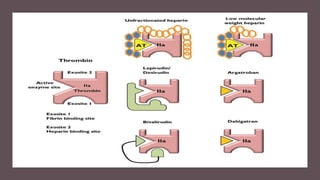
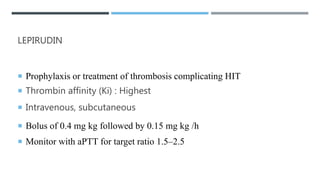
Direct thrombin inhibitors (DTIs) directly inhibit thrombin and do not require interaction with antithrombin. There are bivalent and univalent DTIs. Bivalent DTIs like bivalirudin and lepirudin are used where heparin is contraindicated, while argatroban is used for heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Dabigatran is an oral DTI used to prevent stroke from atrial fibrillation. Each DTI has a specific indication, dosing, and monitoring approach depending on its affinity for thrombin.