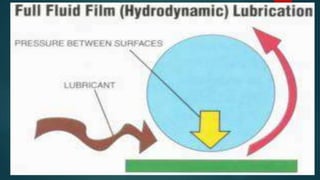
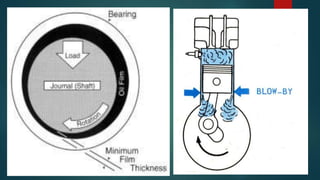
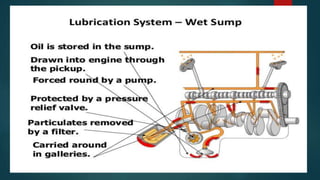
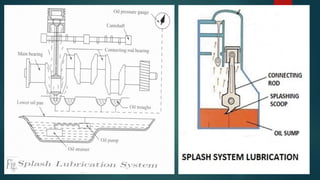
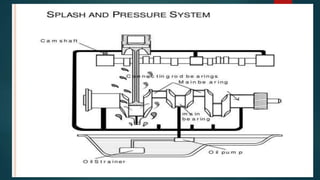
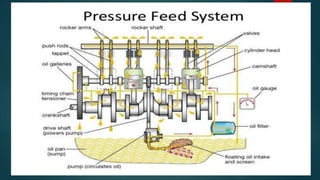
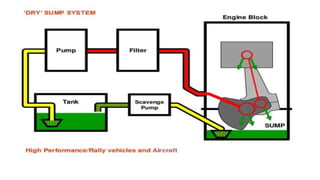
Engine friction is mainly due to sliding and rotating parts. It can be categorized into direct frictional losses, pumping losses, power losses to drive components like the scavenging pump, and power losses to drive auxiliary components. Several factors affect mechanical friction, like engine design, speed, load, temperature, oil viscosity, and lubrication system design. Proper lubrication is essential to reduce friction and wear between engine components. The key types of lubrication systems are mist, wet sump, and dry sump systems. Engine oil must have appropriate properties like viscosity, viscosity index, corrosion resistance, and stability.