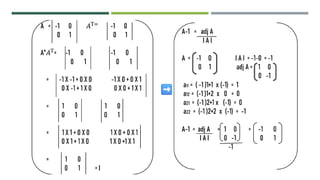
The document discusses orthogonal matrices, defining their properties and significance in various applications such as computer graphics, signal processing, and quantum mechanics. It explains that the product of two orthogonal matrices is also orthogonal, and emphasizes that their transpose is equal to their inverse. The document covers the mathematical qualities and uses of orthogonal matrices in representing transformations.