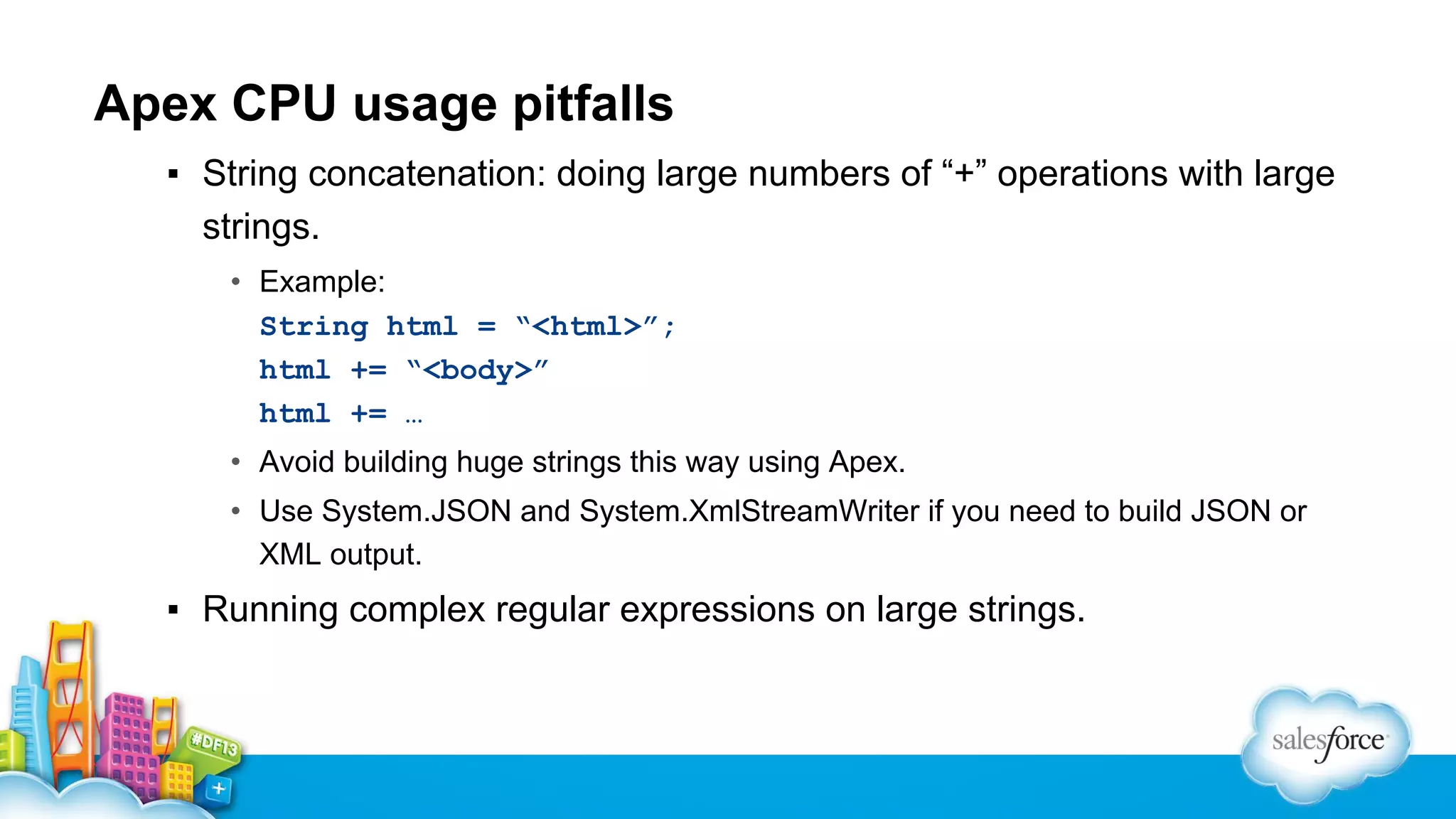
