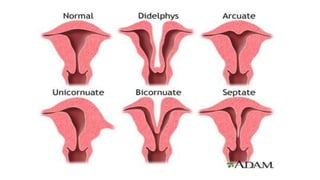
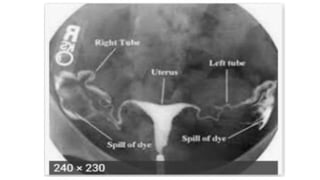
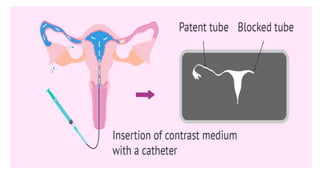
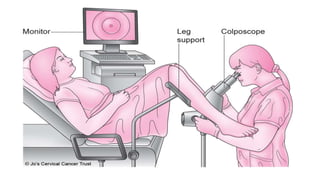
The document outlines various diagnostic and surgical procedures in gynecology, including hysterosalpingography (HSG), dilatation and curettage (D&C), laparoscopy, colposcopy, and hysterectomy. It details indications, contraindications, types of anesthesia, and potential complications for each procedure. The document also highlights the significance of these procedures in diagnosing and treating conditions such as infertility, uterine fibroids, and cancers.