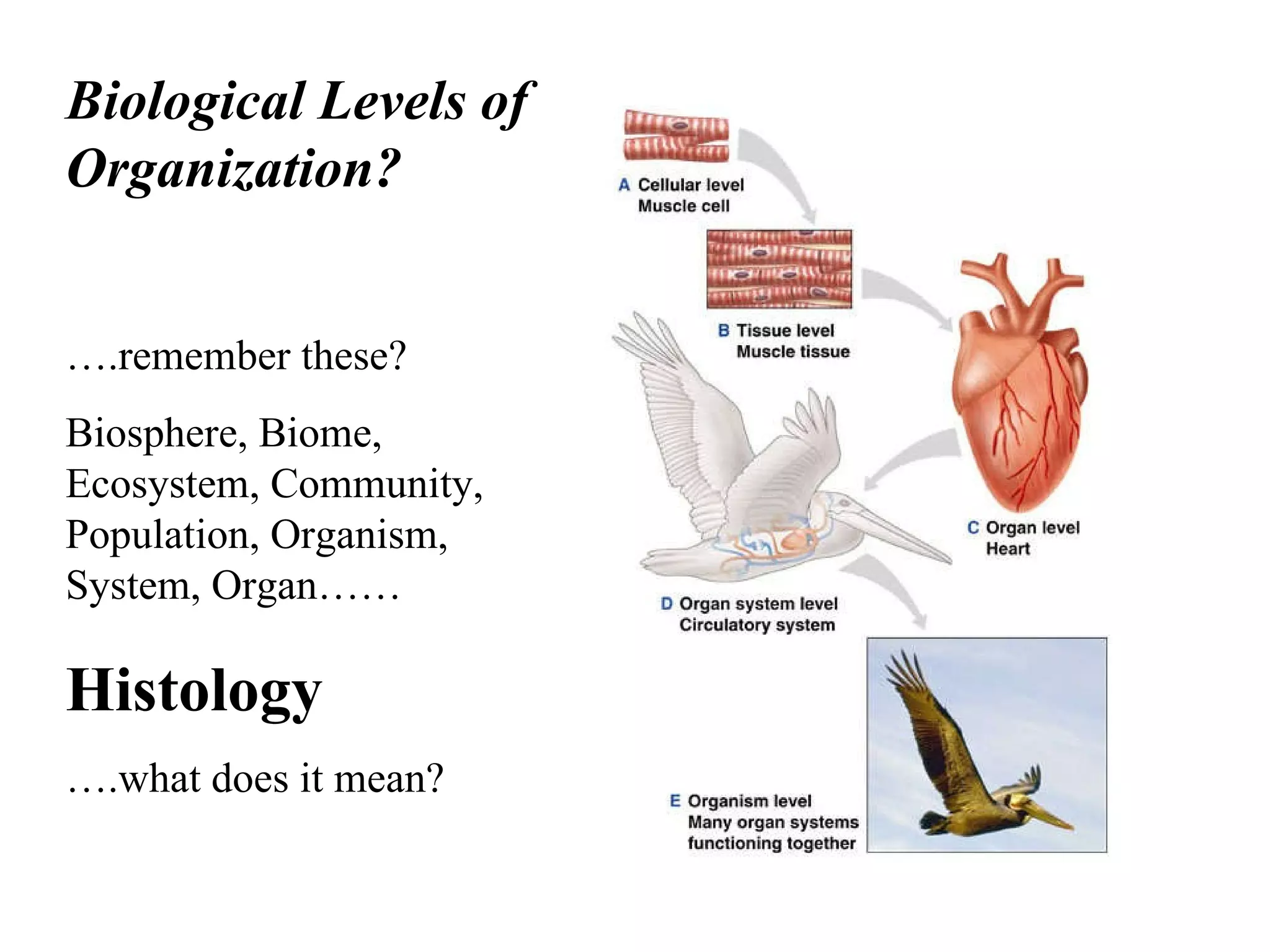
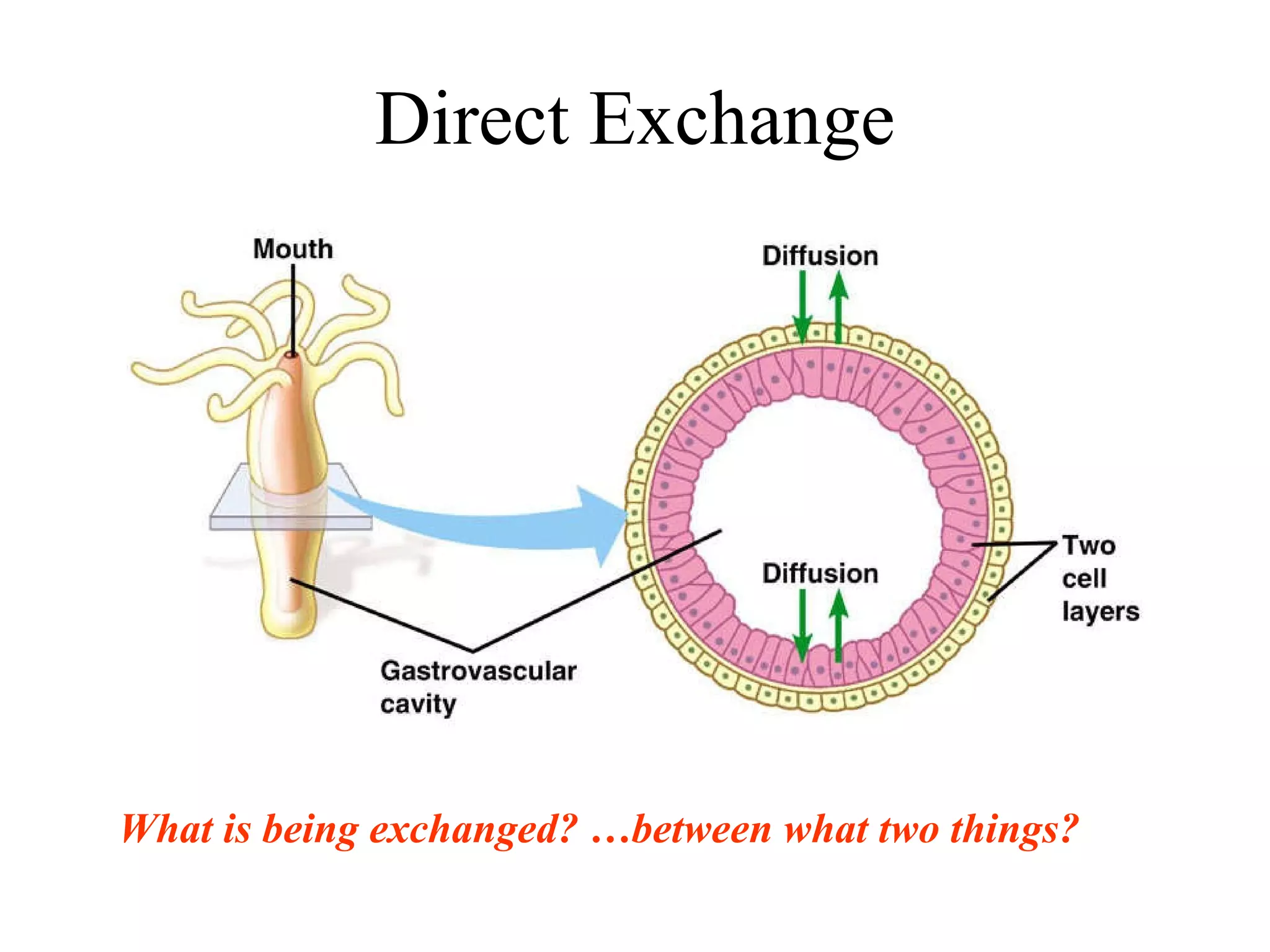
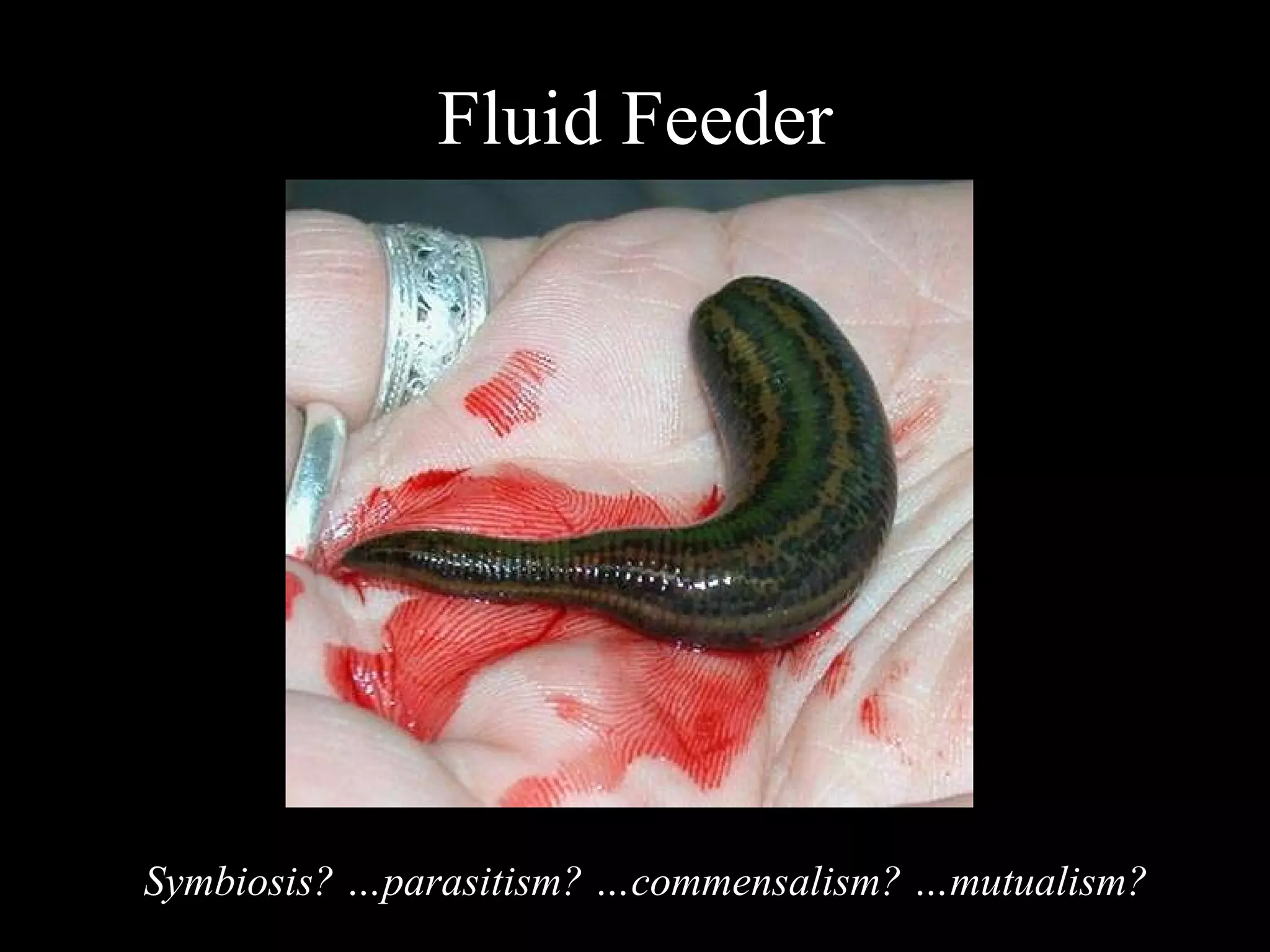
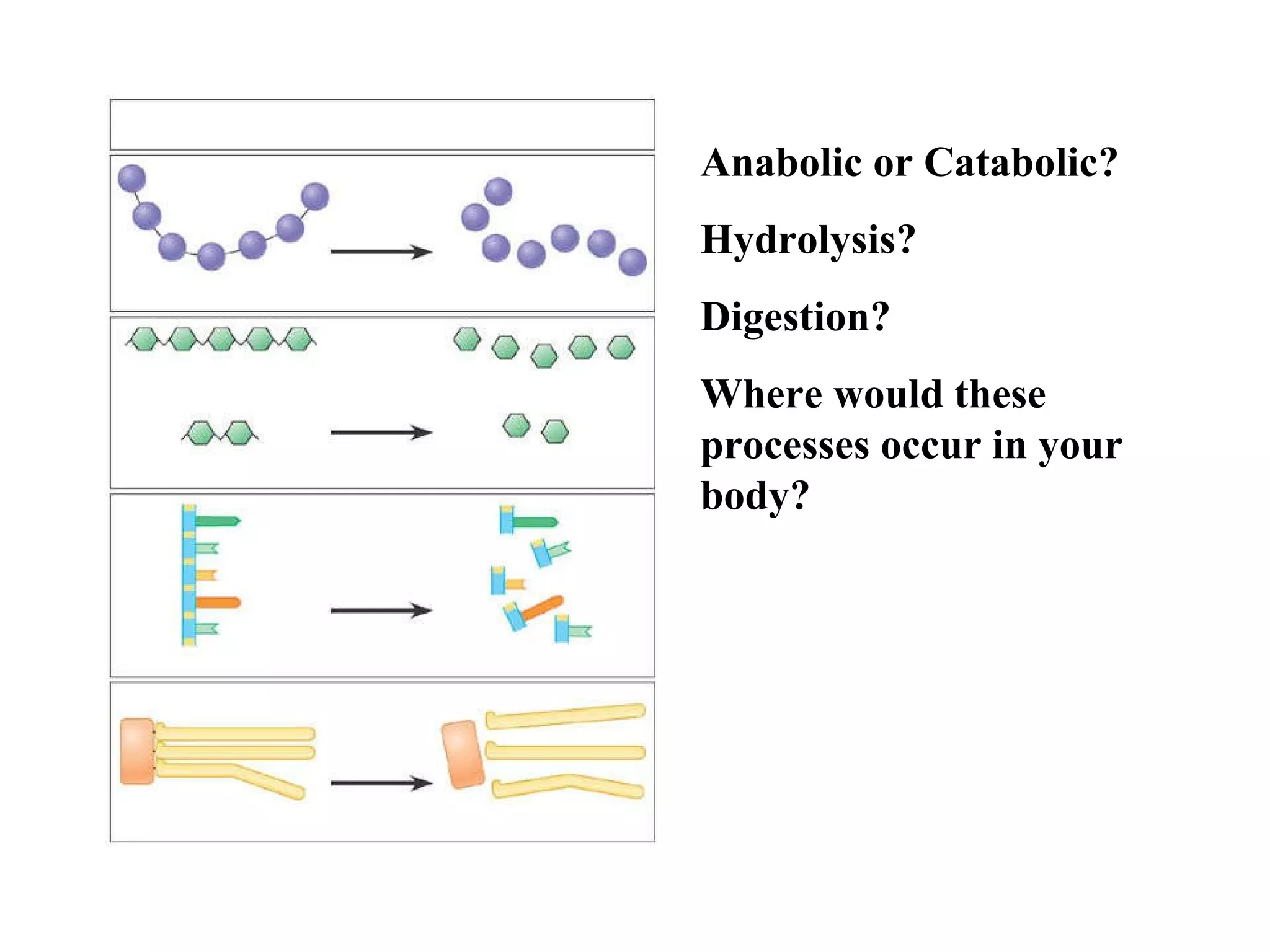