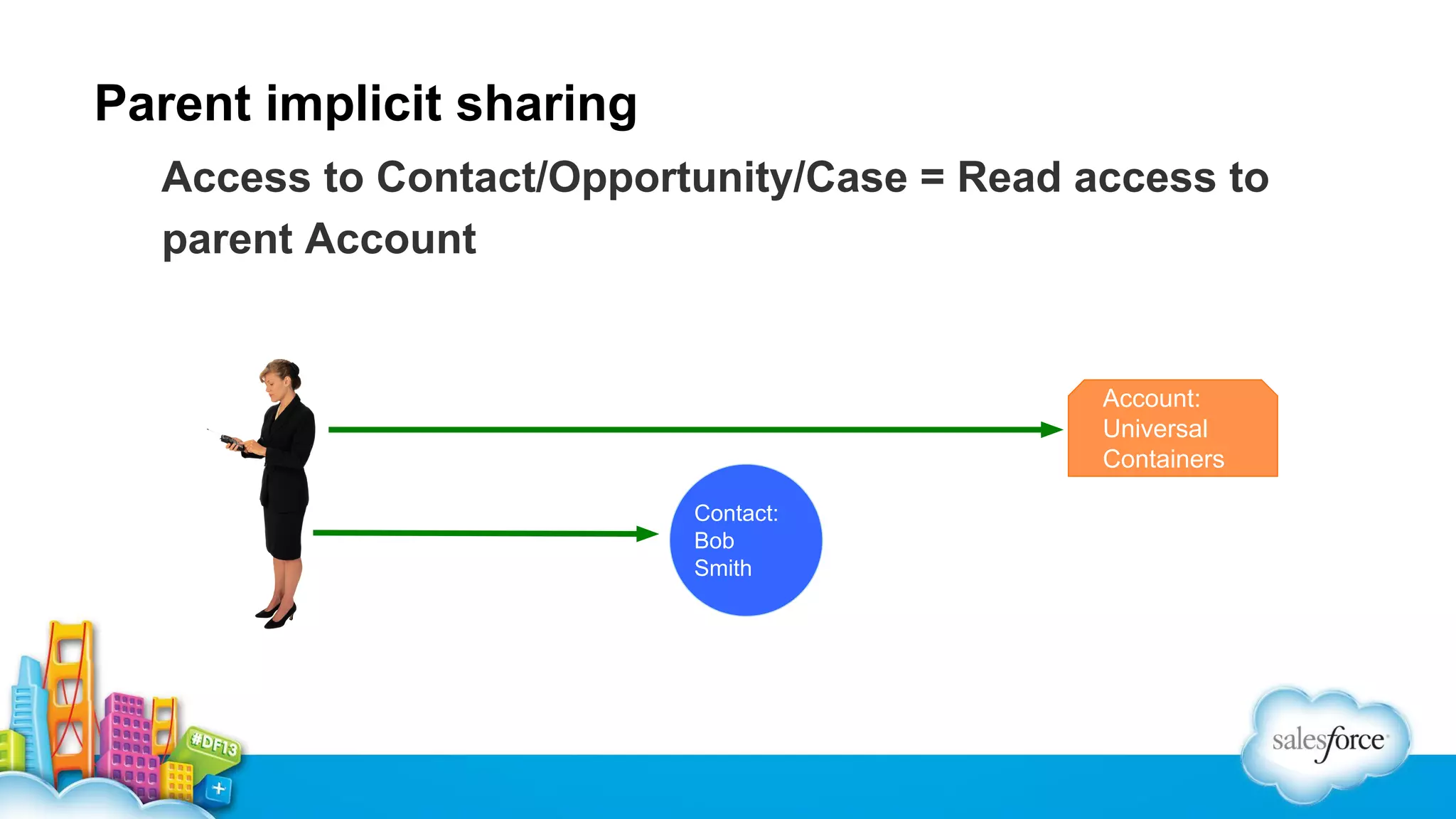
