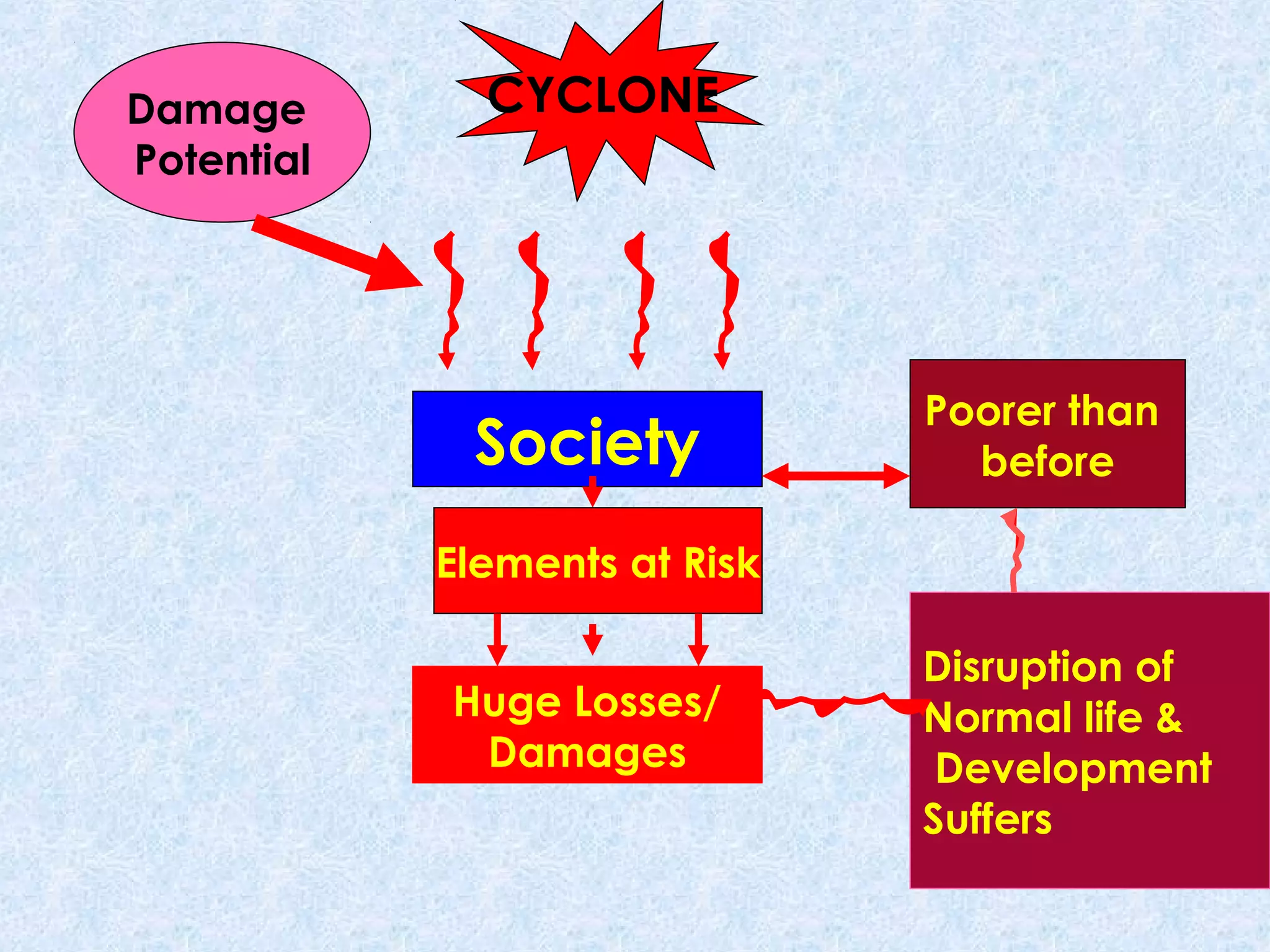
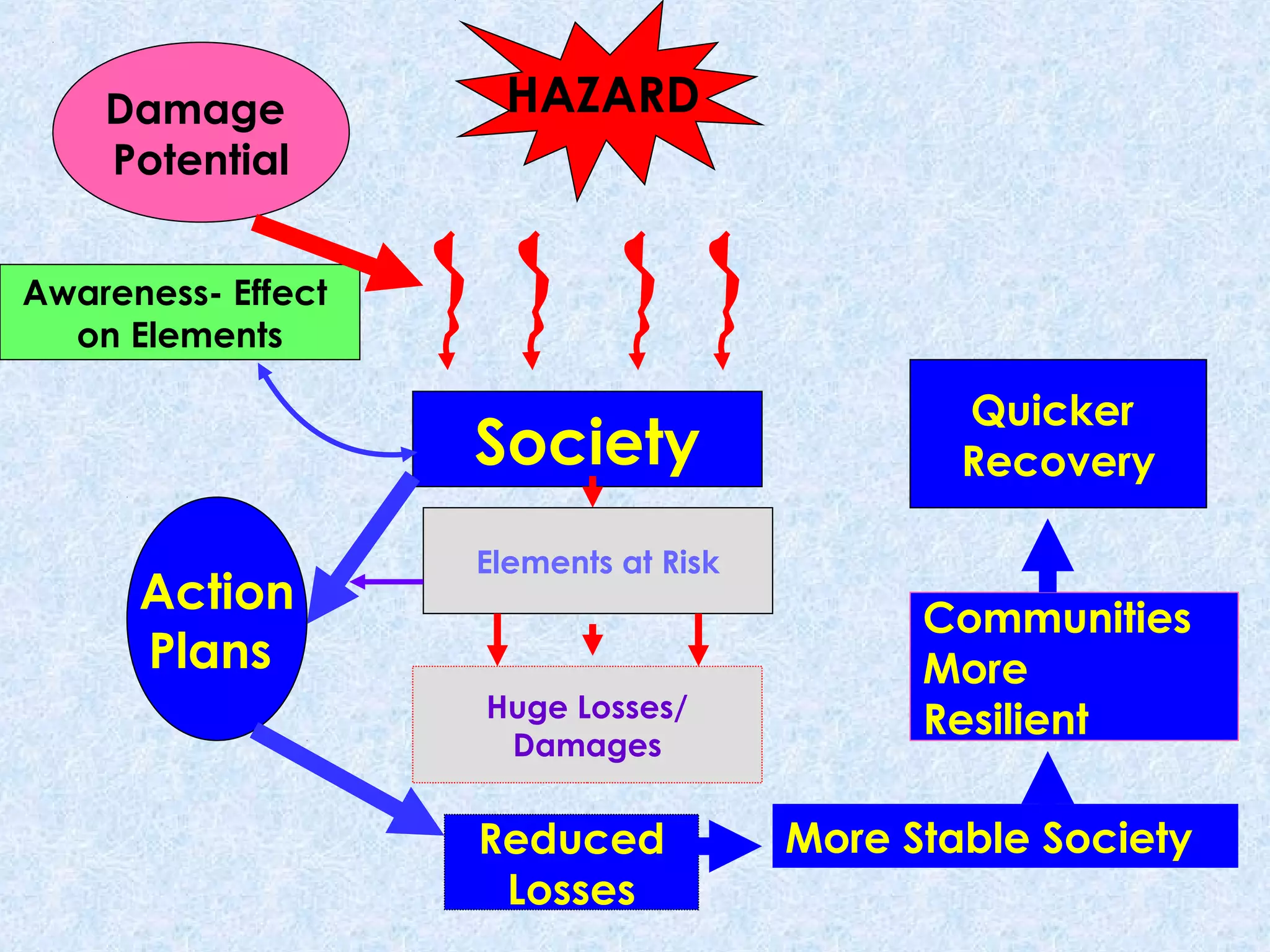
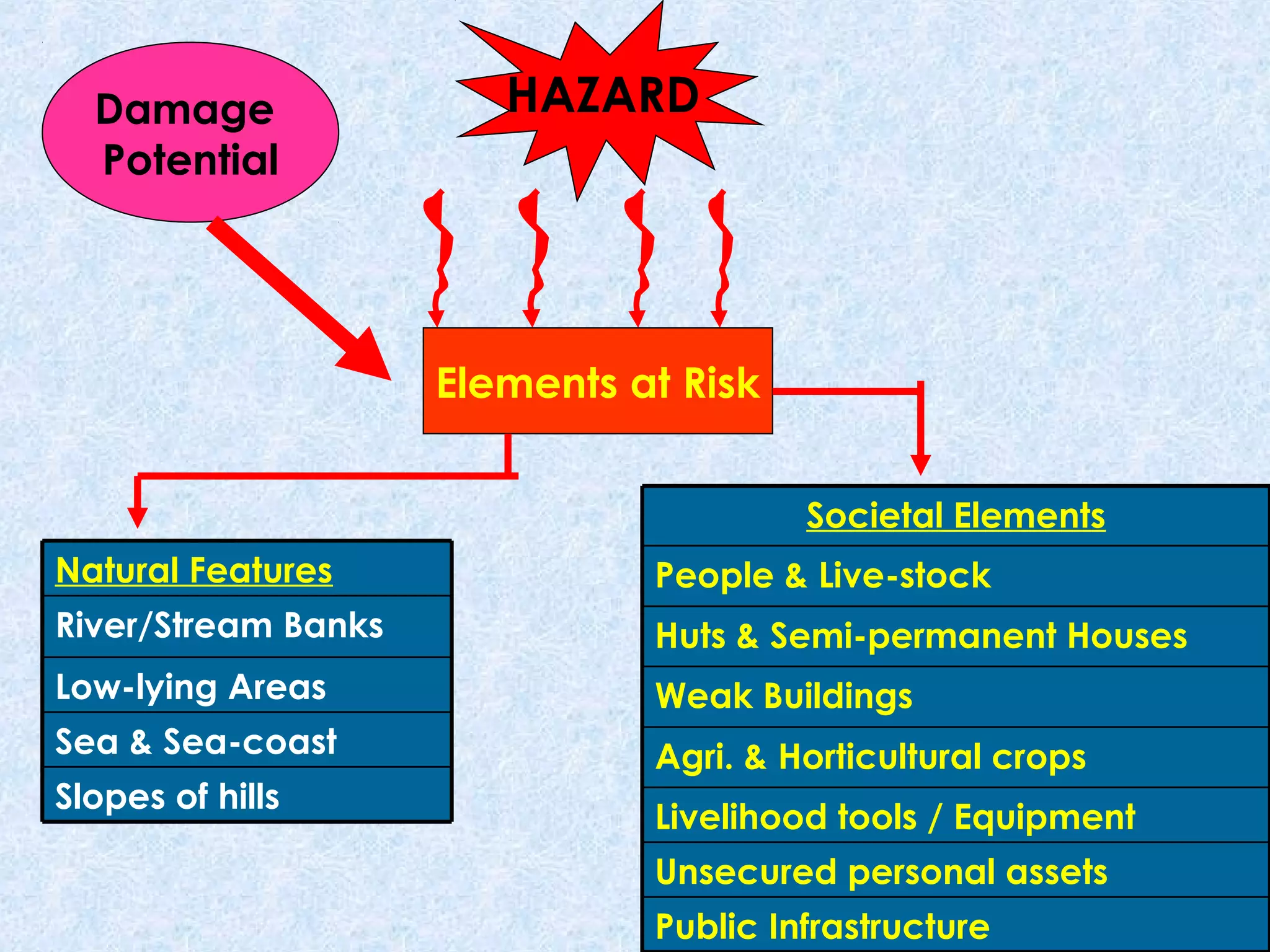
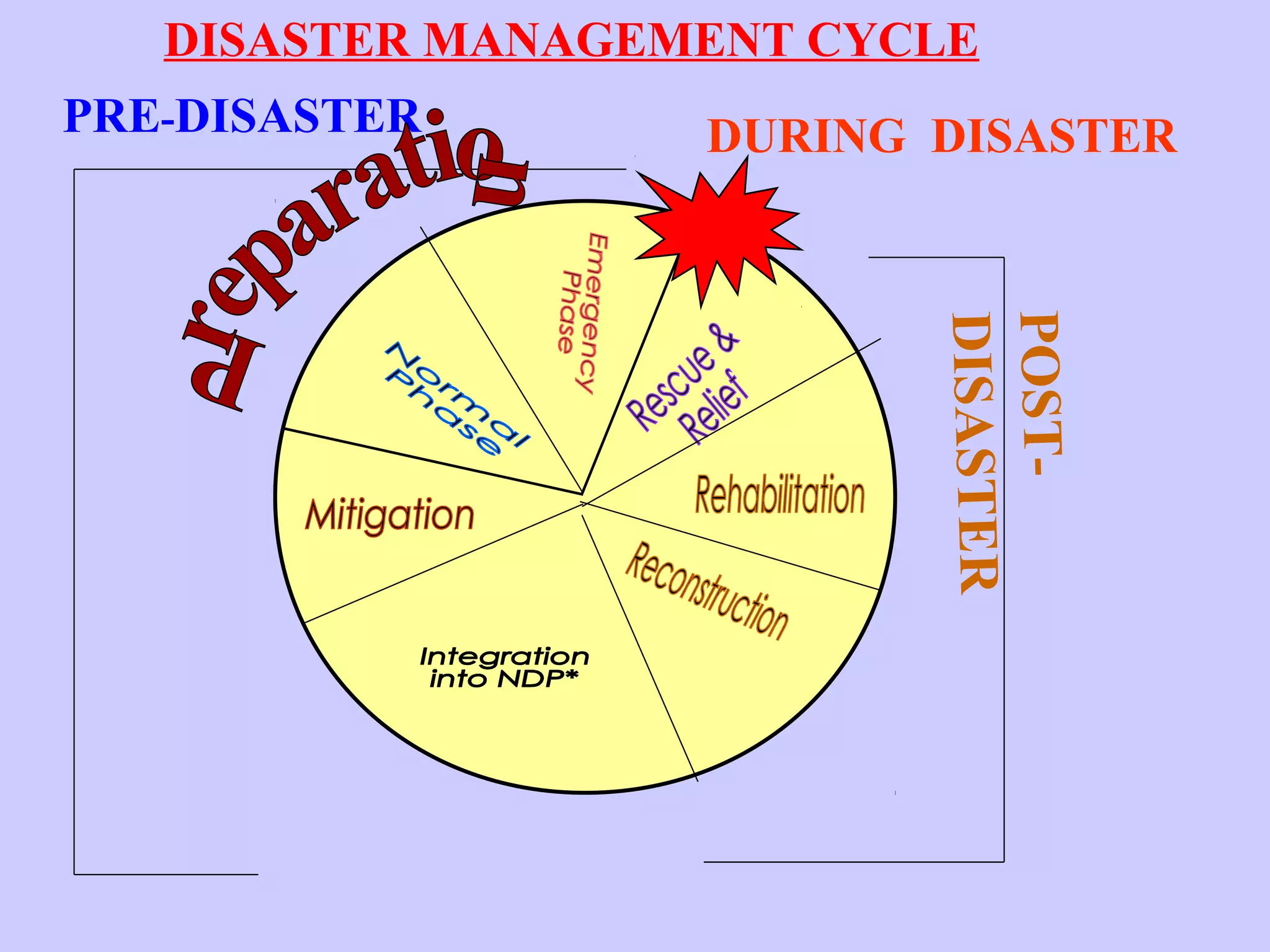
