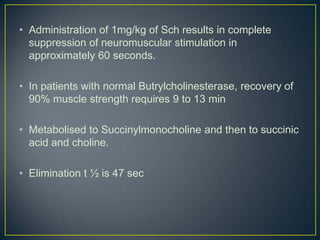
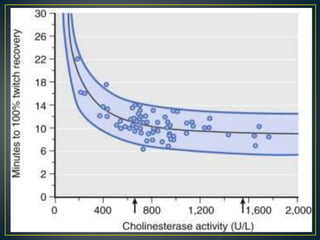
The Dibucaine Number test measures the percentage inhibition of the pseudocholinesterase enzyme by dibucaine. It is used to differentiate individuals with mutations in the butyrylcholinesterase enzyme. Normal individuals have dibucaine numbers of 80 or above, while those with atypical mutations have numbers between 40-60 for heterozygotes and 20 or less for homozygotes. Those with atypical mutations experience prolonged effects from succinylcholine and other neuromuscular blocking drugs.