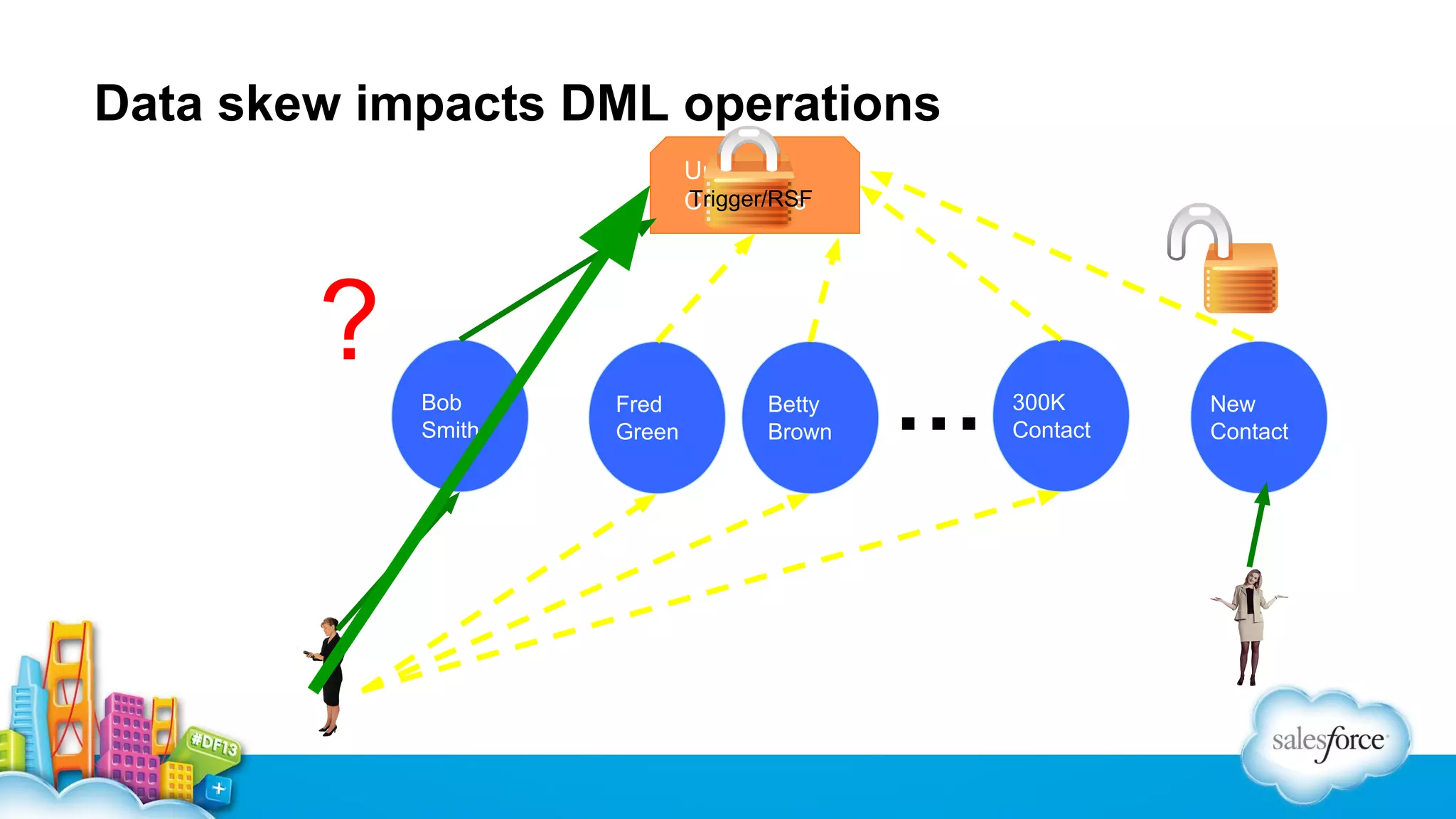