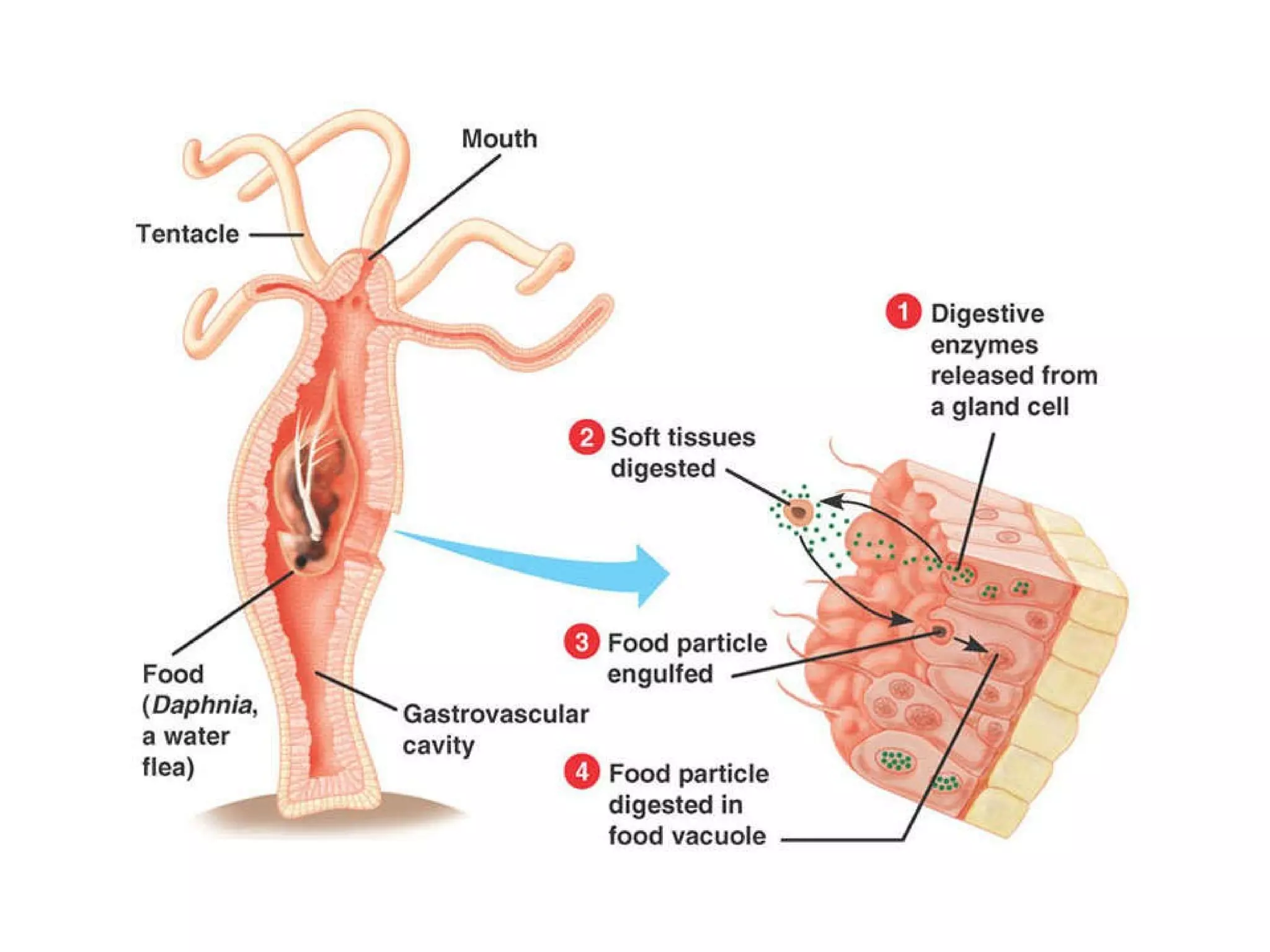
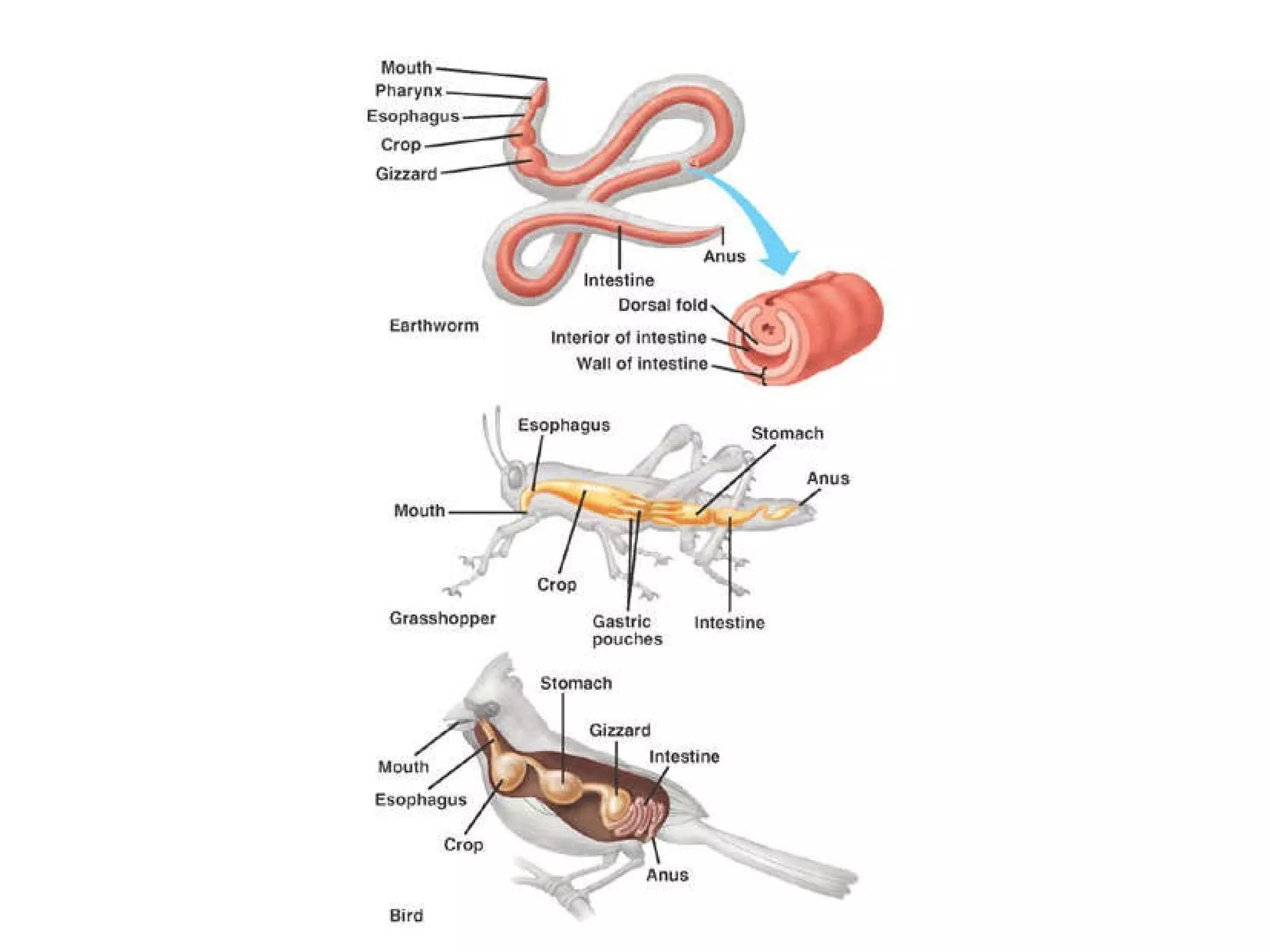
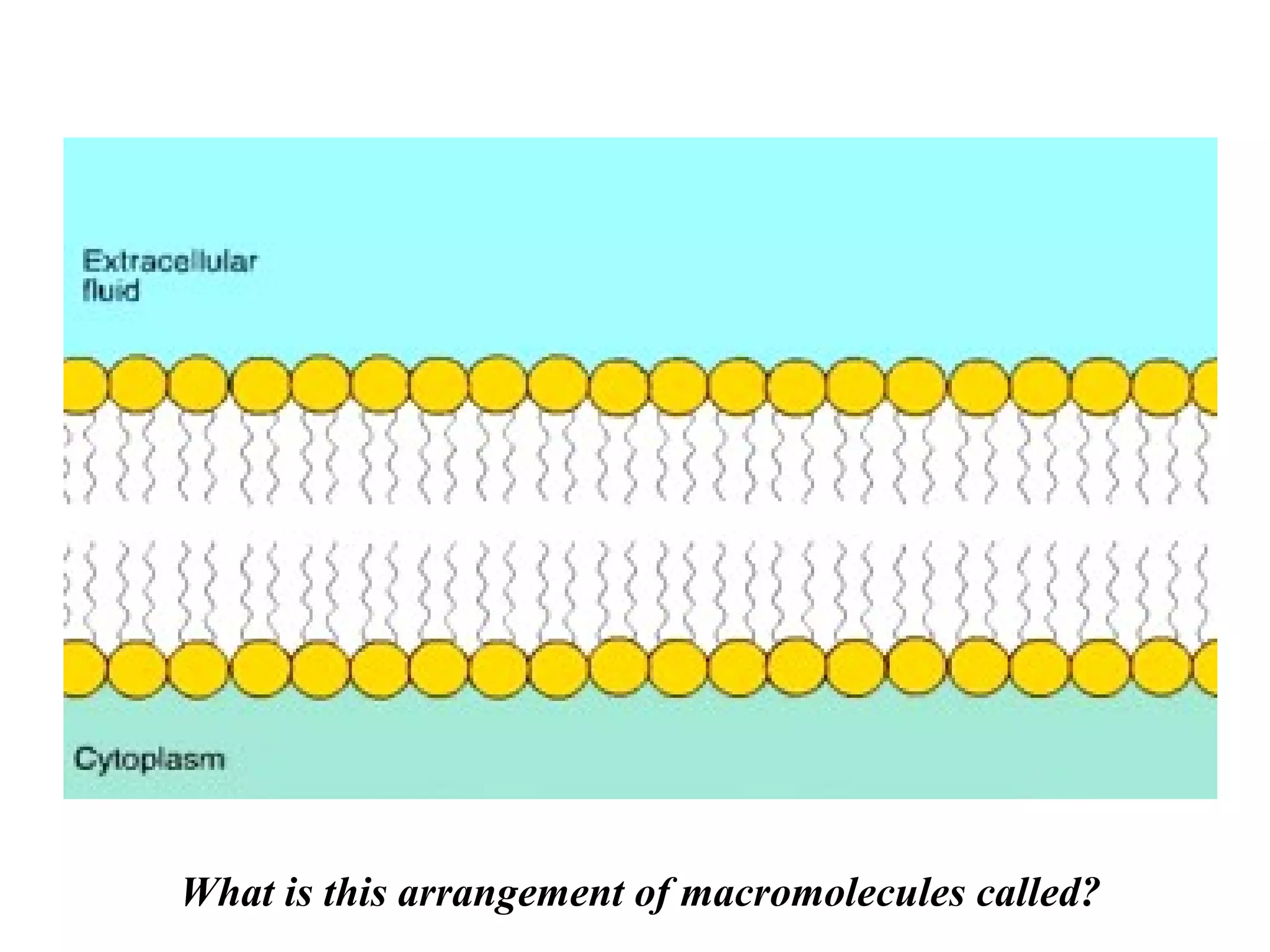
