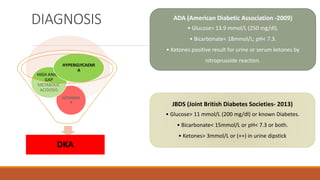
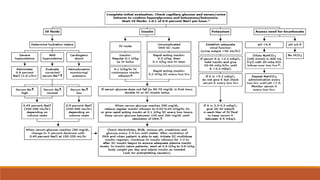
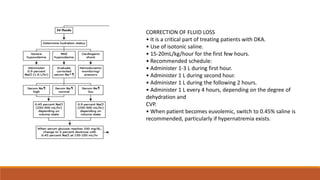
Diabetic ketoacidosis is a life-threatening complication of diabetes caused by insufficient insulin levels. It is characterized by high blood sugar, high ketone levels, and severe acidosis. Treatment involves fluid replacement, insulin therapy to lower blood sugar, and correcting electrolyte and pH imbalances. Education on strict insulin use and management of diabetes is important to prevent future episodes of ketoacidosis.



















![EUGLYCEMIC DKA
• It is essentially DKA without hyperglycemia (Glucose< 200).
• Euglycemic DKA is a rare entity that mostly occurs in patients with Type 1 Diabetes, but also in
Type 2 Diabetes.
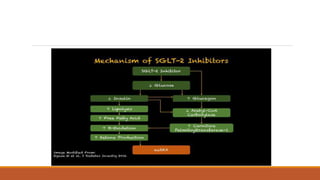
• It has been associated with partial treatment of diabetes, carbohydrate food restriction,
alcohol intake, and with Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 (SGLT-2) inhibitor medications
[Glifozins].
• The exact mechanism of eu DKA is not entirely known.
• Vomiting was the most common symptom.
• Management was same as DKA.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dkascm-221226150051-302c80f0/85/DKA-pptx-23-320.jpg)