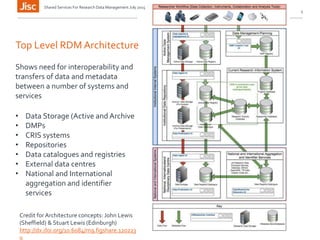
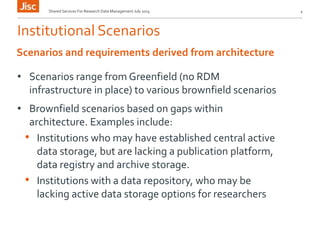
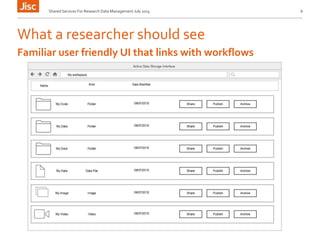
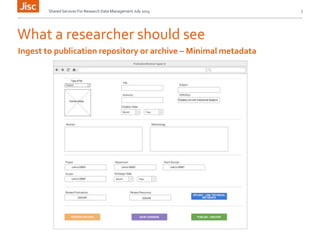
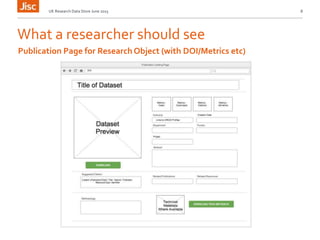
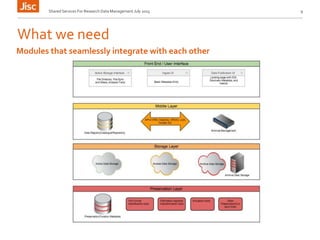
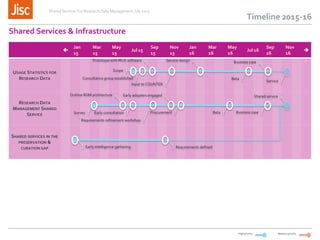
This document discusses the concept of a shared research data management service. It outlines the need for interoperability between data storage, management plans, repositories, and other systems. Various institutional scenarios are presented, from those just starting research data management to those with some existing infrastructure. The vision is for a Jisc-provided shared cloud storage service integrated with publication and archiving functionality to help researchers easily manage the full data lifecycle. Potential technical solutions already exist that could be integrated to develop such a service. Stages of development, benefits, and timelines are proposed.