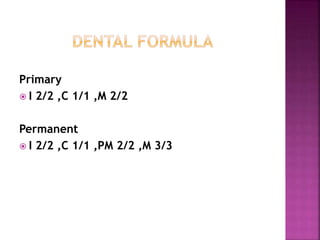
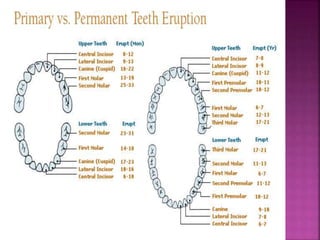
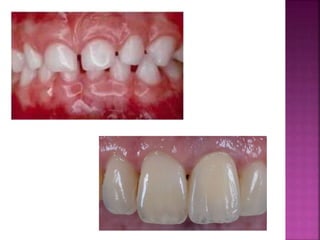
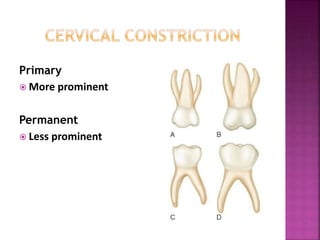
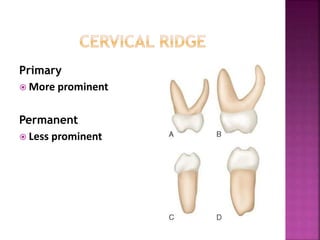
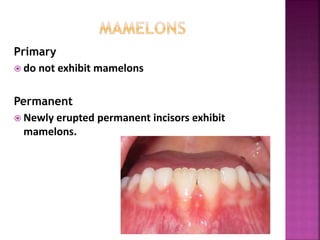
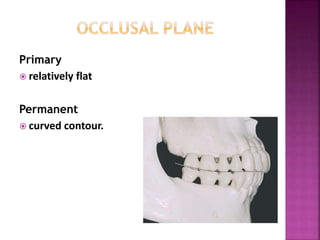
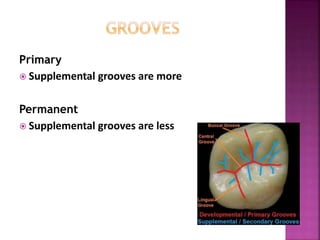
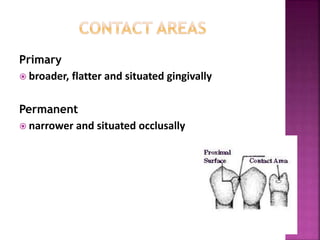
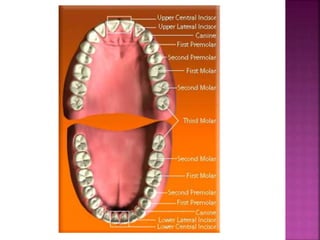
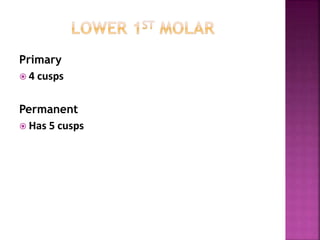
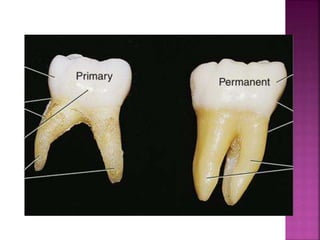
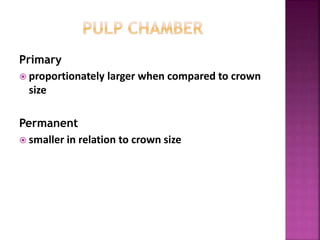
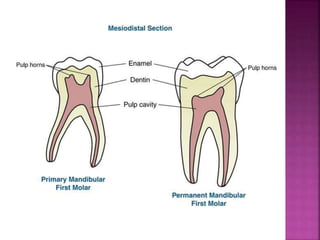
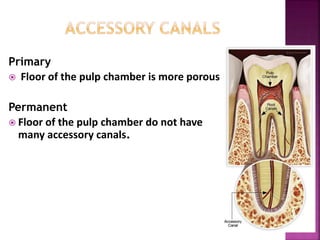
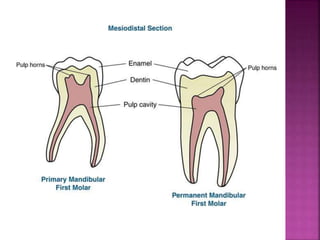
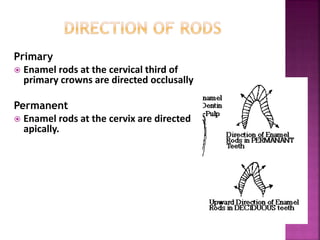
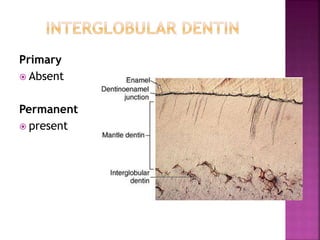
The document compares the anatomical features of primary and permanent teeth. It notes that primary teeth number 20 total with 10 in each jaw and 5 in each quadrant, while permanent teeth number 32 total with 16 in each jaw and 8 in each quadrant. Primary teeth are smaller, lighter in color, and have shorter roots compared to permanent teeth. Primary teeth exfoliate naturally between 6 months and 6 years of age, while permanent teeth erupt around 12 years of age and remain for life.