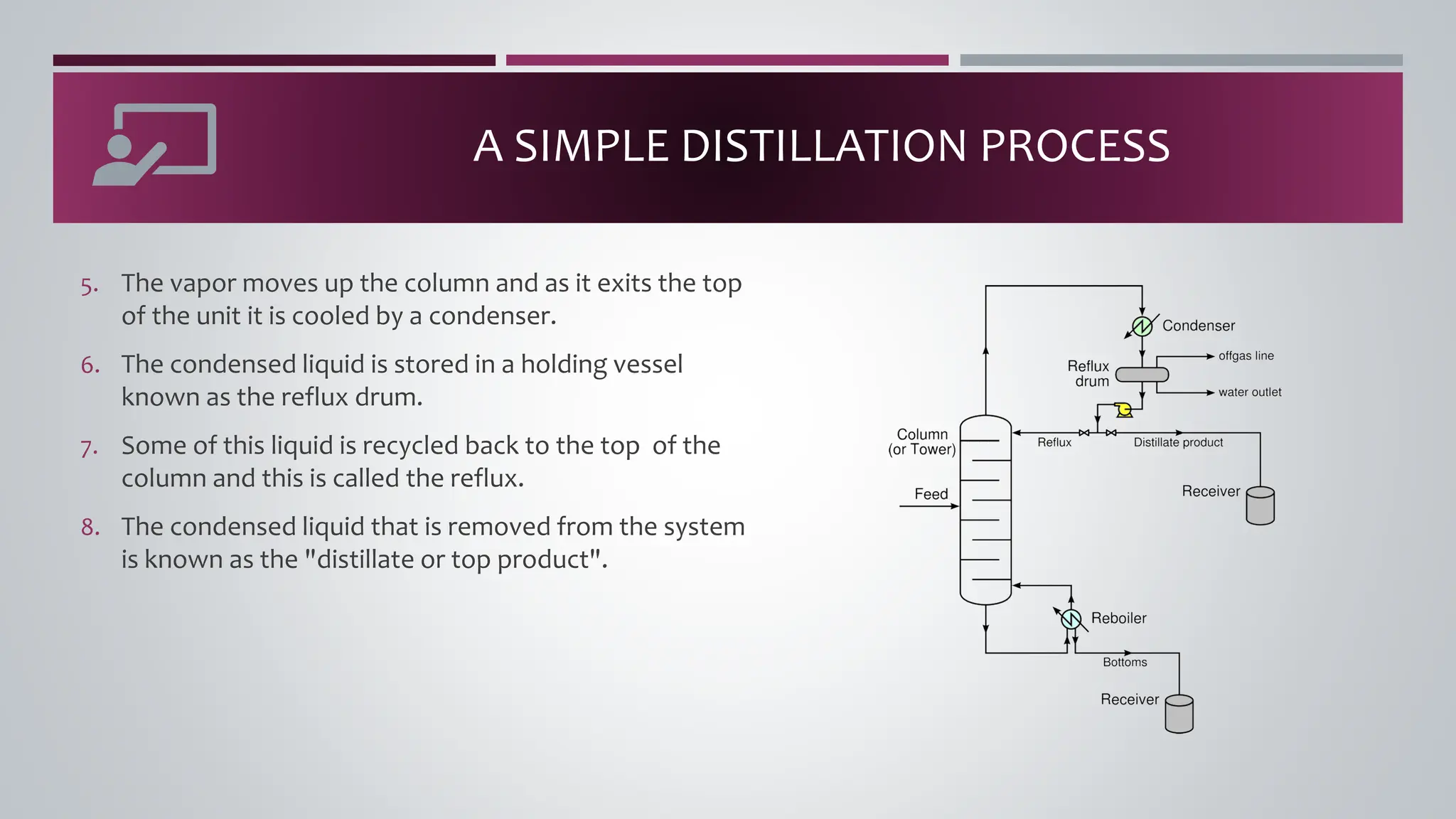
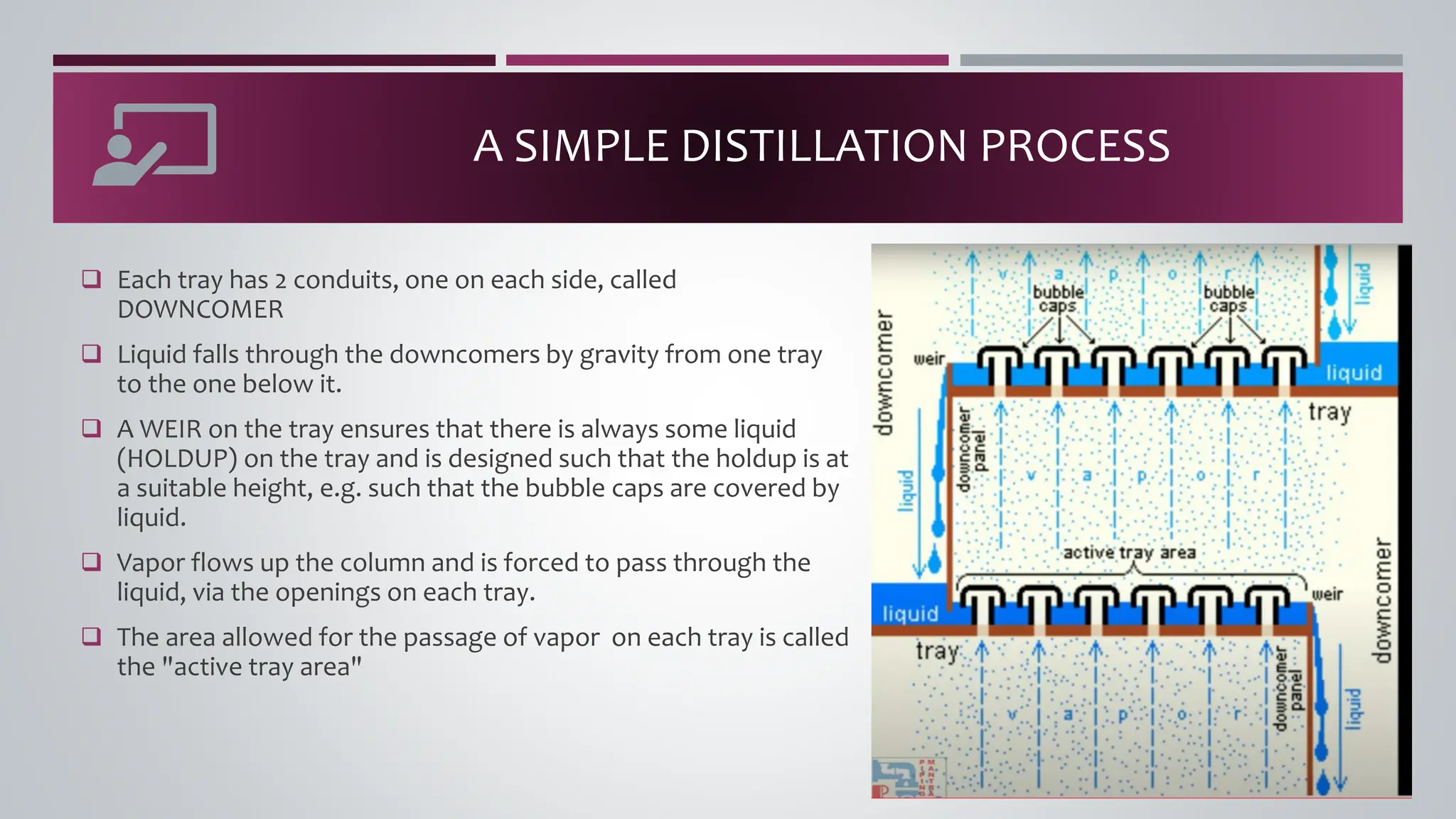
The document discusses the absorption of a solute A from a carrier gas B into a solvent. It provides data on the flow rates and compositions of the gas and solvent streams entering and exiting the absorber. The equilibrium relationship between the solute in the gas and solvent phases is also given. The document calculates the operating line parameters and constructs x-y plots of the equilibrium and operating lines using both mole fraction and solute-free coordinates. It explains that the intersection of the lines represents the limiting condition of the absorption process.