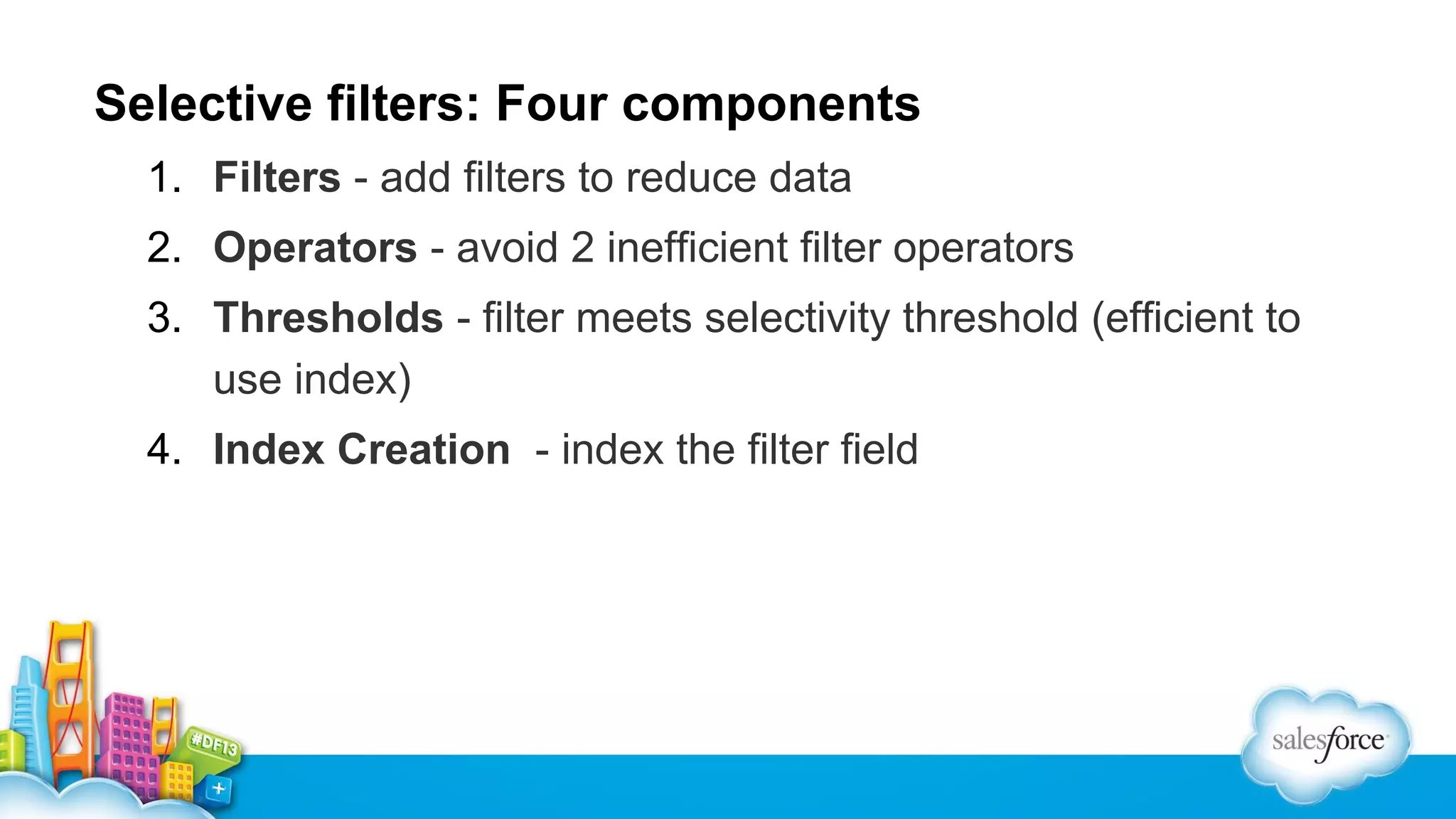
