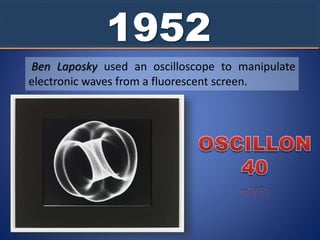
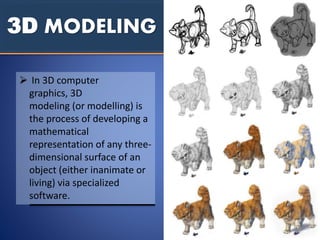
The document traces the history and evolution of digital art from its origins in the 1950s and 1960s through to the present day. It discusses how early digital artists manipulated electronic waves and how computers were initially only accessible to large institutions. It then outlines key developments in the 1970s and 1980s as computers became more affordable and accessible. The document defines digital art and describes various forms it can take including digital photography, vector drawing, algorithms/fractals, photo painting, digital collage, integrated digital art, 2D and 3D digital painting, and 3D modeling. It provides an example of the conceptual digital artist Stephanie Syjuco and her "Black Market" works.