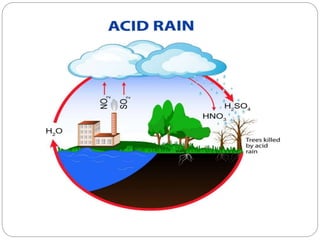
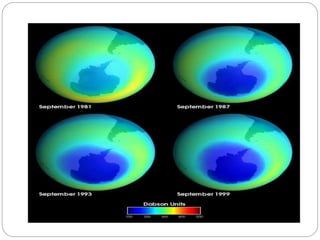
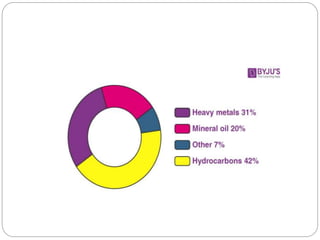
The document discusses environmental pollution, focusing on acid rain, ozone layer depletion, greenhouse effects, water pollution, and soil pollution. It explains the causes and effects of each type of pollution, highlighting their impact on agriculture, human health, and ecosystems. The document emphasizes the importance of addressing these issues to mitigate harmful environmental effects.