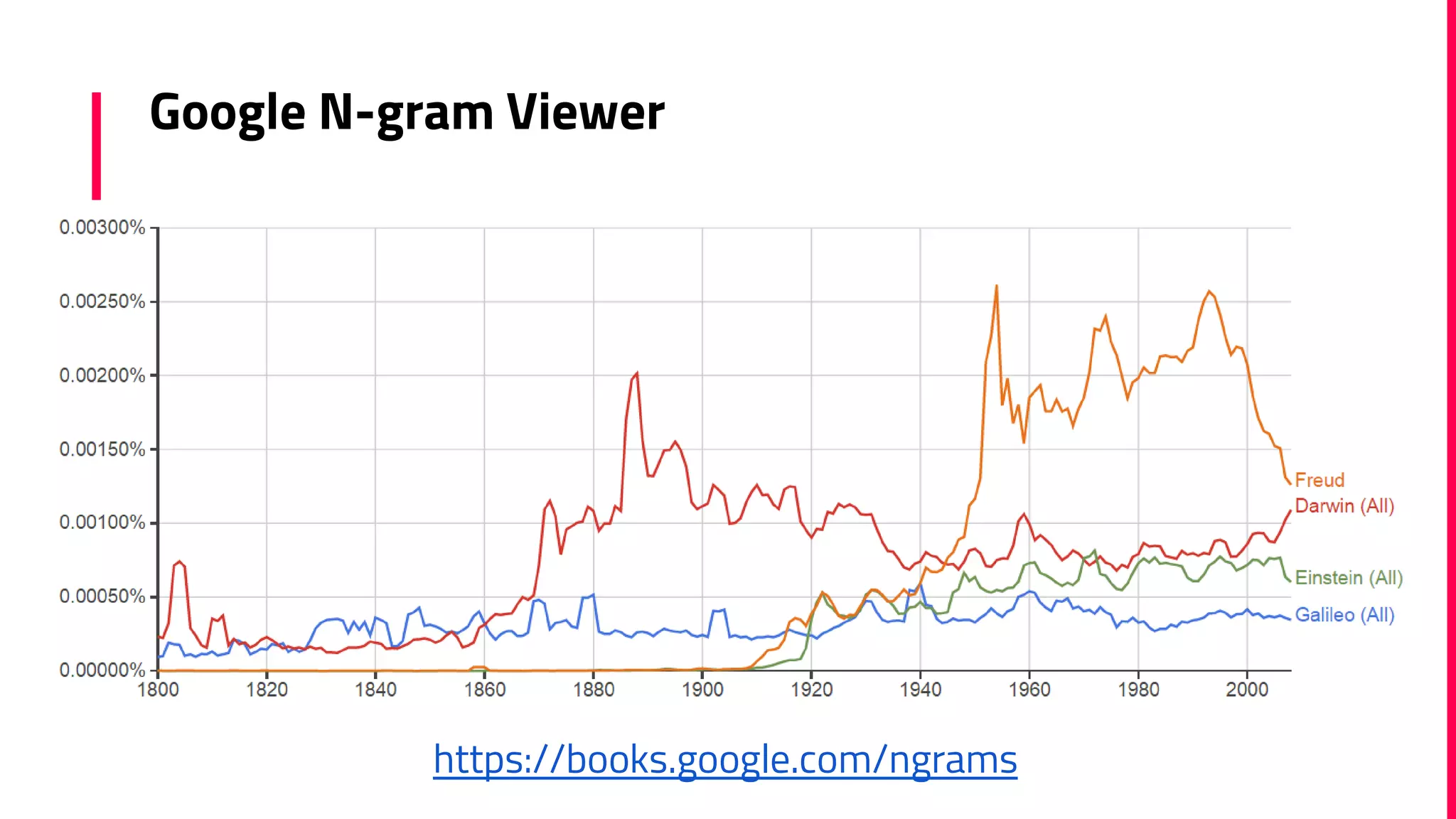
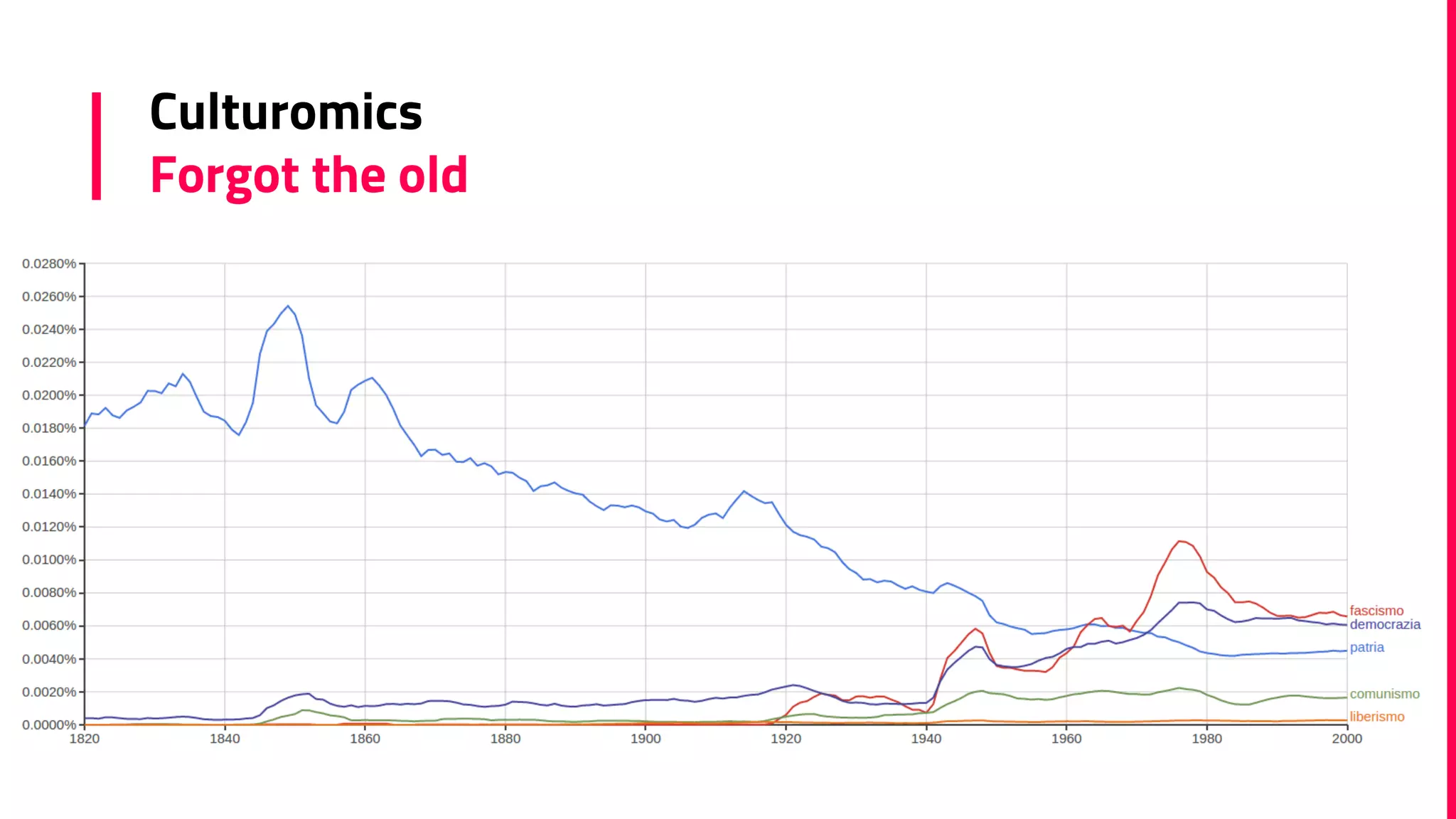
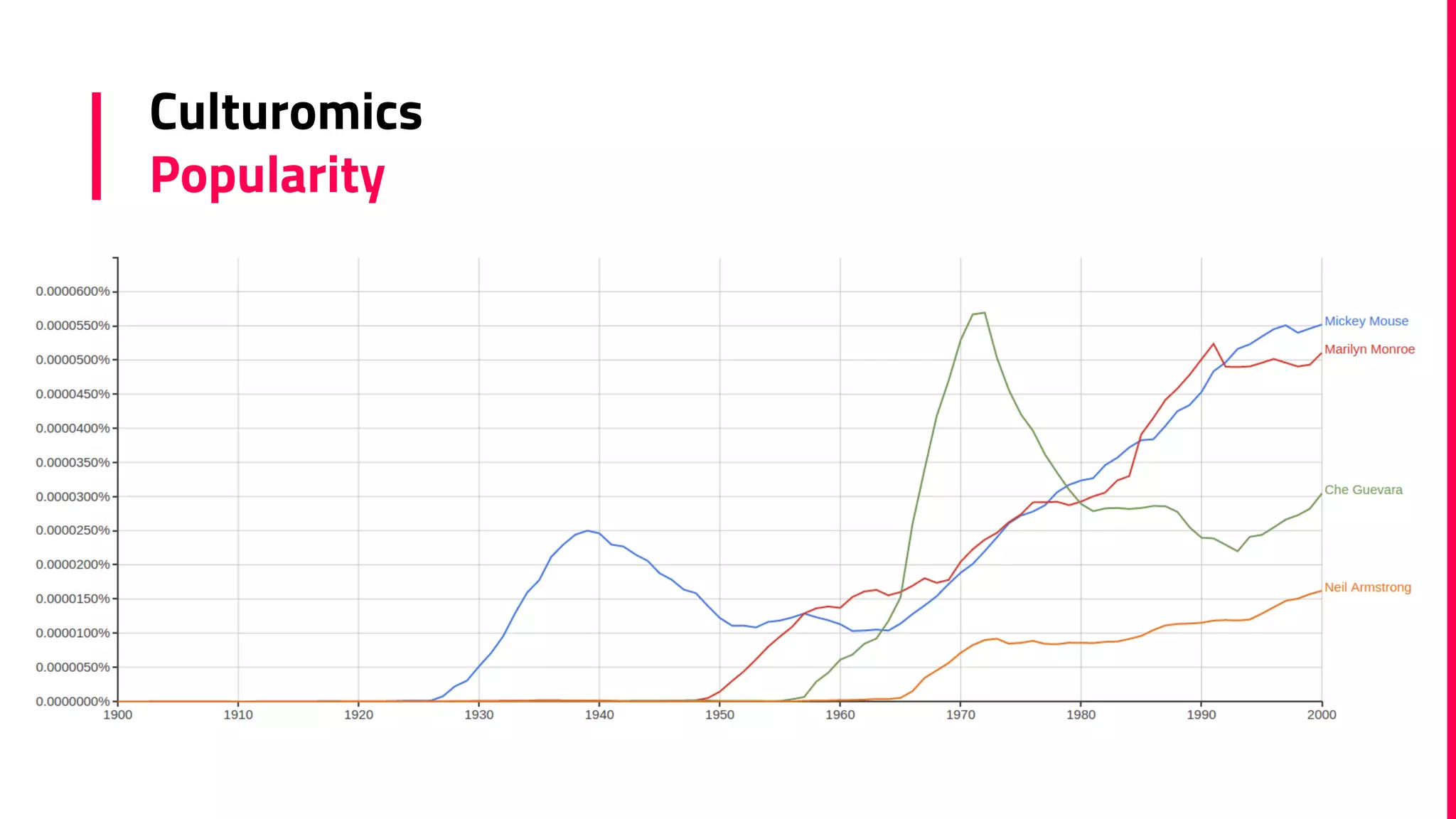
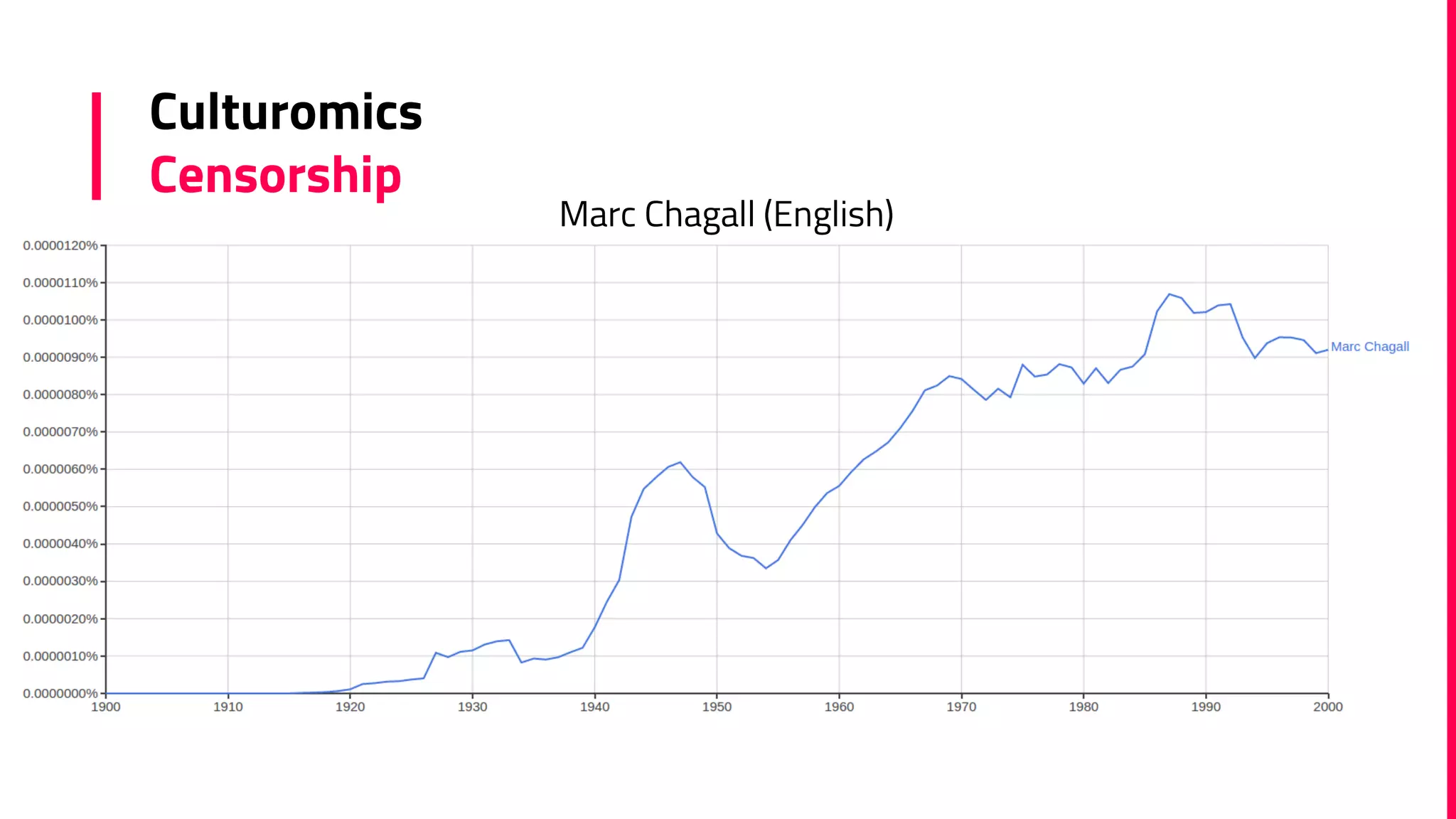