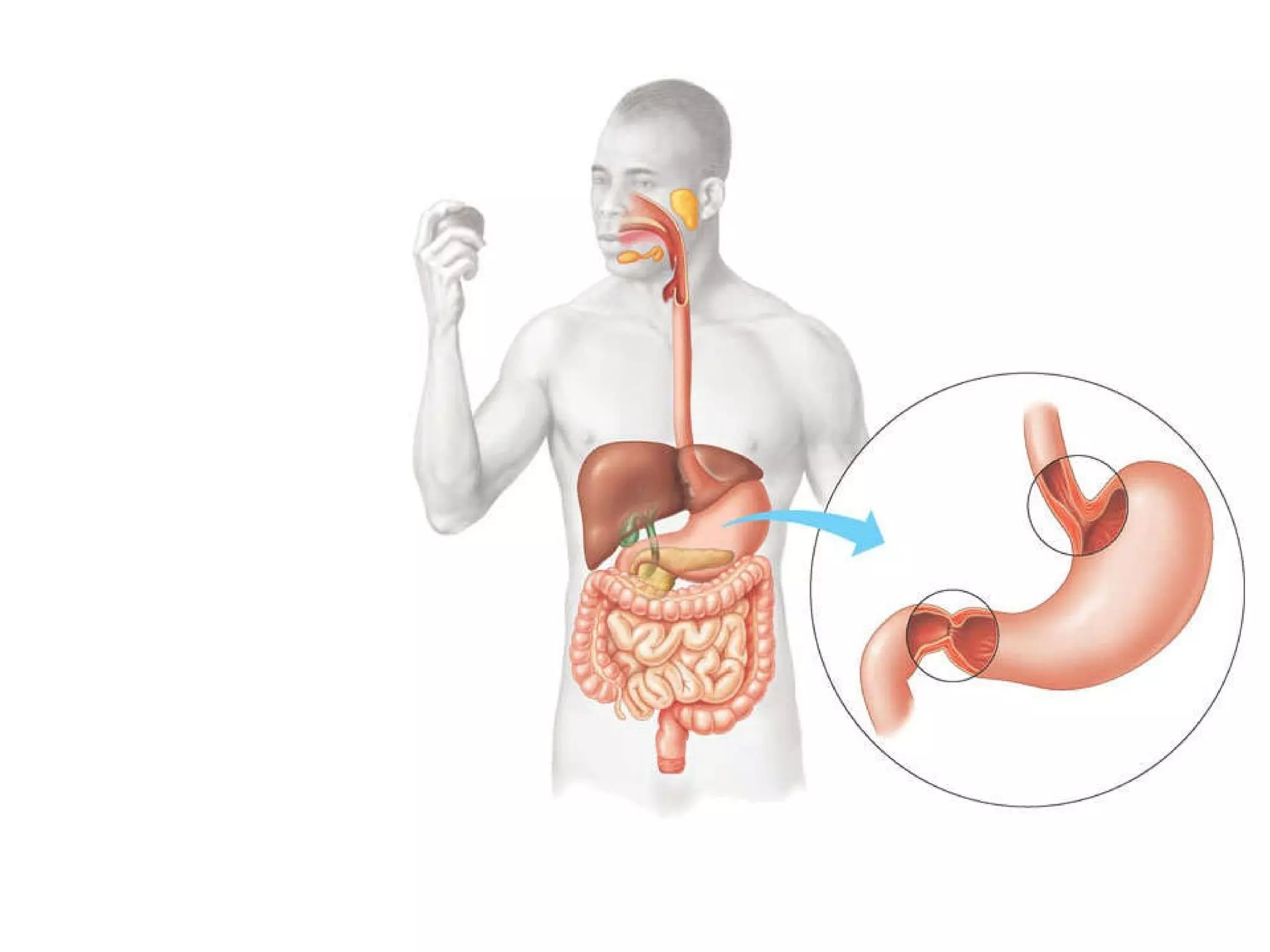
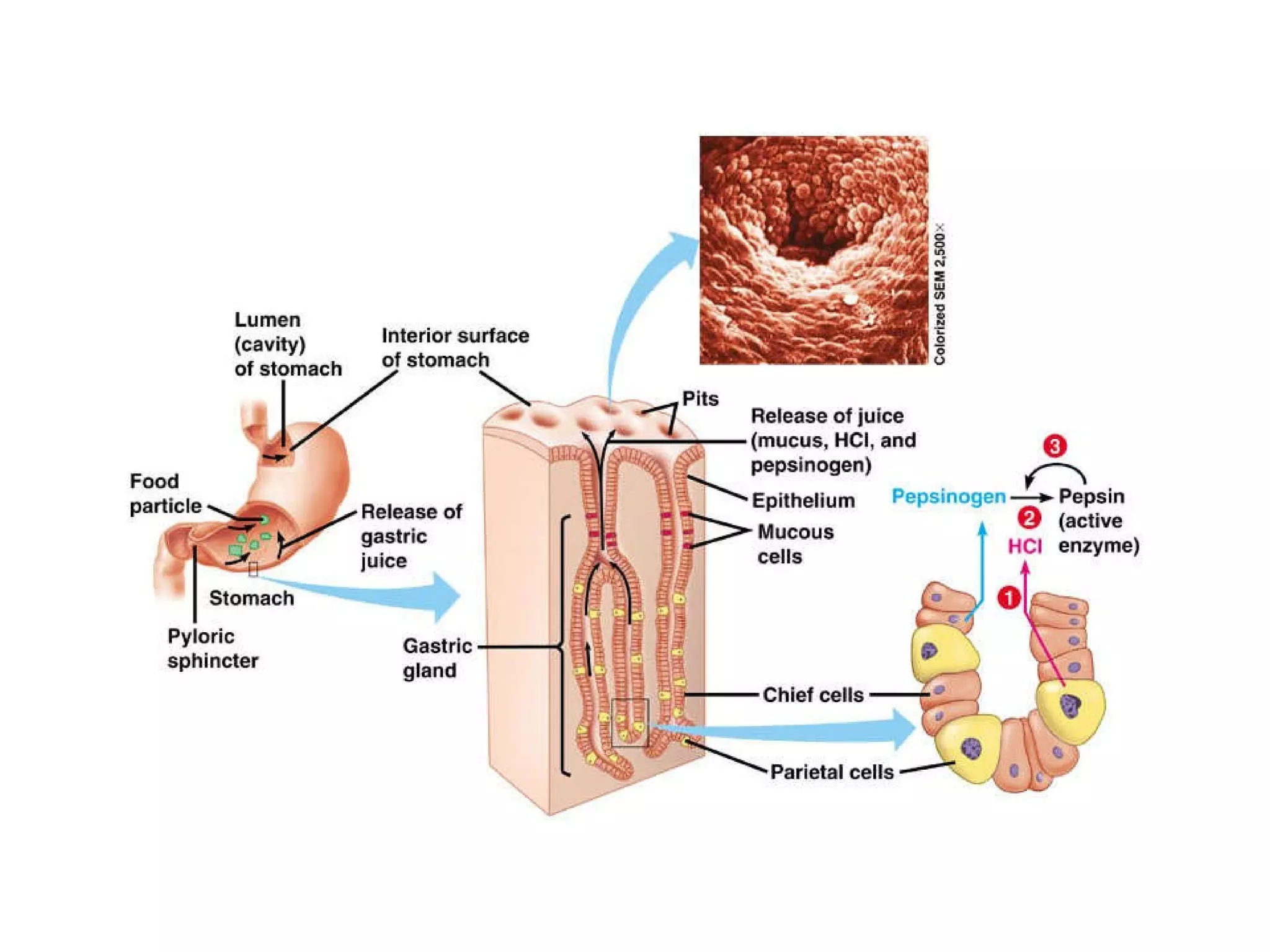
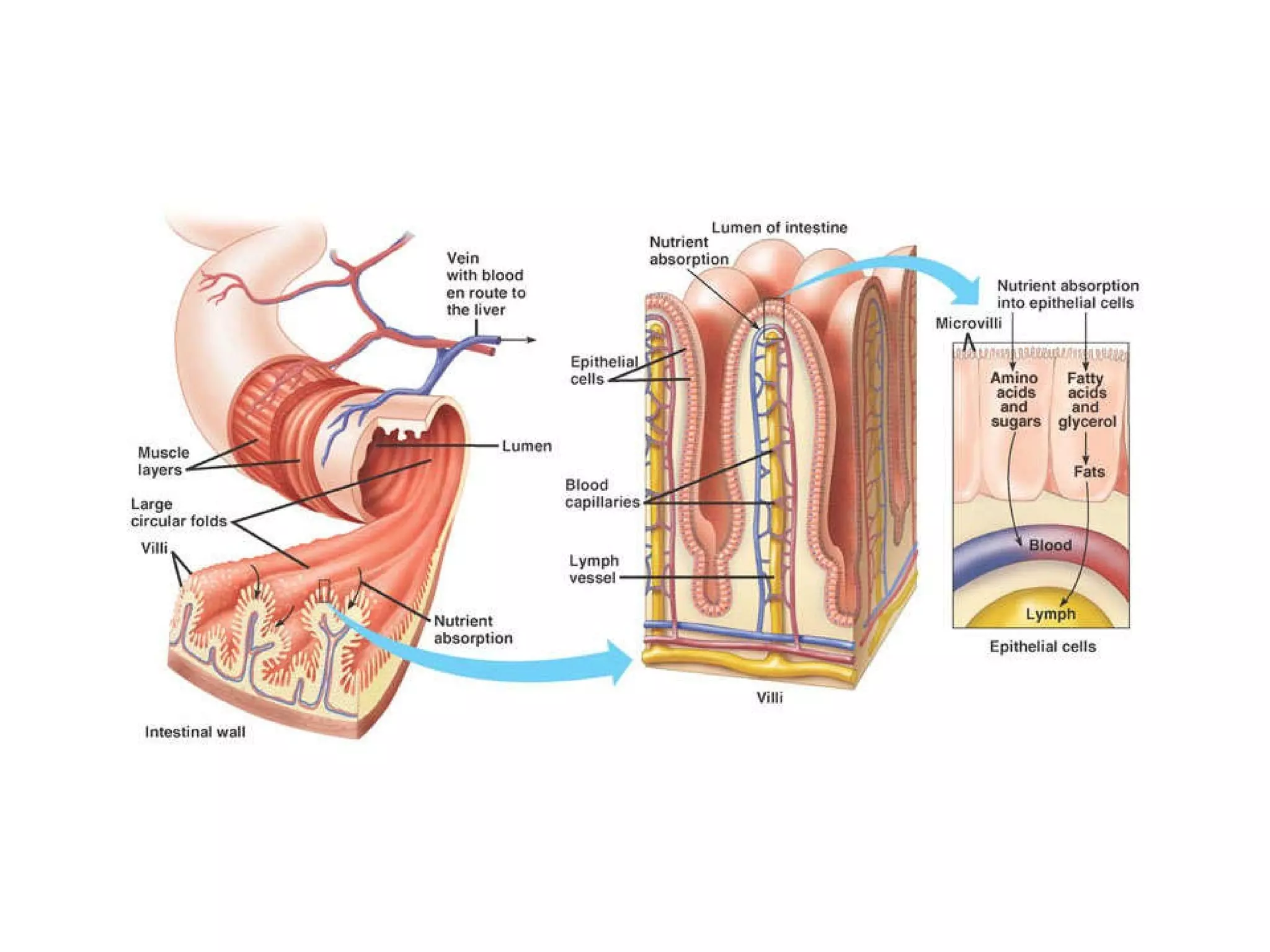
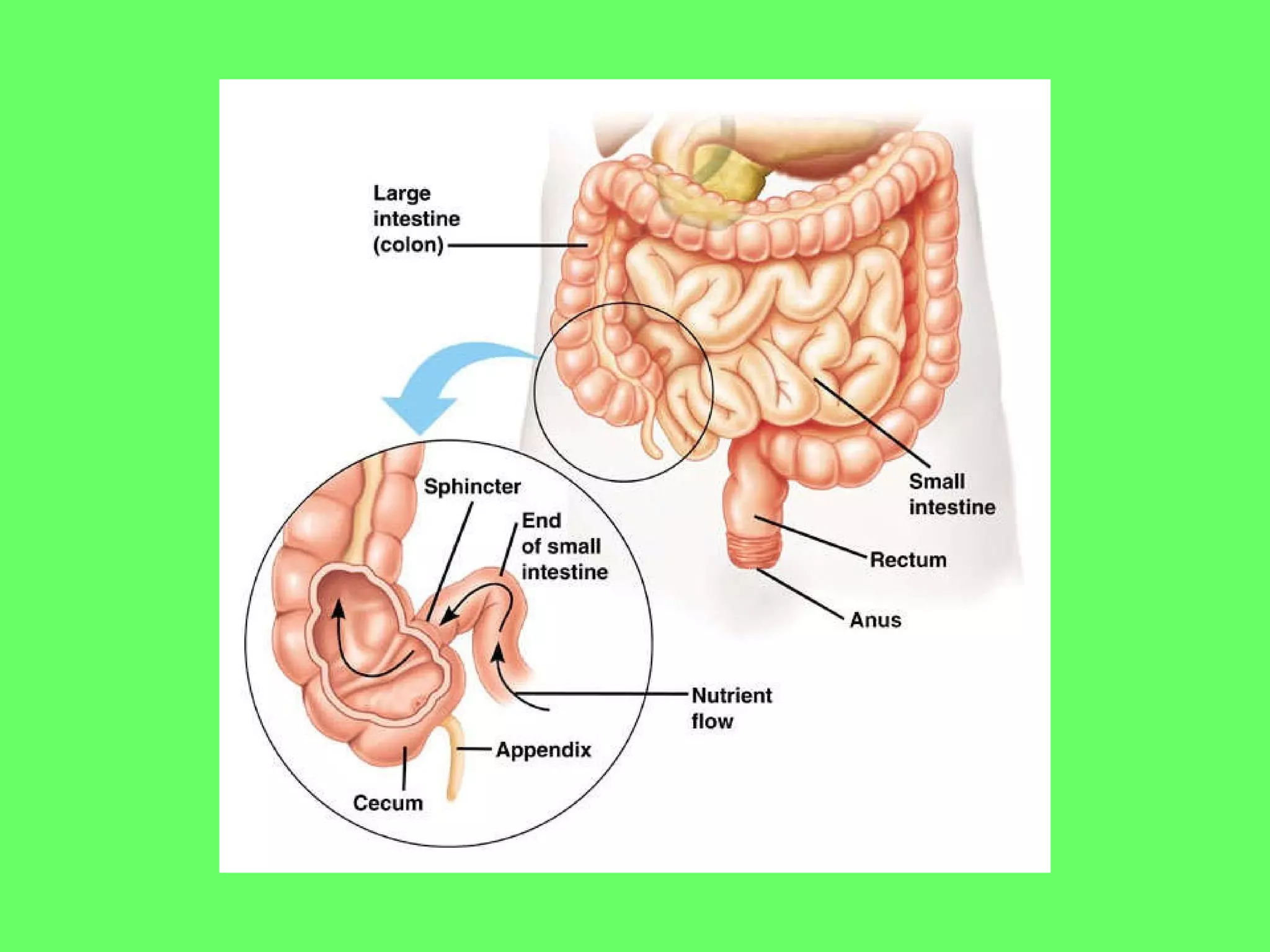
