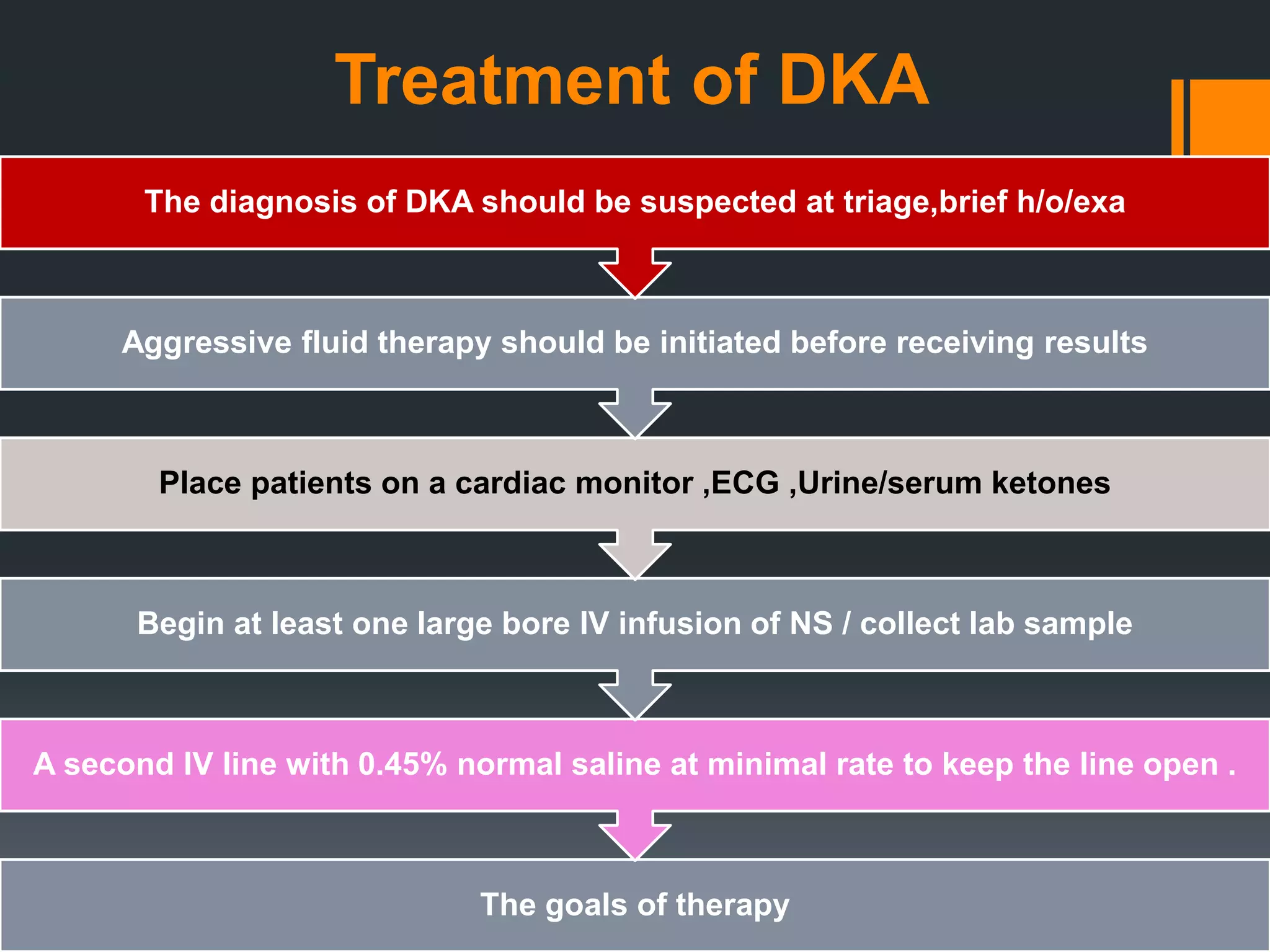
This document provides information on diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA). It begins with an introduction stating that DKA is a life-threatening complication of diabetes mellitus that predominantly occurs in type 1 diabetes but can also occur in 10-30% of newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes cases. It then discusses the pathophysiology of DKA involving a complex relationship between insulin and counterregulatory hormones resulting in hyperglycemia, ketone formation, and metabolic acidosis. Clinical findings are related to hyperglycemia, volume depletion, and acidosis. Treatment goals are volume replacement, correction of hyperglycemia and electrolyte/acid-base imbalances, and treatment of underlying causes. A timeline is provided outlining management from initial presentation


















![1 hour to 2 hour
If initial [k+] > 5.2 initial IV infusion of
regular insulin at 0.1-0.14 units/kg/hr
if initial [k+] >3.3to <5.2 and urine outout
add 20-30 mEq of k+ to each liter of fluid
and insulin drip as above
if initial [k+]<3.3 hold insulin drip and give
k+ @ 20-30 mEq/h until [k+]>3.3 than
insulin drip as above
Comments
Initial lytes;-check
osmolarity,AG,BS,
corrected
[Na+],potassium
Initial [k+]
determinee further
therapy adequate
urine output is
essential before
initial K+ therapy
Repet glu,lytes AG -
If AG > 25 OR
GLUCOSE >800 OR
Significants
comorbidity
,consider ICU
disposition](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/diabeticketoacidosis-180209203116/75/Diabetic-ketoacidosis-22-2048.jpg)

![3 to 4 hours
Active -- adequate fluid infusion
Goal -- insulin infusion
-maintain [k+] 3.3-5.2
-lower glu by 75 mg/dl/h
-maintain adequate lytes.
When CBG apporaches 200 change iv
D5 NS WITH 20-40 mEq kcl / L and
decrease insulin rate to 0.2-0.05
units/kg/h
Comments
If blood sugar does
not decrease by 10%
after 1 hour insulin
therapy,give 0.14
units/kg bolus then
resume previos rate
If blood sugar
decreased faster
than 50-75 mg/dl/h
,decreased insulin
drip
Check glucose
hourly](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/diabeticketoacidosis-180209203116/75/Diabetic-ketoacidosis-24-2048.jpg)



