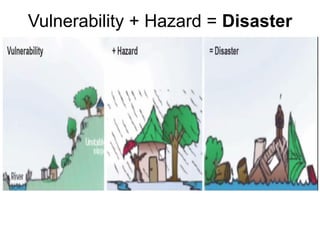
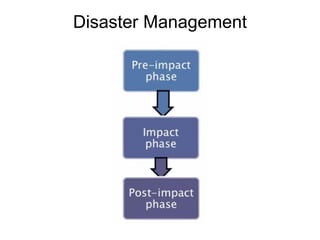
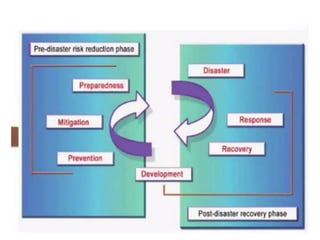
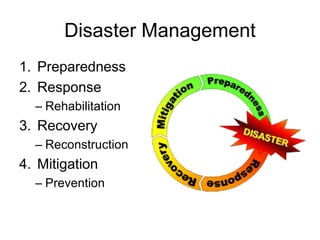
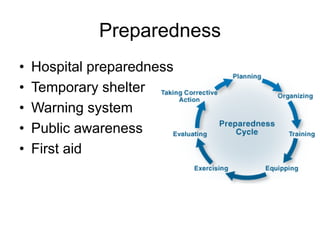
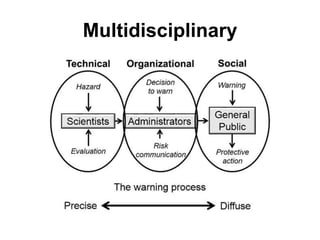
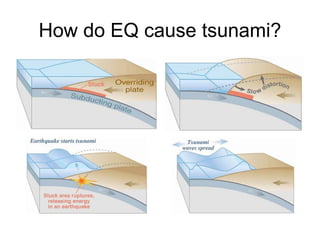
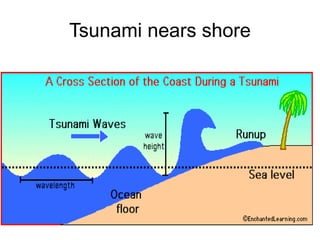
The document discusses disasters caused by natural hazards such as earthquakes and tsunamis. It provides details about the 2011 earthquake and tsunami in Japan, including that an earthquake of magnitude 9 struck off the coast, generating a devastating tsunami. This caused widespread damage and led to a nuclear emergency at the Fukushima power plant. The document also outlines different types of natural disasters and provides information on tsunami formation, preparedness, and response.