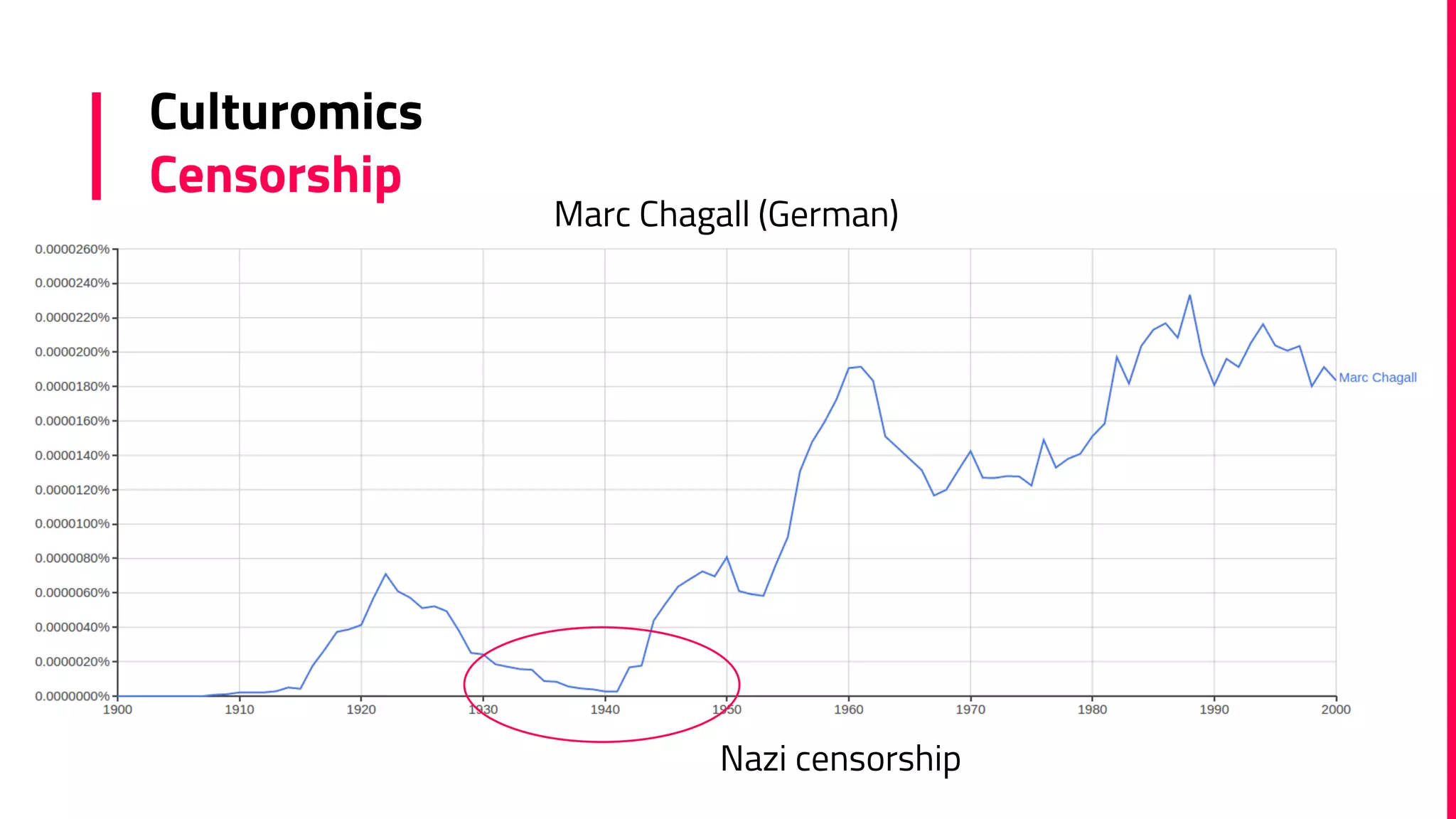
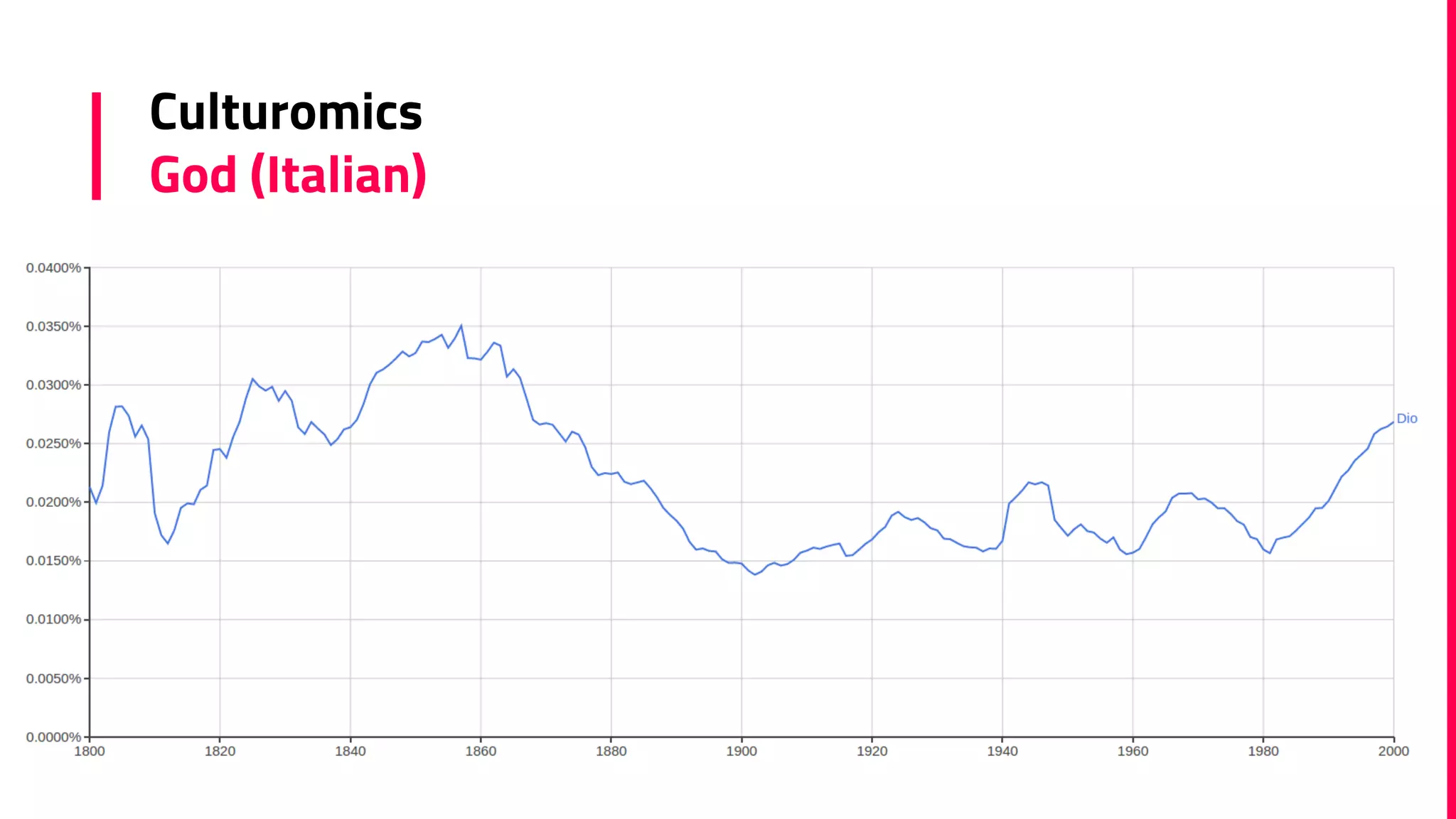
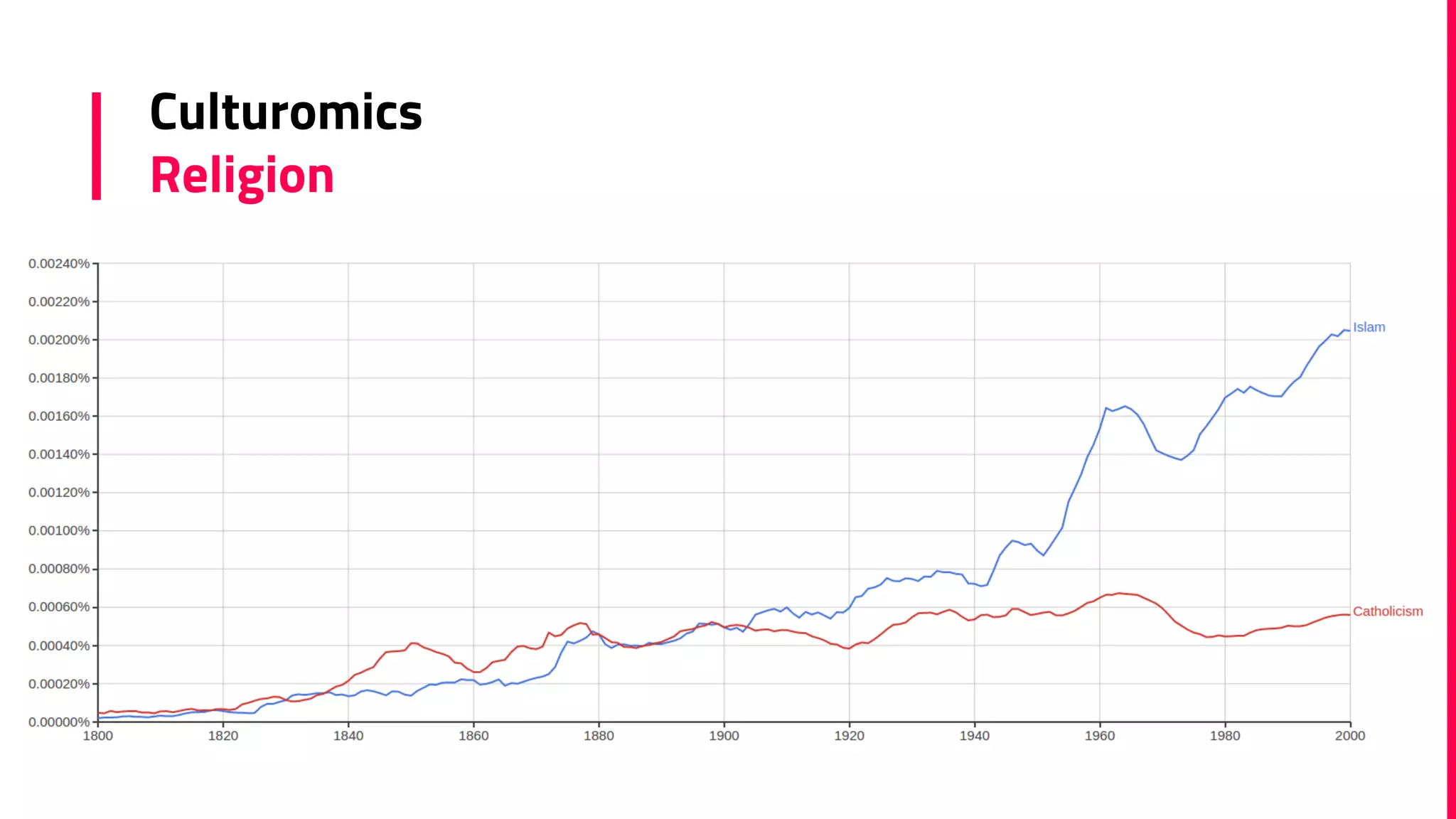
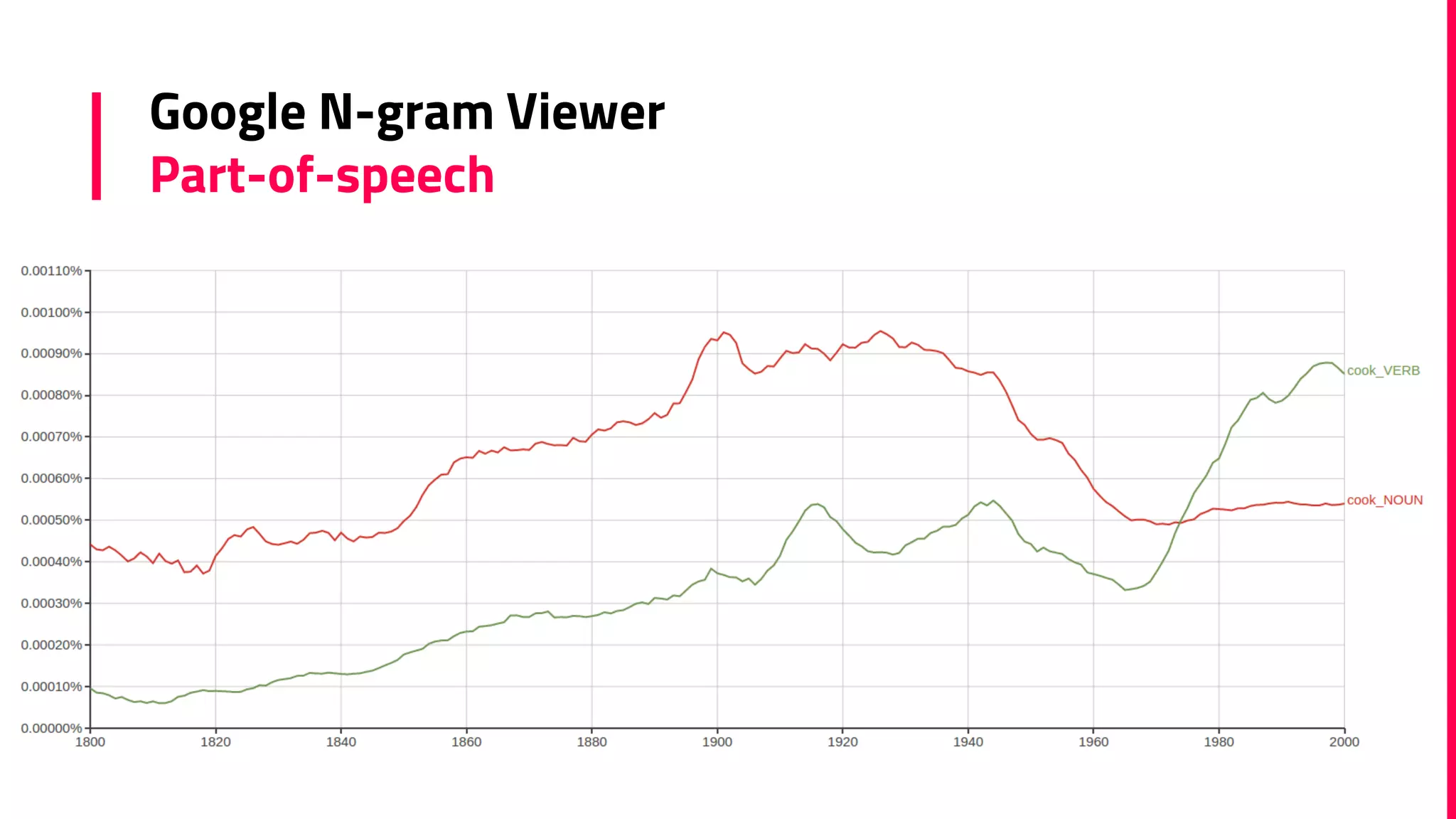
