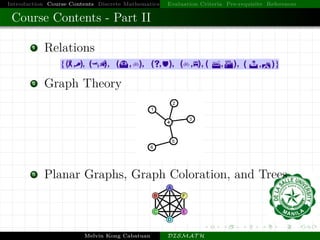
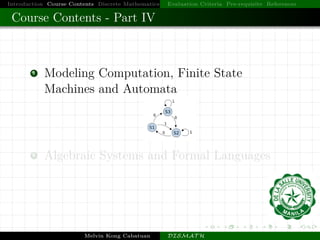
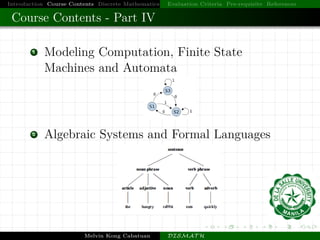
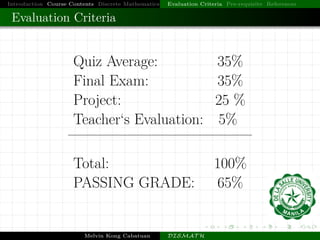
This document introduces a course on discrete mathematics. It provides an overview of the course contents, which are divided into four parts that cover topics like logic, sets, functions, graphs, counting techniques, and computational modeling. The instructor introduces himself and outlines the evaluation criteria, prerequisites, and references for the course. Examples are also provided to illustrate logic puzzles, mathematical reasoning, graph theory, and modeling computation.