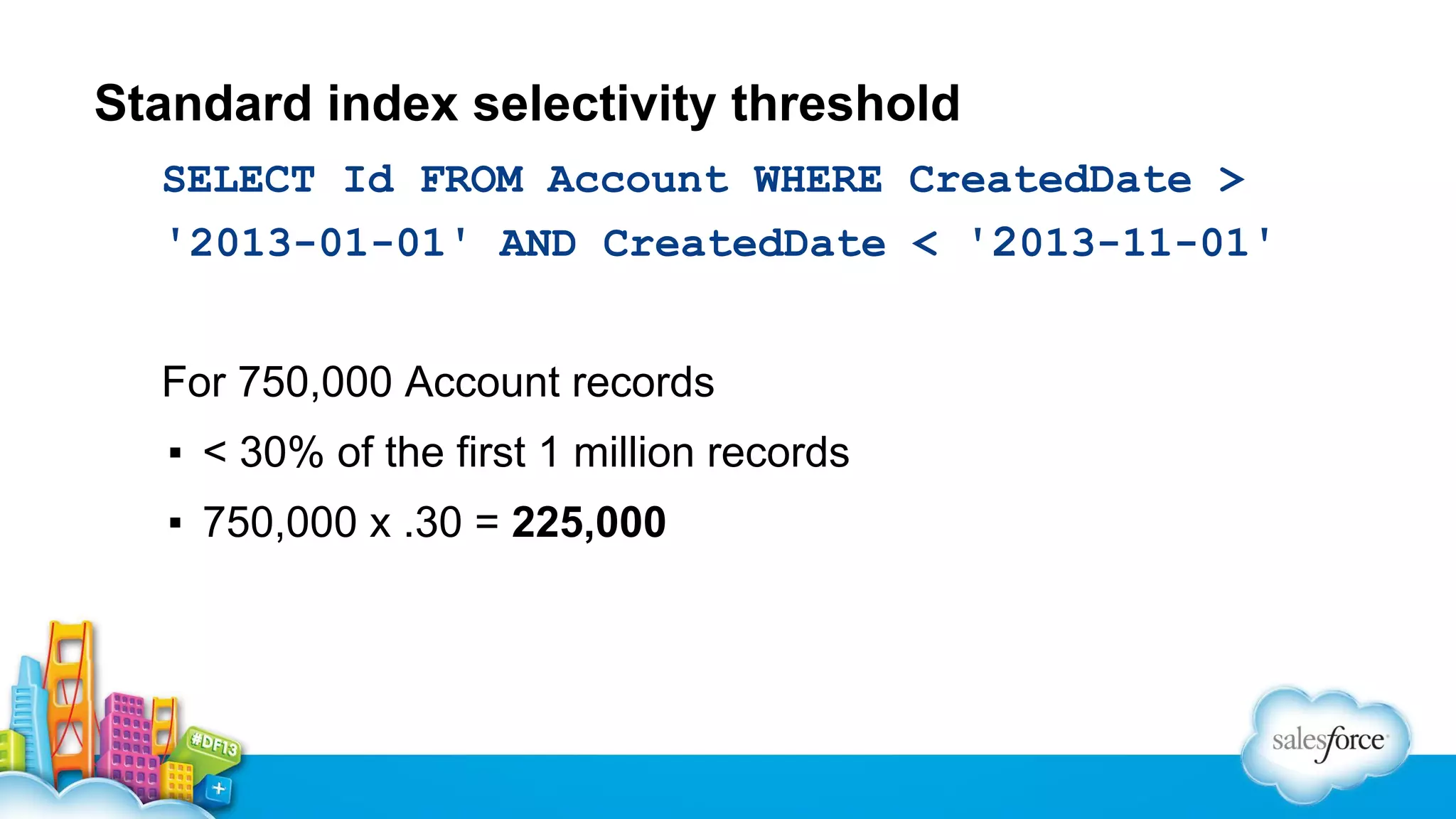
