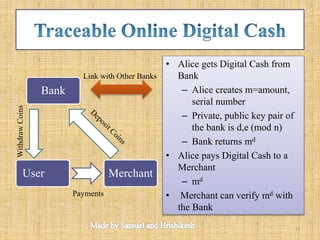
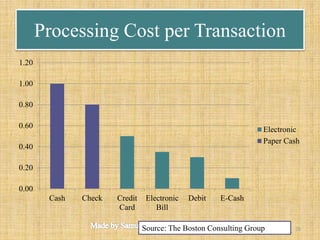
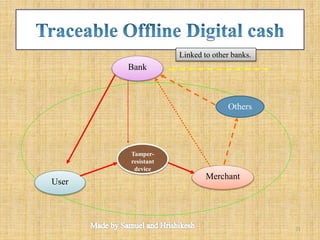
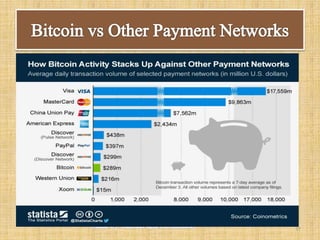
The document discusses the evolution and functionalities of digital cash, highlighting its similarities to traditional cash, enabling features like anonymity and offline transactions. It elaborates on the roles of cryptography, digital signatures, and the potential of e-currencies such as Bitcoin. Additionally, it outlines the pros and cons of digital cash systems, including transaction efficiencies and scalability issues.