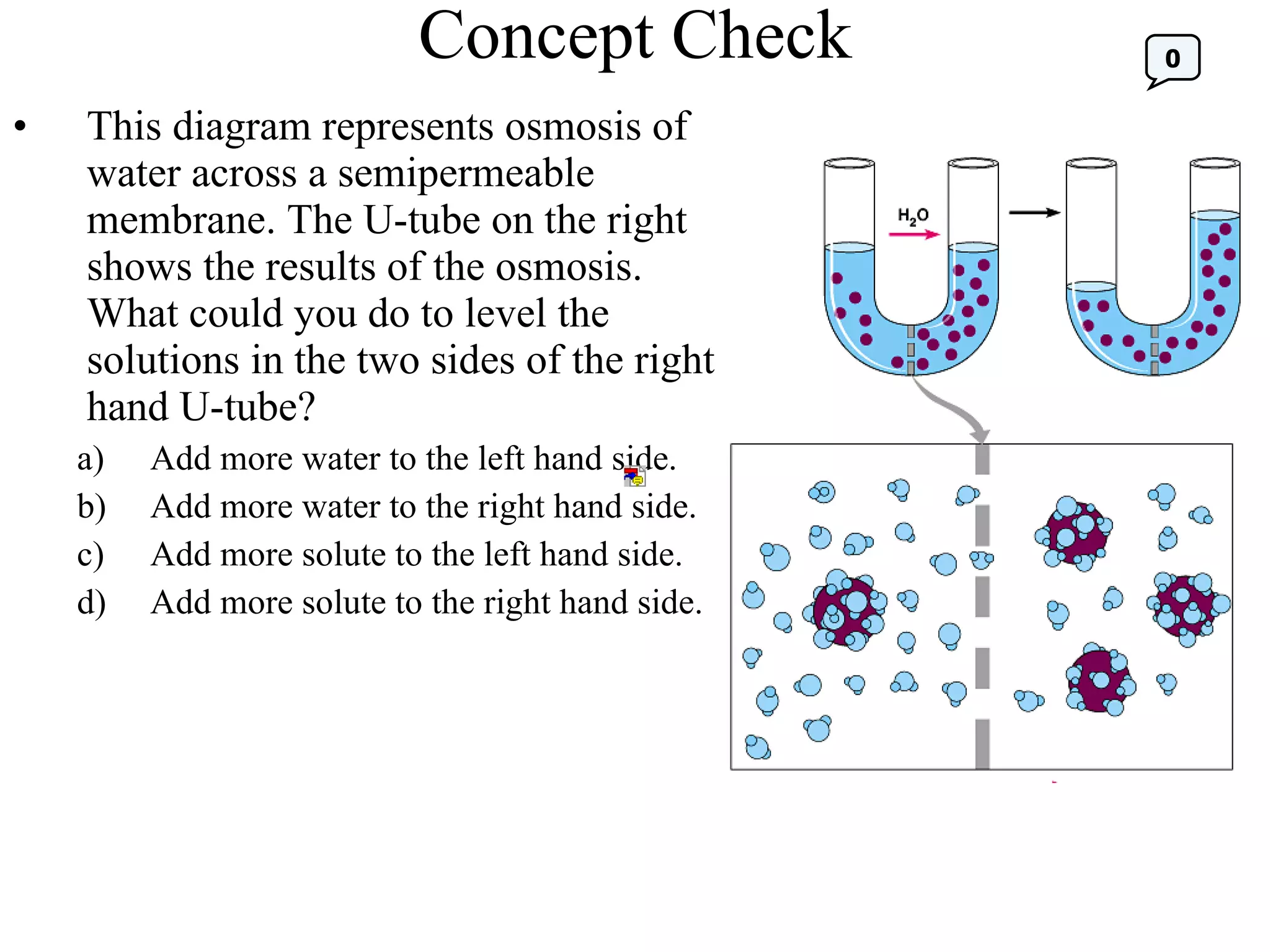
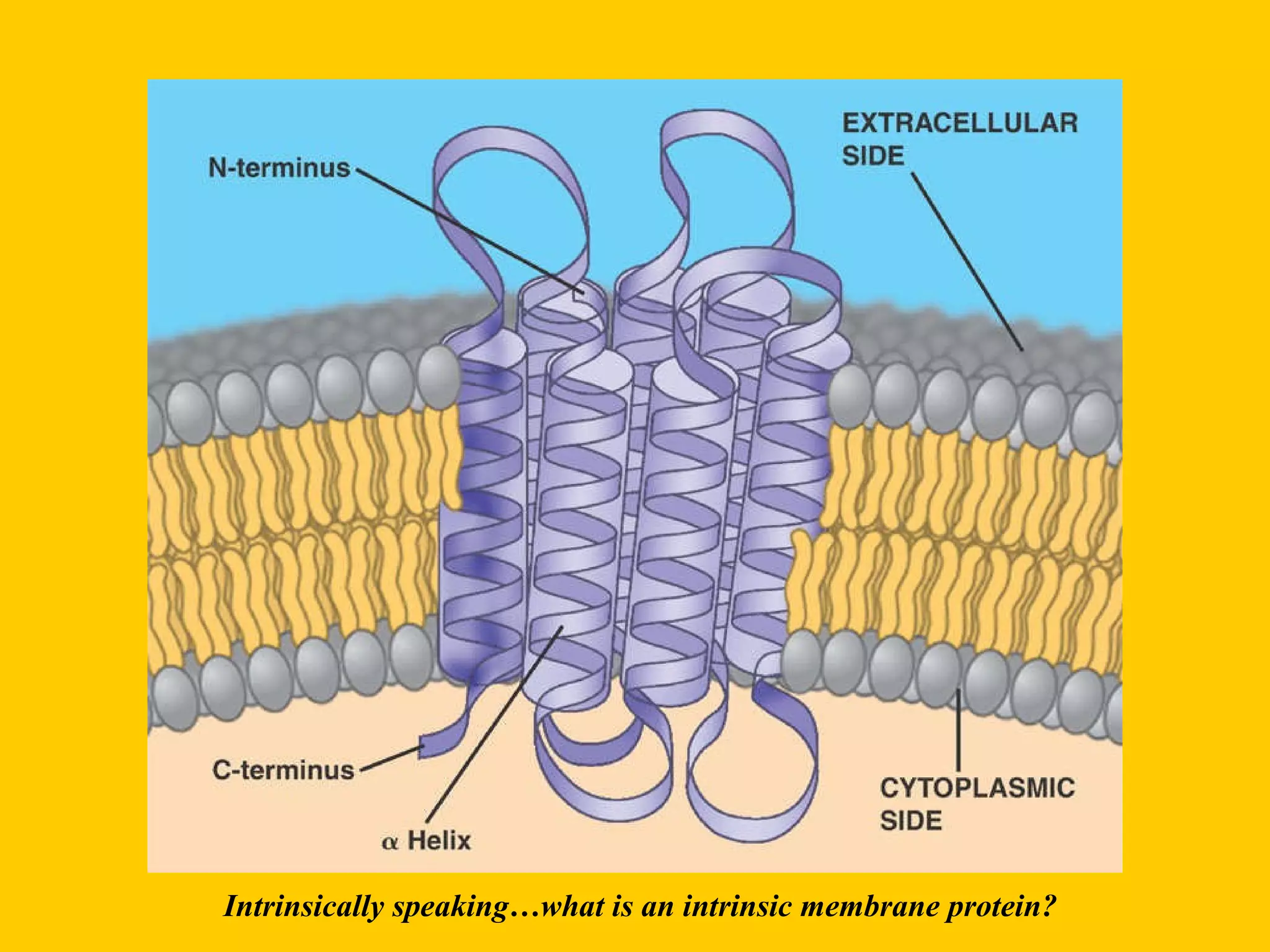
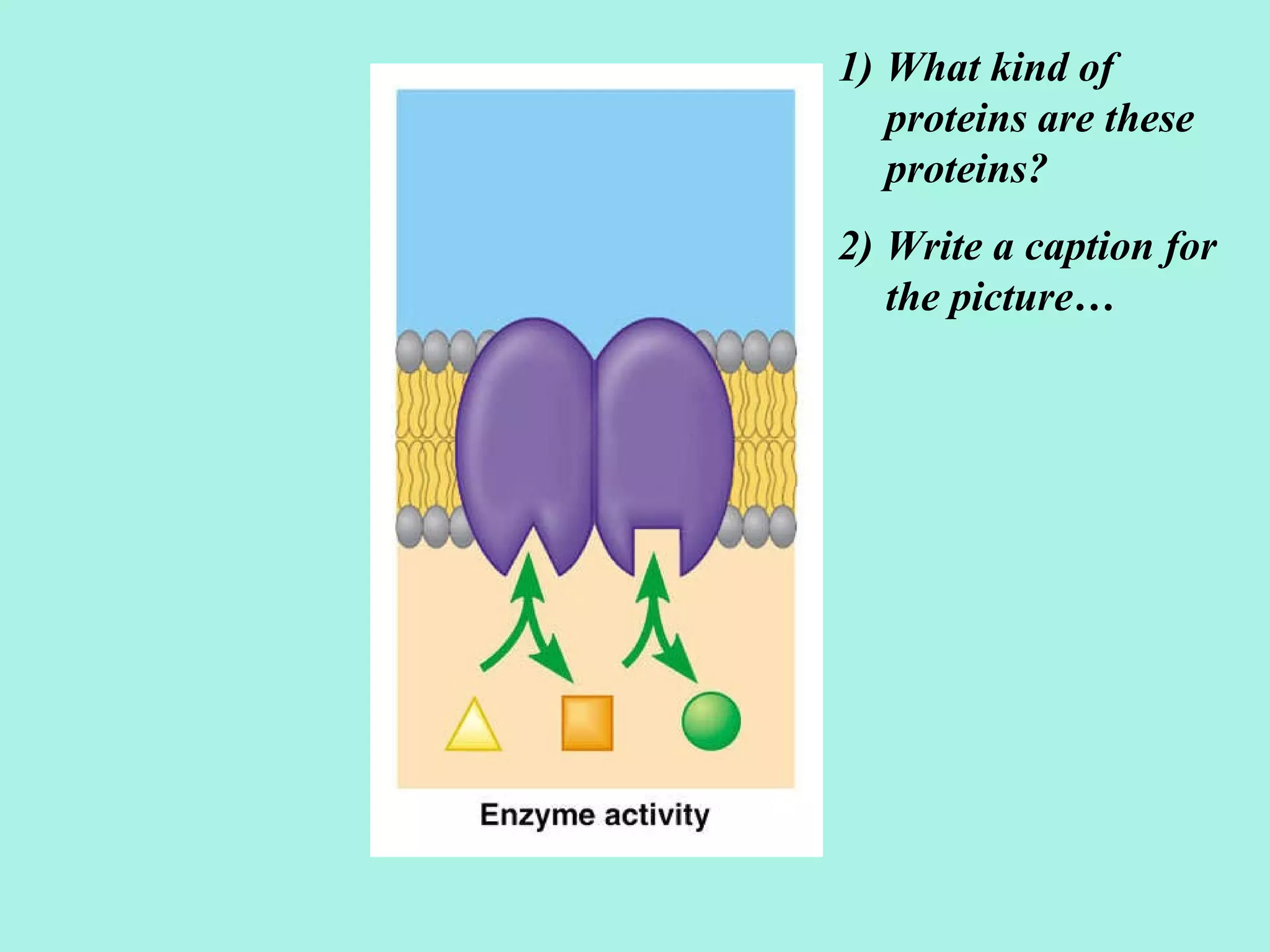
