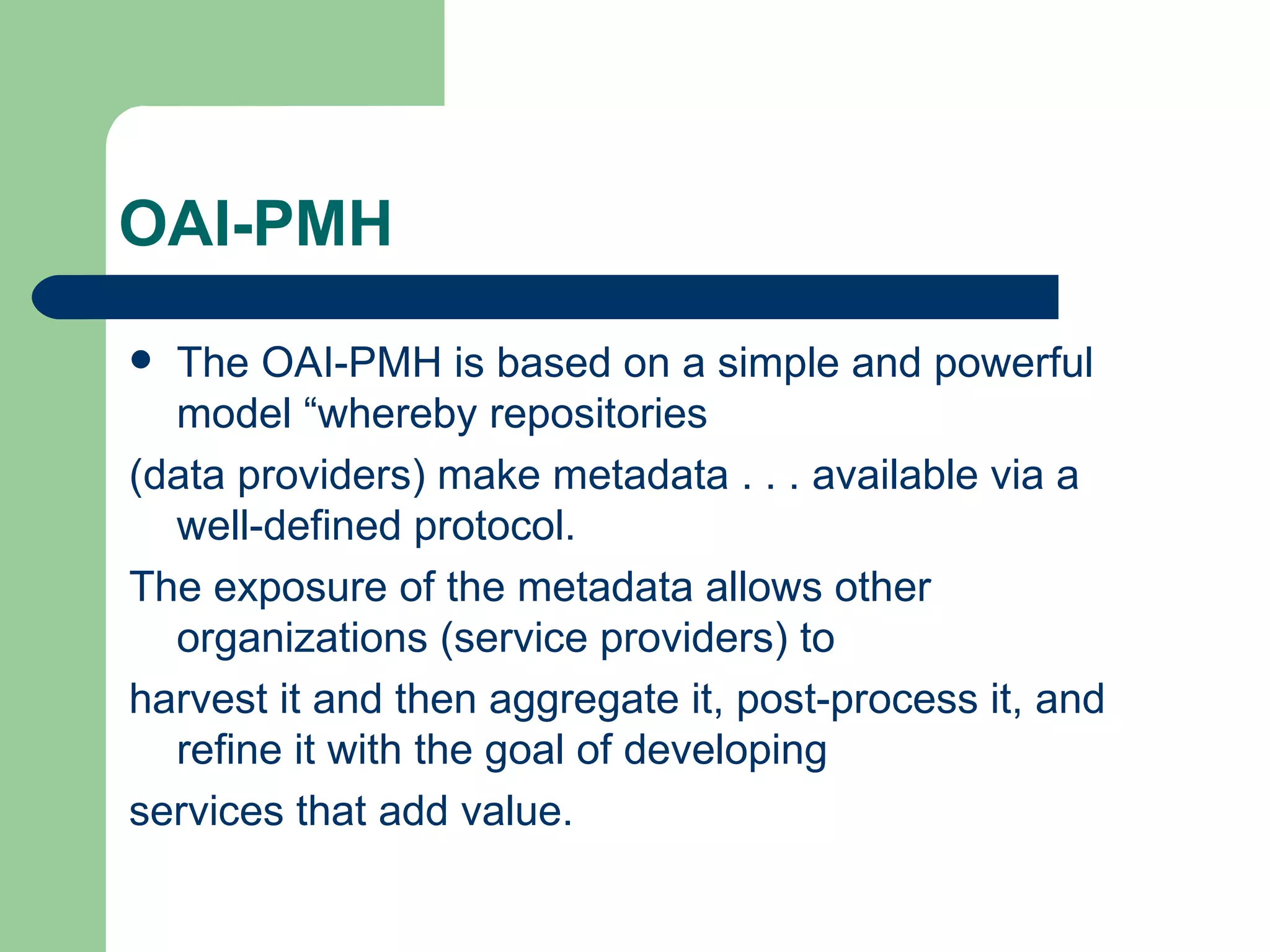
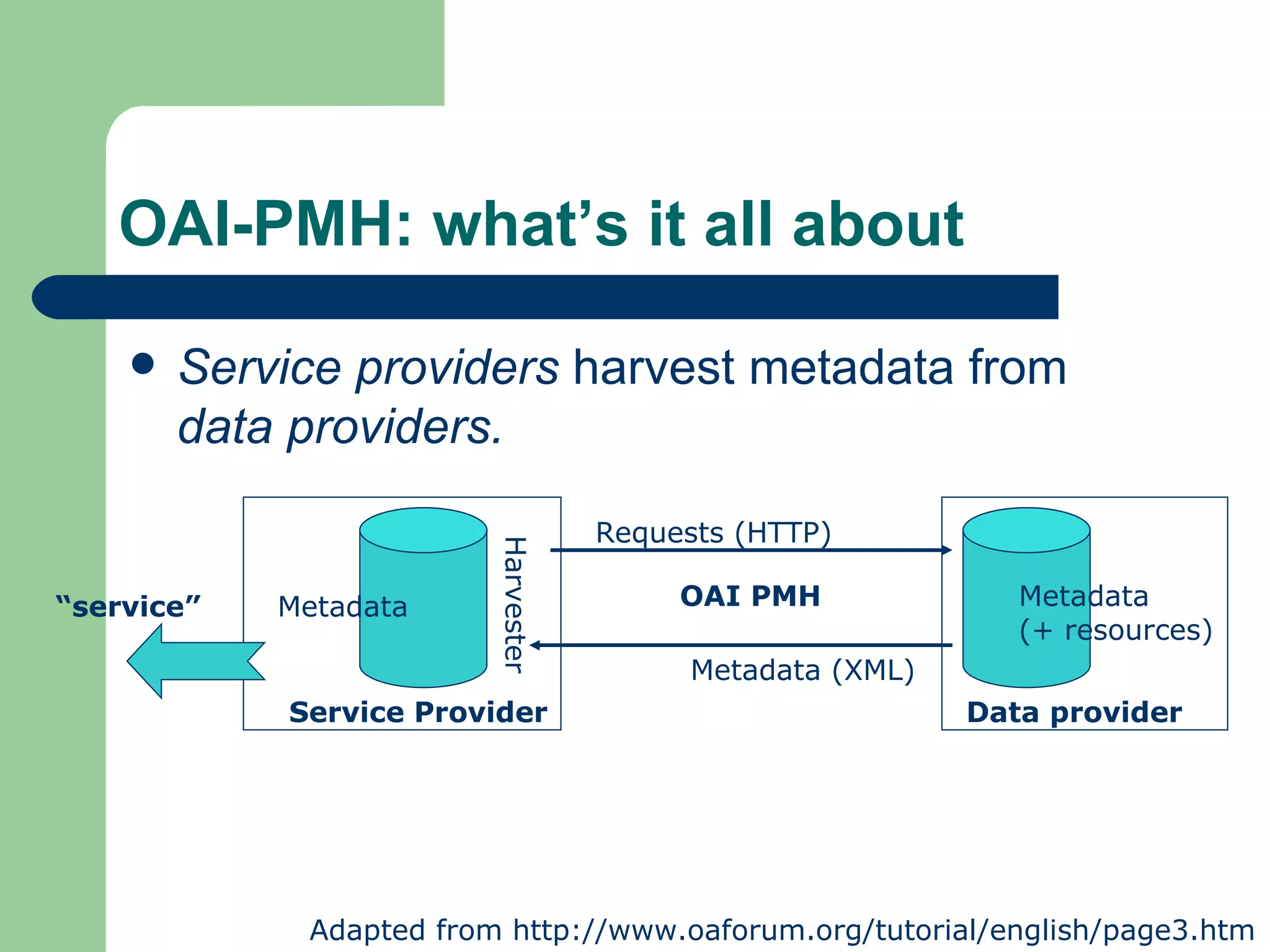
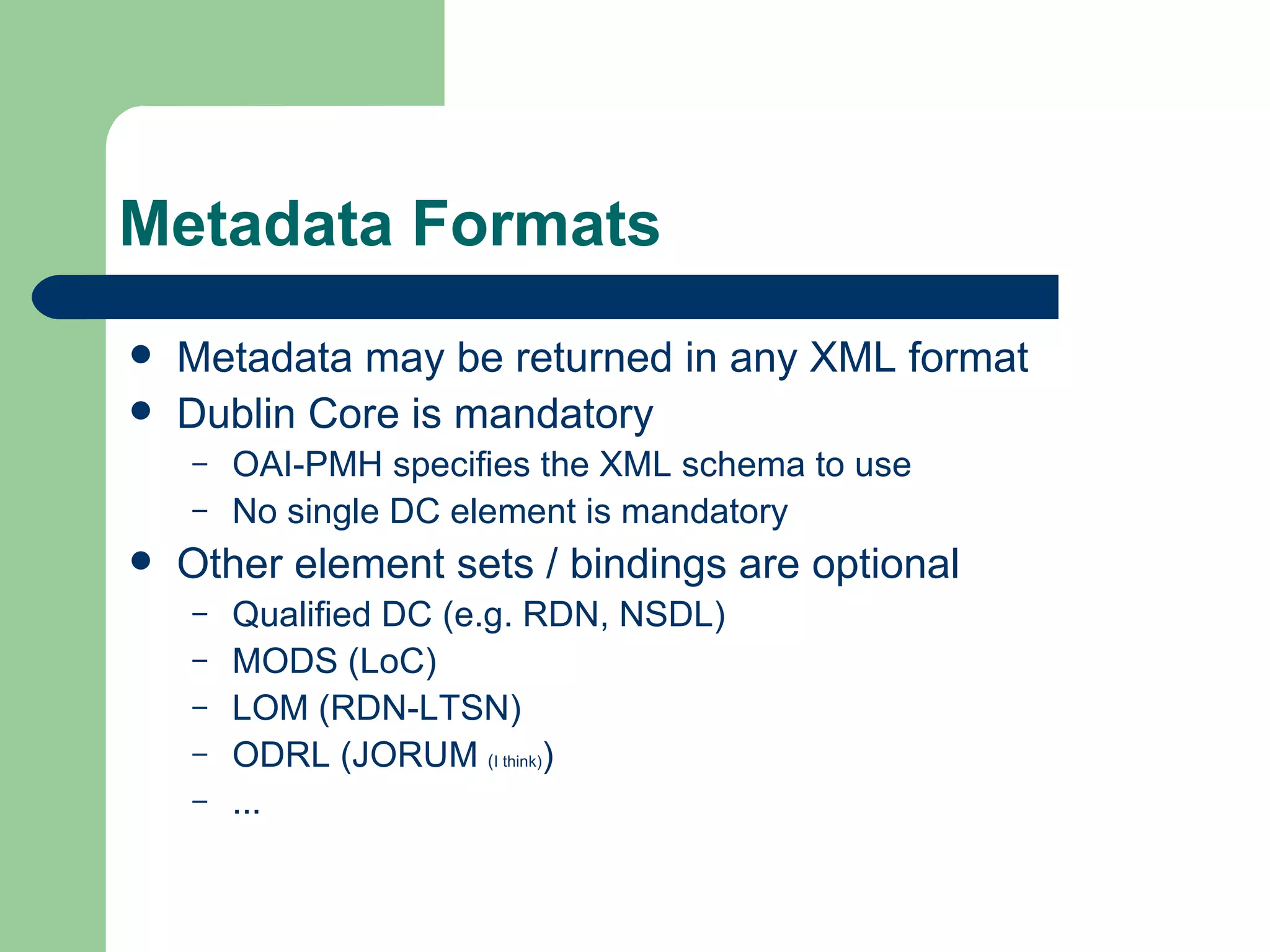
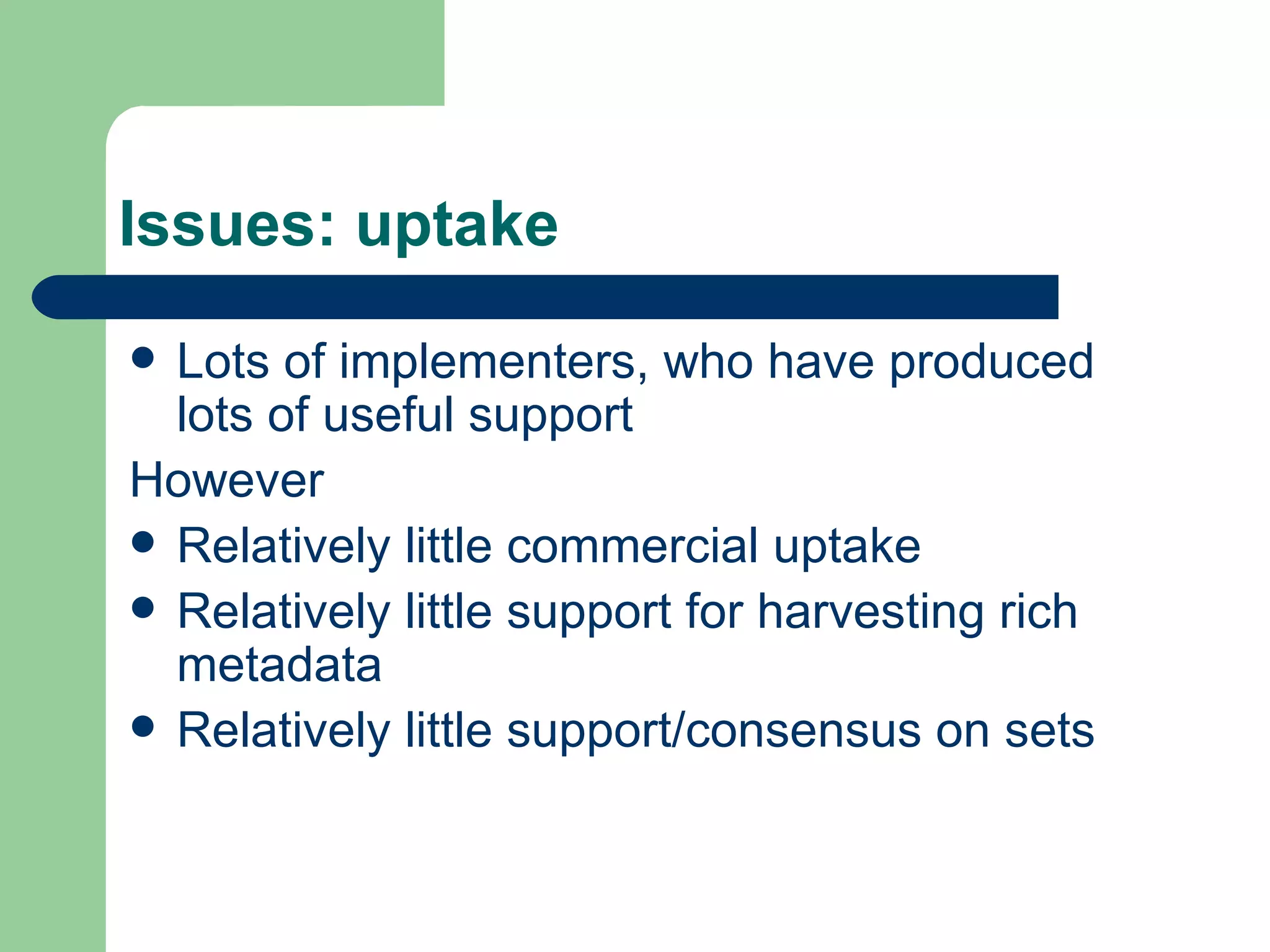
The document discusses the Open Archive Initiative Protocol for Metadata Harvesting (OAI-PMH). It describes OAI-PMH as a standard that allows data providers to make metadata available via HTTP so that service providers can harvest the metadata to develop value-added services. It provides details on the various requests and operations that are part of the OAI-PMH protocol. The document also discusses some implementation issues and examples of service providers that utilize OAI-PMH harvested metadata.
![Open Archive Initiative – Protocol for metadata Harvesting (OAI-PMH) Surinder Kumar Technical Director NIC, New Delhi [email_address] , 011-24305503](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/digitisationandinstitutionalrepositories3-101015013520-phpapp02/75/Digitisation-and-institutional-repositories-3-1-2048.jpg)












![Contd… SAIL-eprints (Search, Alert, Impact and Link) http://eprints.bo.cnr.it/ April 2003 SAIL-eprints (Search, Alert, Impact and Link) is “an electronic open access service provider for finding scientific or technical documents, published or unpublished, in Chemistry, Physics, Engineering, Materials Sciences, Nanotechnologies, Microelectronics, Computer Sciences, Astronomy, Astrophysics, Earth Sciences, Meteorology, Oceanography, . . . [Agriculture], and related . . . [subjects].”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/digitisationandinstitutionalrepositories3-101015013520-phpapp02/75/Digitisation-and-institutional-repositories-3-18-2048.jpg)