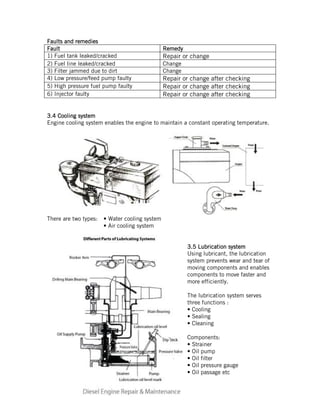
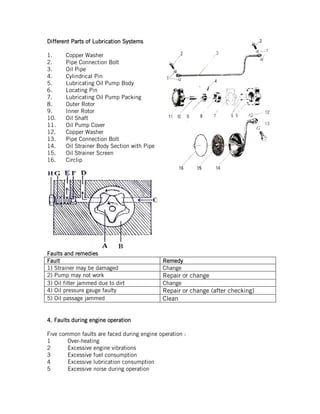
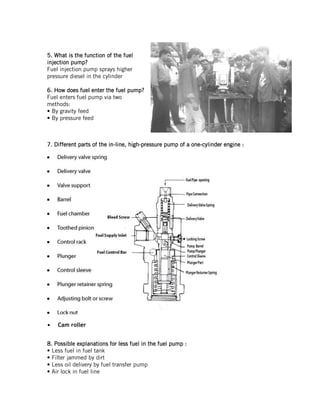
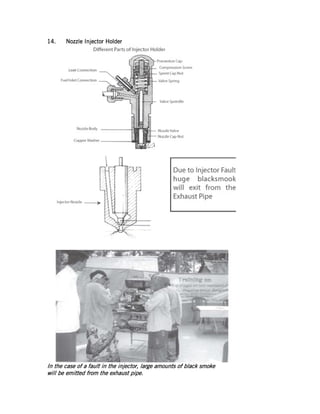
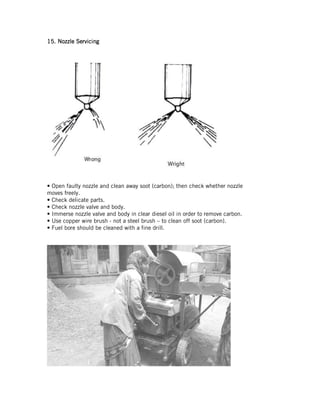
This document provides instructions for repairing and maintaining diesel engines. It begins with introductions to what engines and diesel engines are. It then describes the main systems of a diesel engine - intake and exhaust, starting, fuel, cooling, and lubrication. For each system it explains the components and common faults/remedies. The document also discusses operating issues like overheating, vibration, and noise and their potential causes. Finally it covers specific engine parts like the fuel injection pump and nozzle and provides maintenance tips.