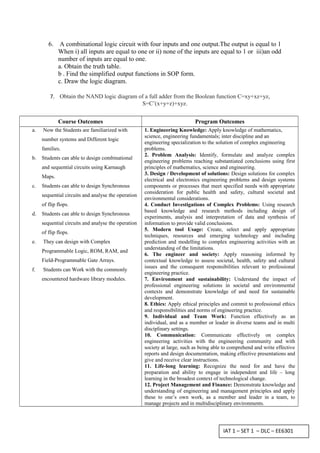
This document contains two sets of exam questions for a Digital Logic Circuits course. Set 1 and Set 2 each contain 10 short answer questions and 5 long answer questions. The questions cover topics such as number representation, logic gates, logic families, combinational logic circuits, and sequential circuits. The document also lists the course outcomes related to students gaining knowledge of number systems, logic design techniques, sequential circuits, and programmable logic.
![DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS
IAT 1 – SET 1 – DLC – EE6301
ENGINEERING
IAT - I AUGUST 2014
SET-I
Sem & Branch : III & EEE(A/B) Date: 12th August, 2014
Subject : DIGITAL LOGIC CIRCUITS Duration : 3Hrs
Sub.code : EE 6301 Max.Marks: 100
Answer All Questions
Part-A [10 x 2 = 20Marks]
1. Convert (4021.2)5 to its equivalent decimal
2. Represent the decimal 8620 in BCD and Binary.
3. Perform subtraction using 9’s complement:5250-321
4. What are the advantages of CMOS?
5. Compare the various digital logic families.
6. What is meant by parity bit?
7. Implement OR gates using only NAND gates
8. State De Morgan’s theorem
9. How does don’t care condition in K map help for circuit simplification
10. Why digital circuits are more frequently constructed with NAND and NOR gates?
Part - B [5 x 16 = 80Marks]
[Answer any Five]
1. Demonstrate the CMOS logic circuit configuration and characteristics in detail.
2. Explain the concept, working and characteristics of TTL logic families.
3. Construct a Hamming code group for the information bits 100101 that enables single
error correction plus double error detection where the most significant bit of the code
group is for the overall even parity bit. Assume that errors occur in bit positions 2 and
9 of the above code group. Show how the double error is detected.
4. Simplify the Boolean expression: f(w,x,y,z)=Σm(0,1,3,7,8,12) +dc(5,10,13,14) using
SOP and POS form.
5. Implement the following function with either NAND or NOR gates. Use only four
gates. F=w’xz+w’yz+x’yz’+wxy’z, d=wyz](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iat1dlc-141026020827-conversion-gate02/85/Iat-1-320.jpg)

![DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS
IAT 1 – SET 1 – DLC – EE6301
ENGINEERING
IAT - I - AUGUST – 2014
SET-II
Sem & Branch : III & EEE (A/B) Date: 12th August, 2014
Subject : DIGITAL LOGIC CIRCUITS Duration : 3Hrs
Sub.code : EE 6301 Max.Marks: 100
Answer All Questions
Part-A [10 x 2 = 20Marks]
1. How does open collector output differ from the totem-pole outputs?
2. Write the 20 decimal digits in base 3.
3. Obtain the 2’s complements of the following numbers:1010101
4. Perform subtraction using 10’s complement:5250-321
5. Convert the hexadecimal number-A2BEF to Binary
6. Simplify X+XY.
7. Draw the truth table and logic circuit of half adder
8. State the important characteristics of TTL family
9. Which IC family offers (a) low propagation delay, (b) low power dissipation?
10. Define fan out.
Part - B [5 x 16 = 80Marks]
[Answer any Five]
1. Explain the concept, working and characteristics of DTL logic families.
2. Discuss the following: i).Totem pole output configuration ii) open collector output
configuration.
3. Construct a Hamming code group for the information bits 100101 that enables single
error correction plus double error detection where the most significant bit of the code
group is for the overall even parity bit. Assume that errors occur in bit positions 2 and
9 of the above code group.
4. Show how the double error is detected. Simplify the Boolean expression:
f(w,x,y,z)=Σm(0,1,3,7,8,12) +dc(5,10,13,14) using SOP and POS form.
5. Implement the following function with either NAND or NOR gates. Use only four
gates. F=w’xz+w’yz+x’yz’+wxy’z, d=wyz](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iat1dlc-141026020827-conversion-gate02/85/Iat-3-320.jpg)