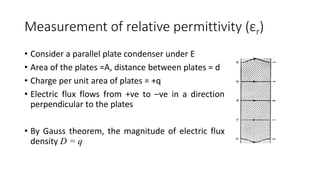
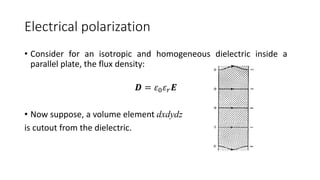
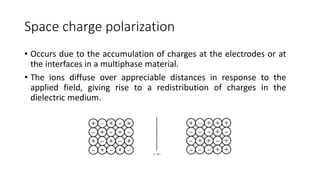
Dielectric materials are able to transmit electric force without conduction. When an external electric field is applied to a dielectric material, it induces several types of polarization within the material. The main types are electronic, ionic, orientational, and space charge polarization. Electronic polarization occurs due to the displacement of nuclei and electrons within atoms. Ionic polarization is the displacement of cations and anions in ionic solids. Orientational polarization is the alignment of permanent molecular dipoles in materials like CH3Cl. Space charge polarization results from the accumulation of charges at interfaces in multiphase materials. The total polarization of a material is the sum of these contributions and results in an increased electric flux density and relative permittivity compared to vacuum