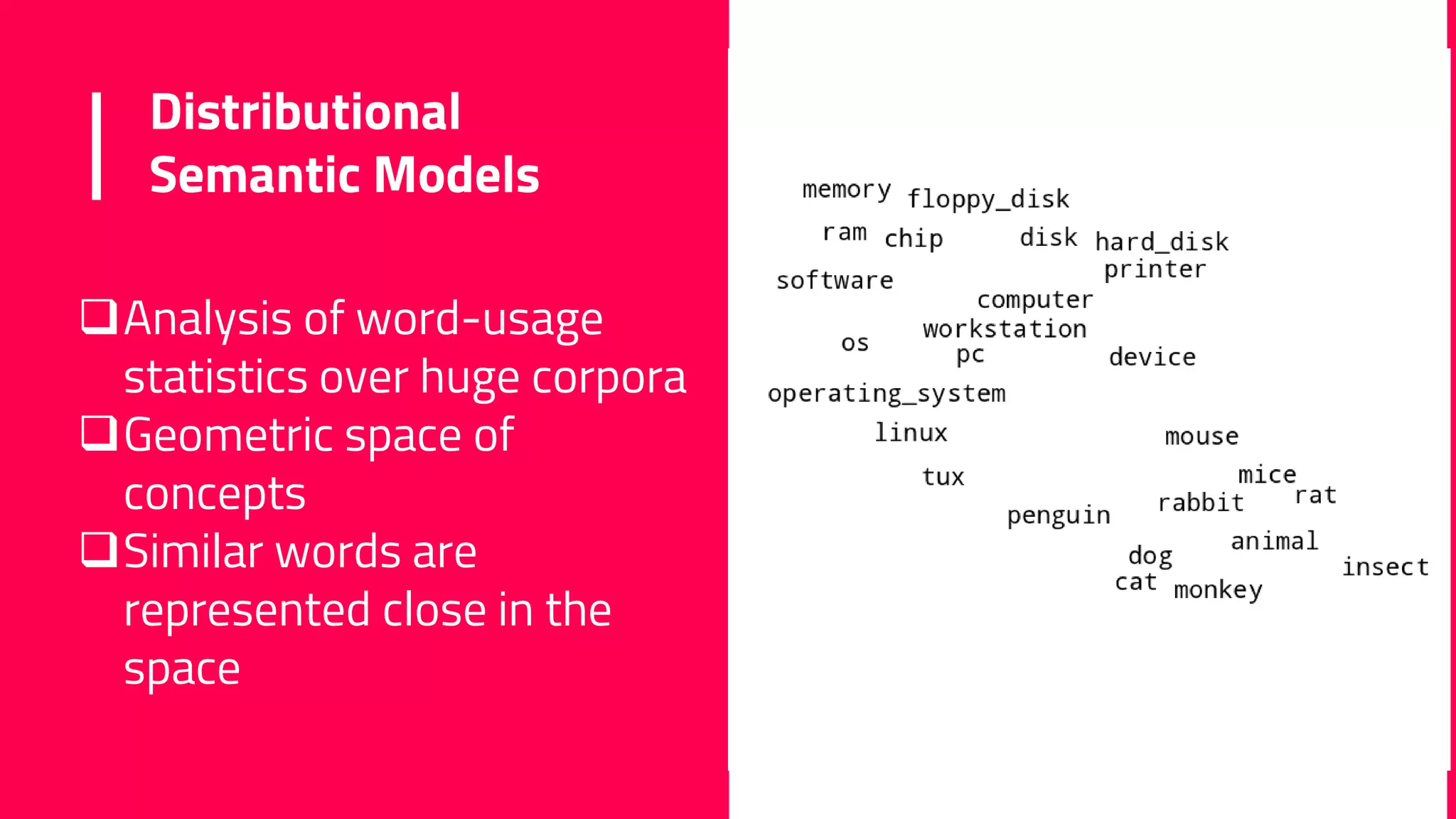
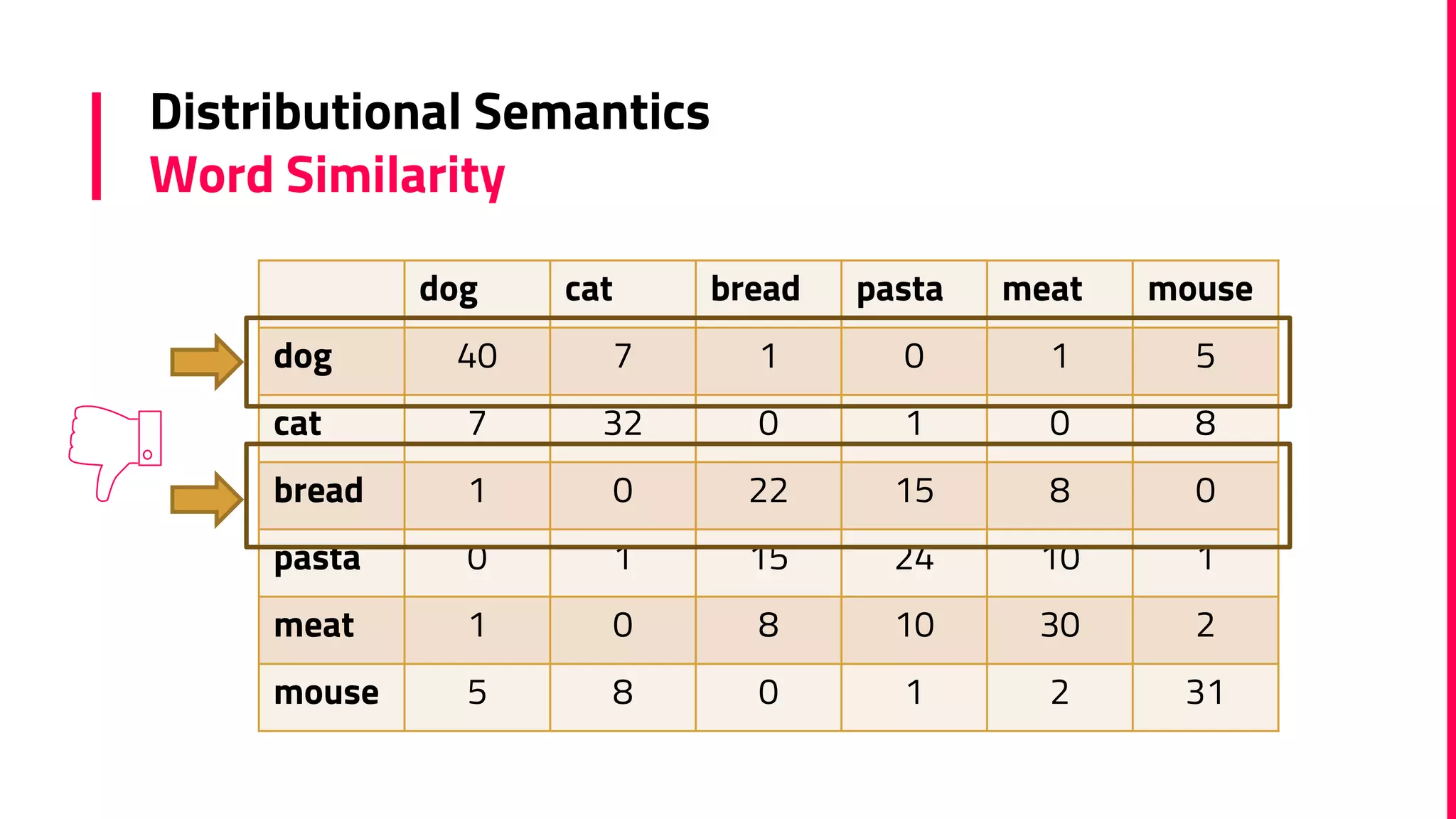
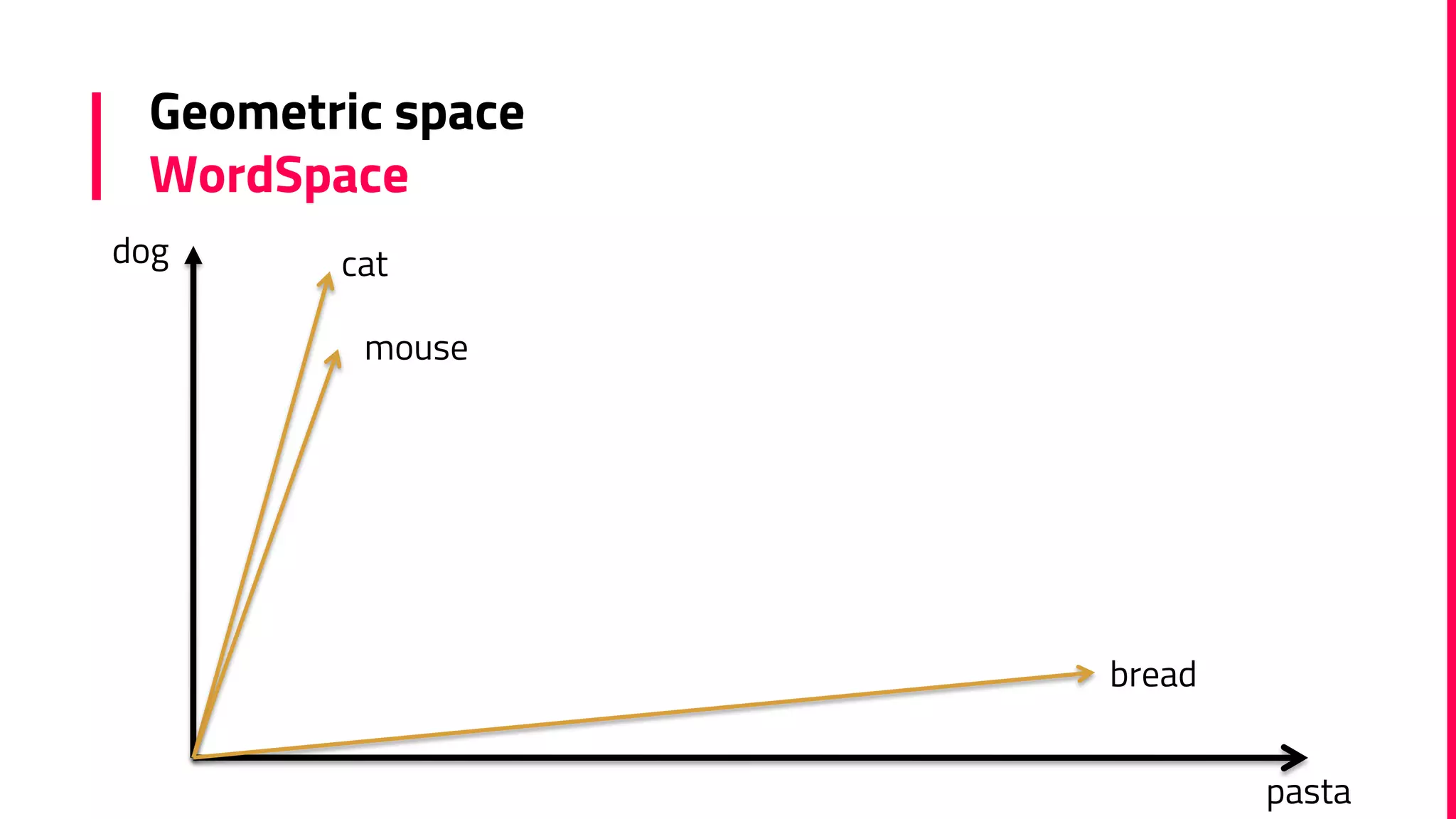
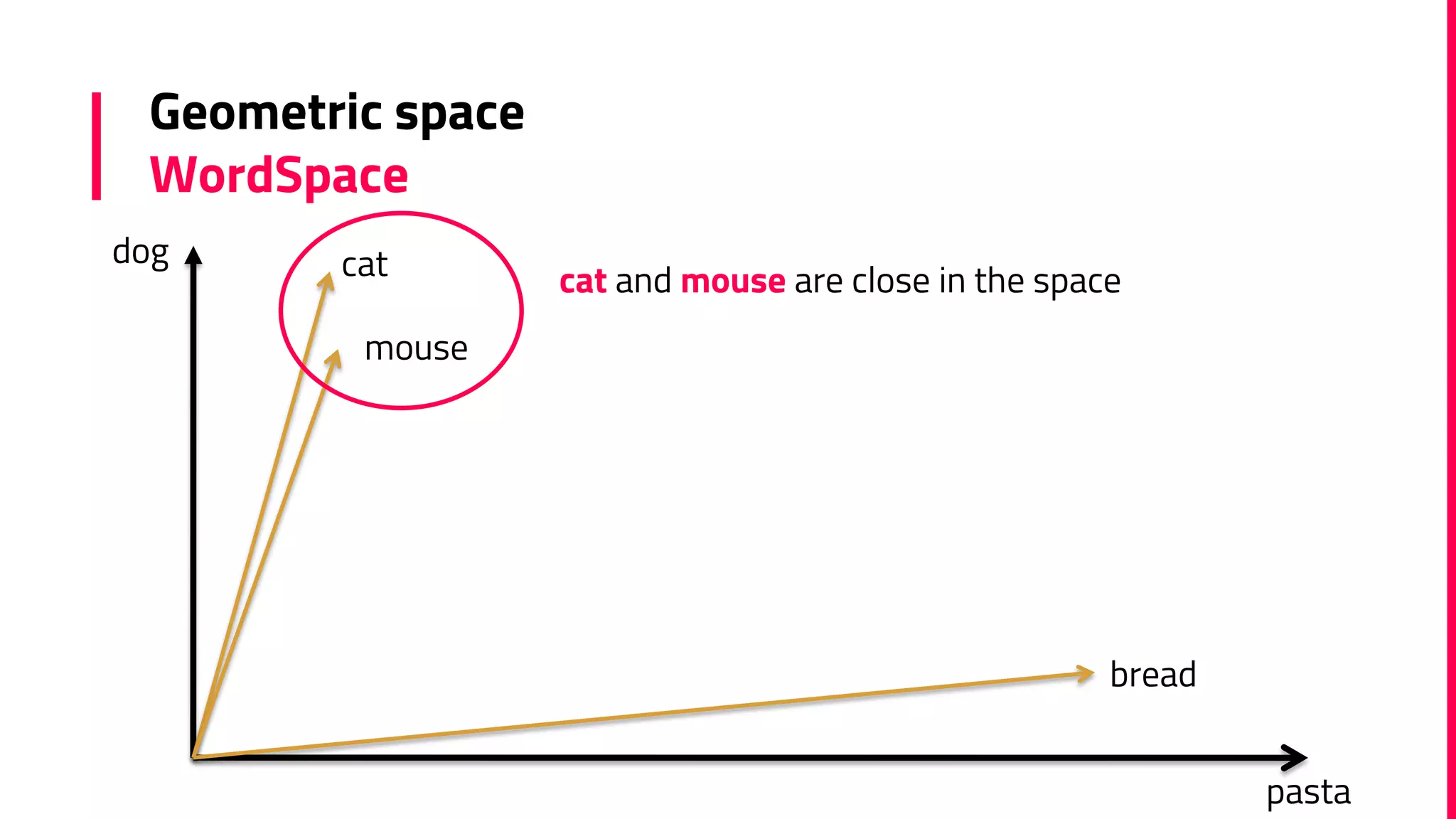
The document discusses the field of natural language processing (NLP) and its applications, including information retrieval, machine translation, and personal assistants. It also explores diachronic linguistics, which studies language change over time, and introduces tools like the Google N-gram Viewer for analyzing language evolution. The author emphasizes the importance of semantics in NLP, particularly in the context of computational linguistics and distributional semantic models.











![Issues in Syntax
Chunking: identify basic structures (phrases)
[the dog]-NP [ate]-VP [my homework]-NP
Shallow parsing
the dog->subject ate->predicate my homework->object
“the dog ate my homework”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/analisidiacronica-161121165739/75/Diachronic-Analysis-13-2048.jpg)