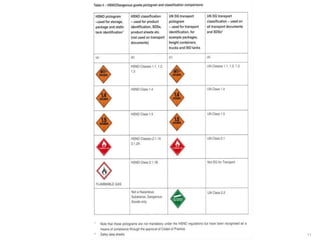
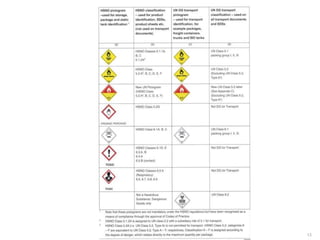
This document provides an overview of the UN classification system for dangerous goods. It discusses how dangerous goods can be substances or articles, and explains key identifiers like the proper shipping name, UN number, and classification. The proper shipping name is the most accurate description of the item and must be used on all documentation. The UN number overcomes language barriers and ranges from 0001-3472. Classification assigns the item to one of nine classes based on its hazards. Packing groups indicate the degree of danger and determine handling and transport requirements. Multiple hazards on a product use the highest assigned packing group.