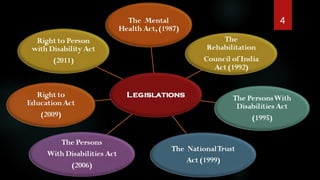
This document summarizes the key disability-related legislation in India from 1966 to 2016 in 3 paragraphs:
Paragraph 1 discusses early legislation from 1966 to 1987 which aimed to promote education for children with disabilities, including the Rehabilitation Council of India Act in 1992 which established the Rehabilitation Council of India.
Paragraph 2 covers legislation from the 1990s including the Persons with Disabilities Act of 1995 which defined and categorized disabilities and established rights and entitlements, as well as the National Trust for the Welfare of Persons with Autism, Cerebral Palsy, Mental Retardation and Multiple Disabilities Act of 1999.
Paragraph 3 discusses more recent developments including the Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act of