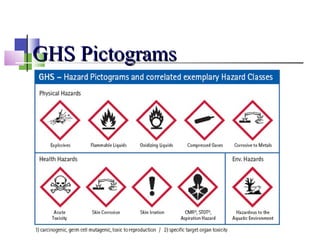
The document discusses the Globally Harmonized System (GHS) for classifying and labeling chemicals. The GHS aims to standardize hazard communication by having consistent criteria for classification of health, physical and environmental hazards, as well as standardized labels and safety data sheets. This will help facilitate international trade by eliminating the need for multiple labels and safety data sheets in different countries. It will also help protect workers by ensuring they receive consistent information about chemical hazards no matter where in the world they are located.