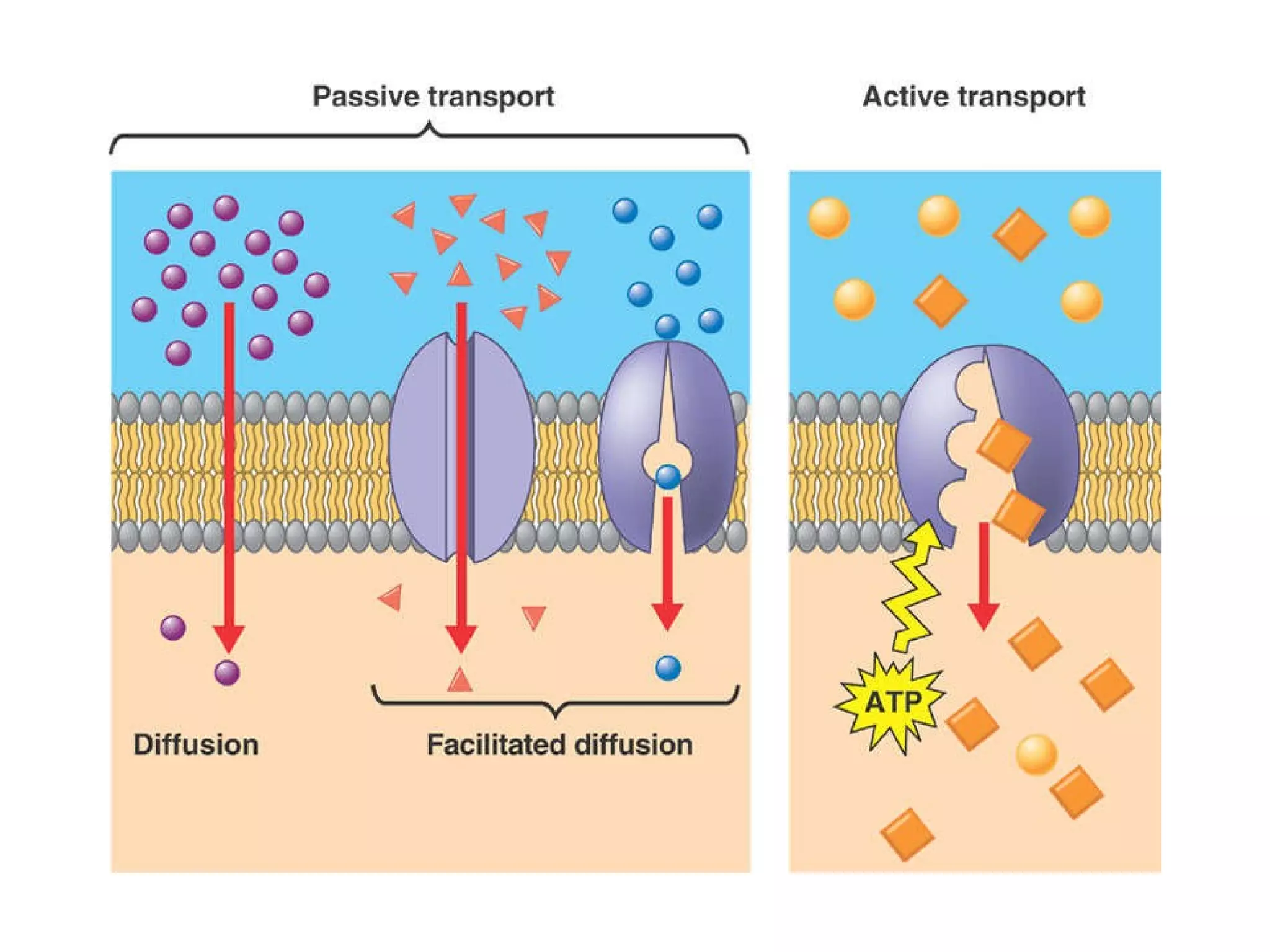
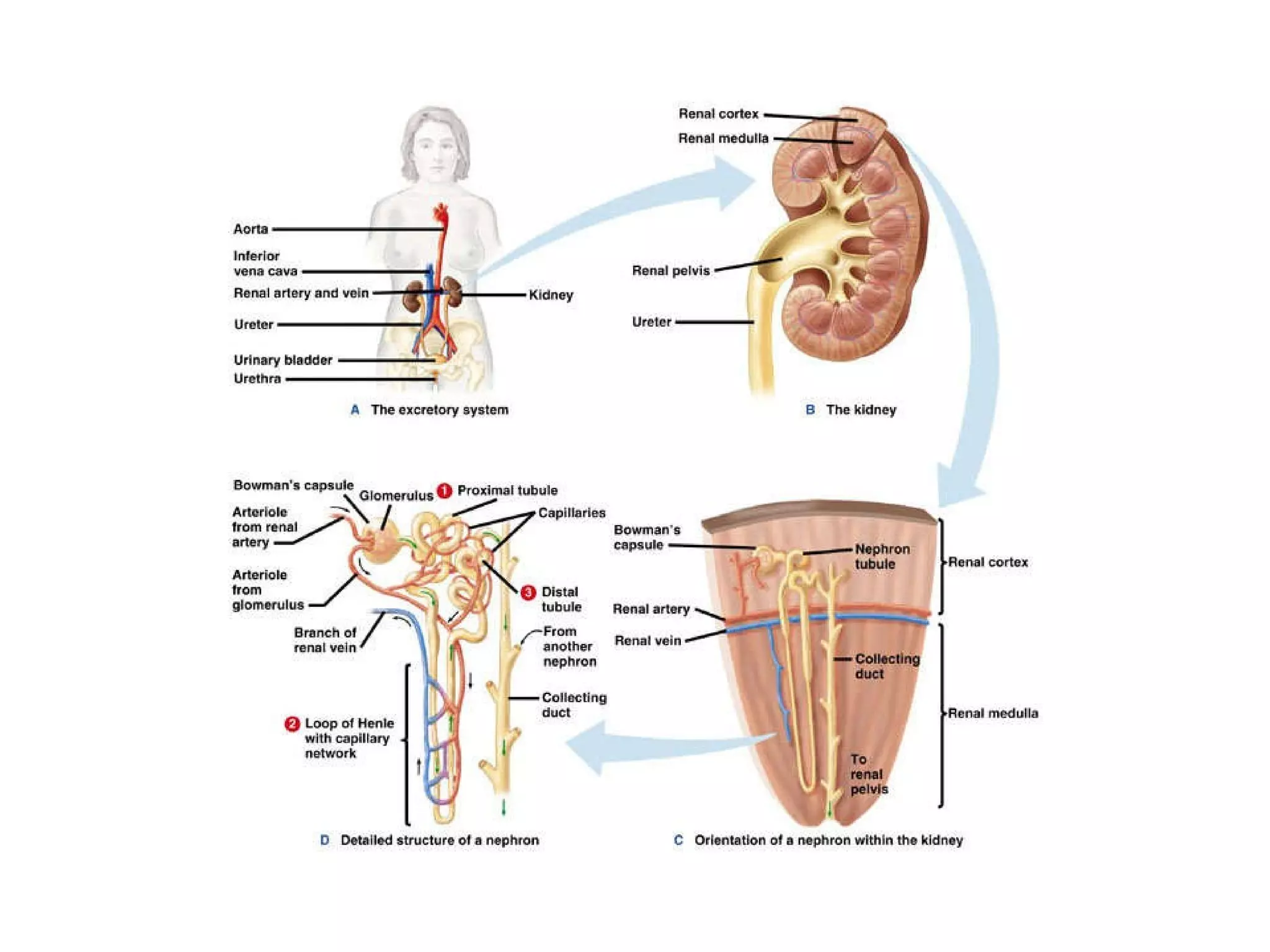
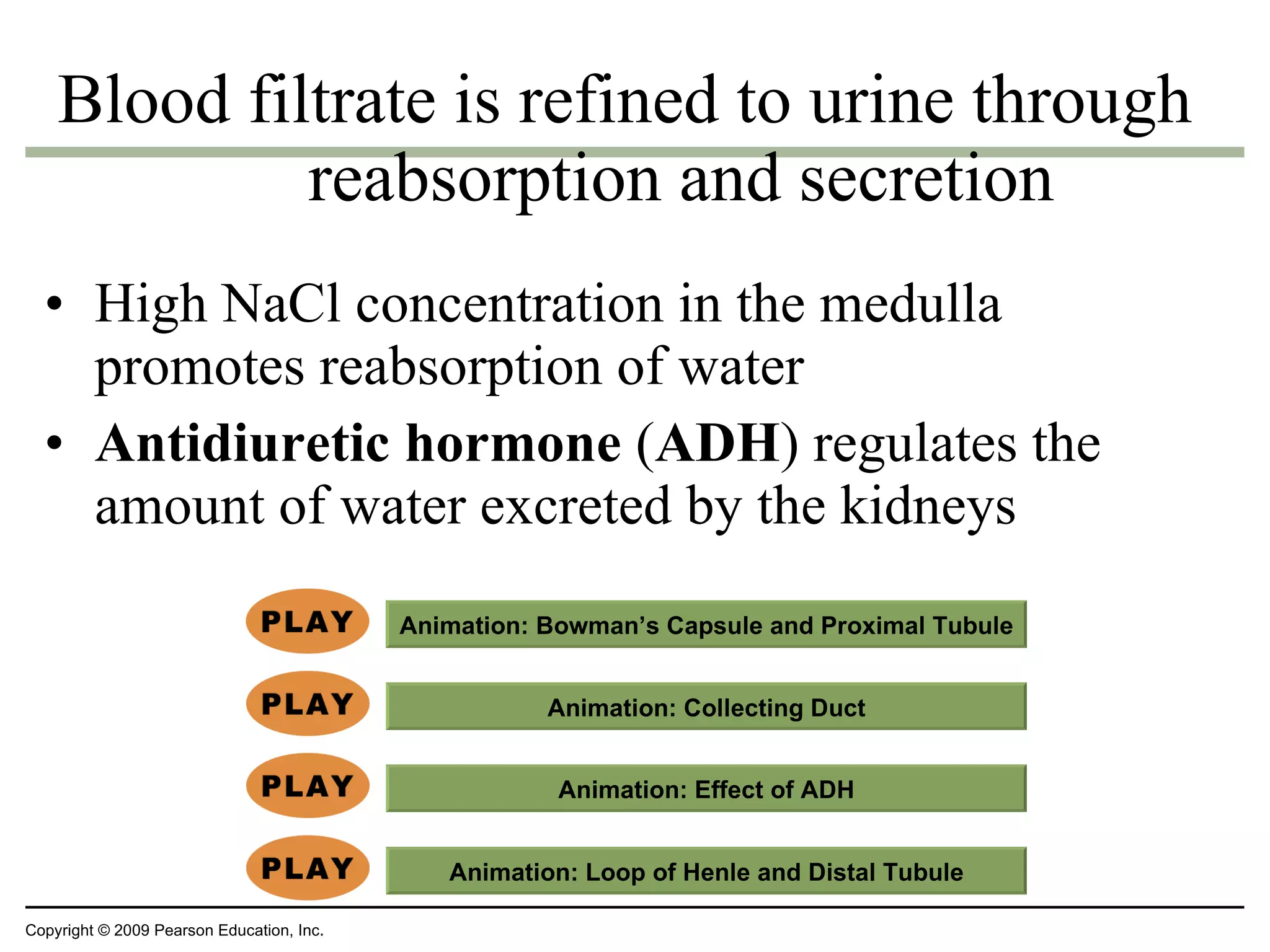
The document discusses various biological processes related to digestion, transport, and excretion. It includes topics like the levels of biological organization, different modes of nutrient acquisition like suspension feeding and substrate feeding, and membrane transport mechanisms like diffusion, osmosis, and aquaporins. It also covers organ system functions, comparing the digestive and excretory systems of carnivores and herbivores, as well as osmoregulation in fish and mammals.