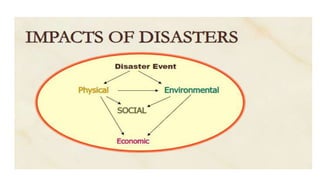
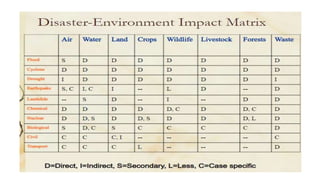
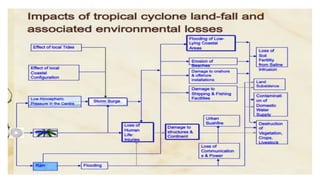
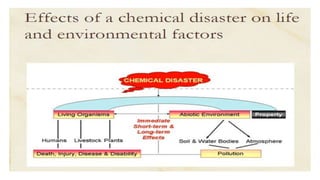
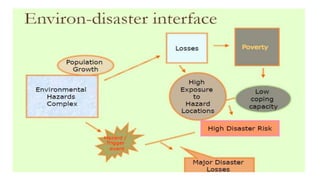
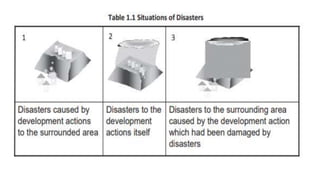
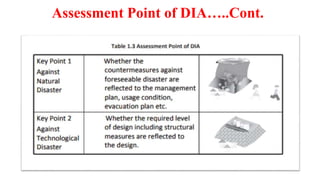
The document discusses disasters and their impacts. It defines a disaster as a sudden event that disrupts normal life and exceeds available resources. Disasters can be natural or man-made. The impacts of disasters include physical damage and injury as well as social and economic disruption. A disaster impact assessment evaluates development projects to identify risks and ways to reduce damages from potential disasters. It considers natural hazards like floods as well as technological hazards caused by infrastructure failures. The assessment aims to incorporate appropriate countermeasures into project design, construction, and management.