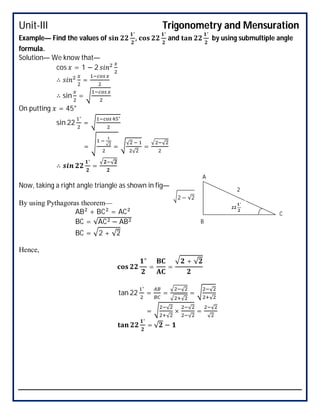
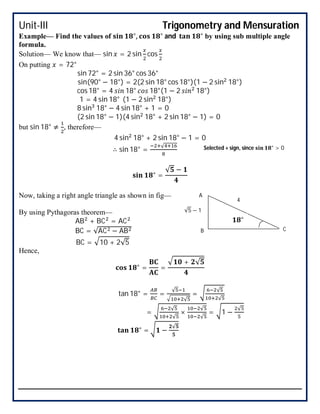
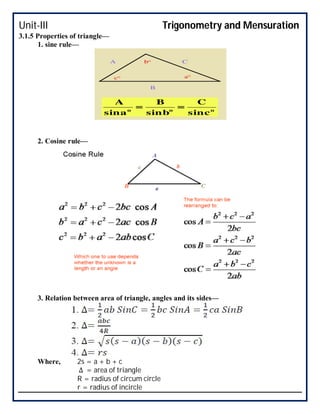
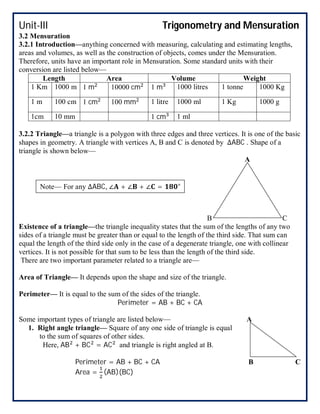
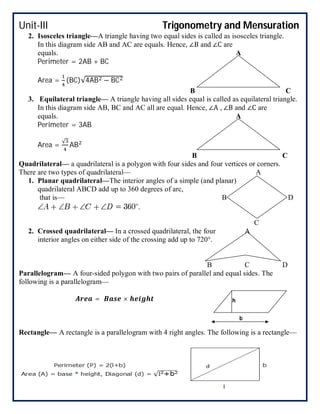
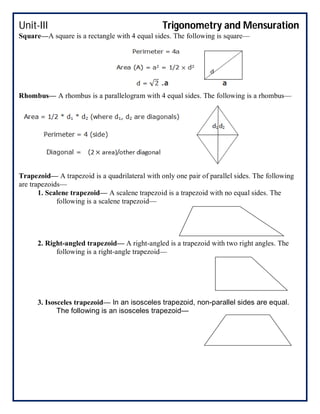
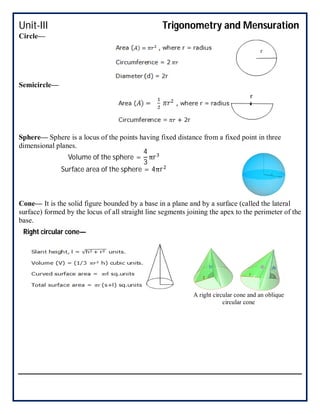
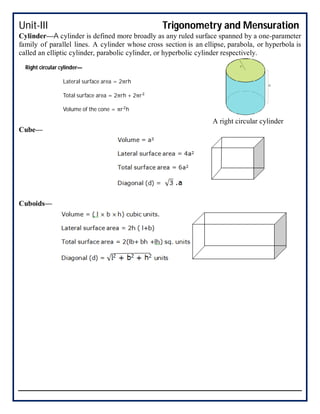
This document covers trigonometry and mensuration topics including trigonometric identities, compound angle formulas, double angle formulas, sub-multiple angle formulas, properties of triangles, and mensuration of triangles, quadrilaterals, circles, spheres, cones, cylinders, cubes and cuboids. Examples are provided to demonstrate using sub-multiple angle formulas to find trigonometric values of particular angles. Exercises at the end test comprehension of finding trigonometric values, properties of different types of triangles including area calculations, volumes of cones and cylinders, and references are listed.