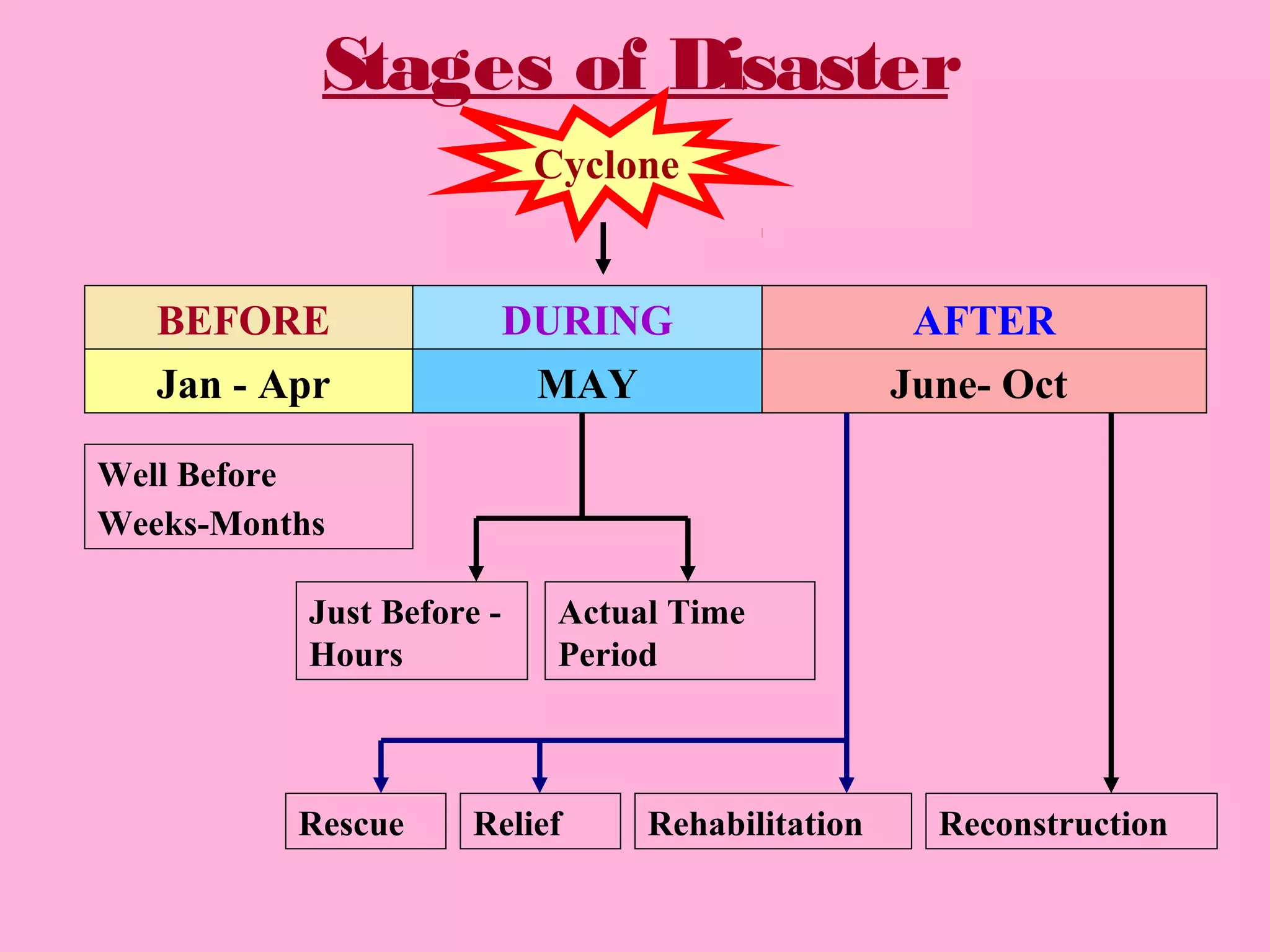
The document discusses disaster management and preparedness for cyclones. It outlines key elements at risk from cyclones like housing, crops, and infrastructure. Effective preparedness requires assessing vulnerabilities, planning response mechanisms, and educating the public. Response activities during a cyclone include evacuation, search and rescue, emergency relief, and expediting post-disaster rehabilitation and reconstruction. Preparedness aims to minimize losses by taking precautionary actions and ensuring timely emergency response.