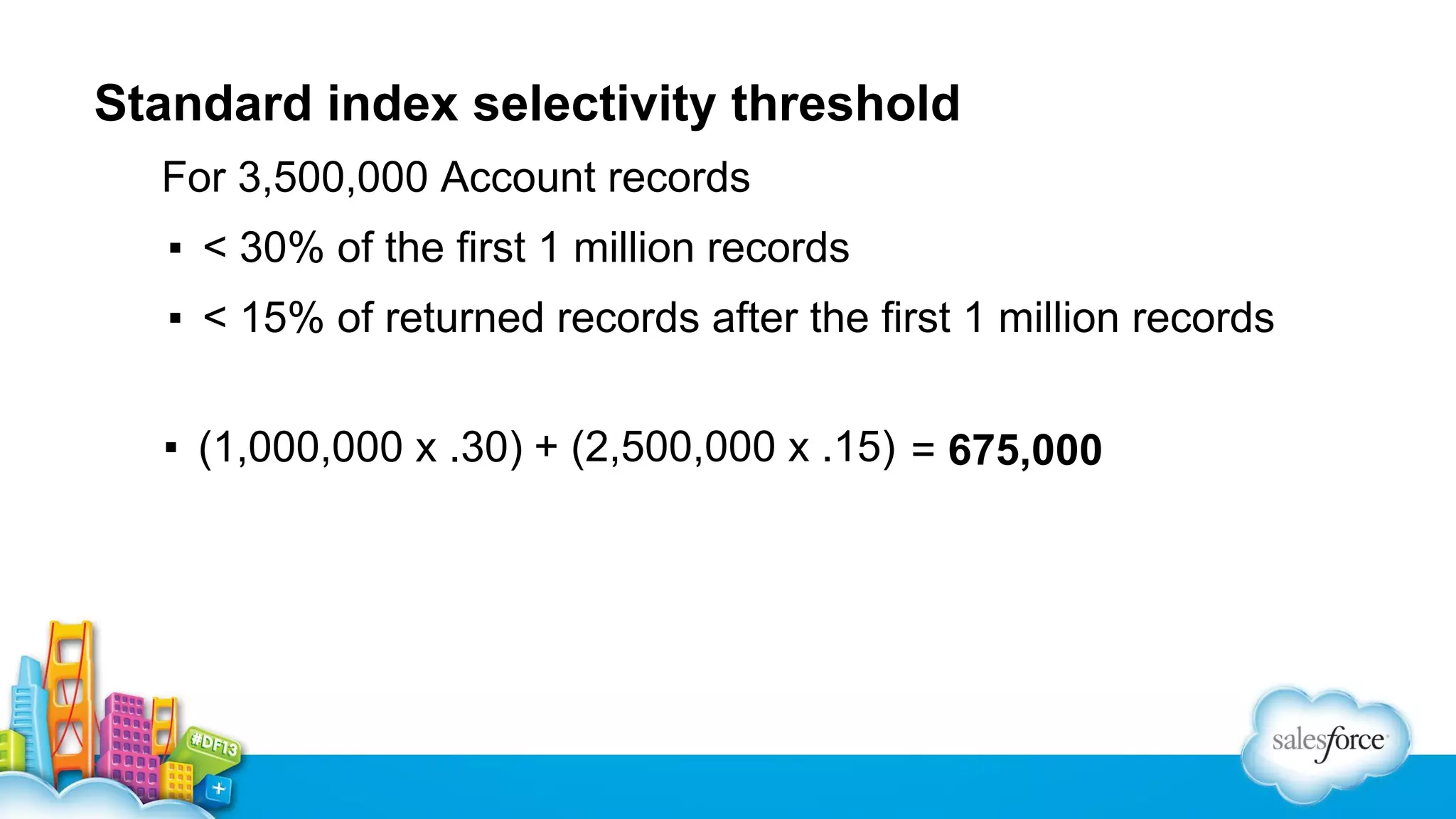
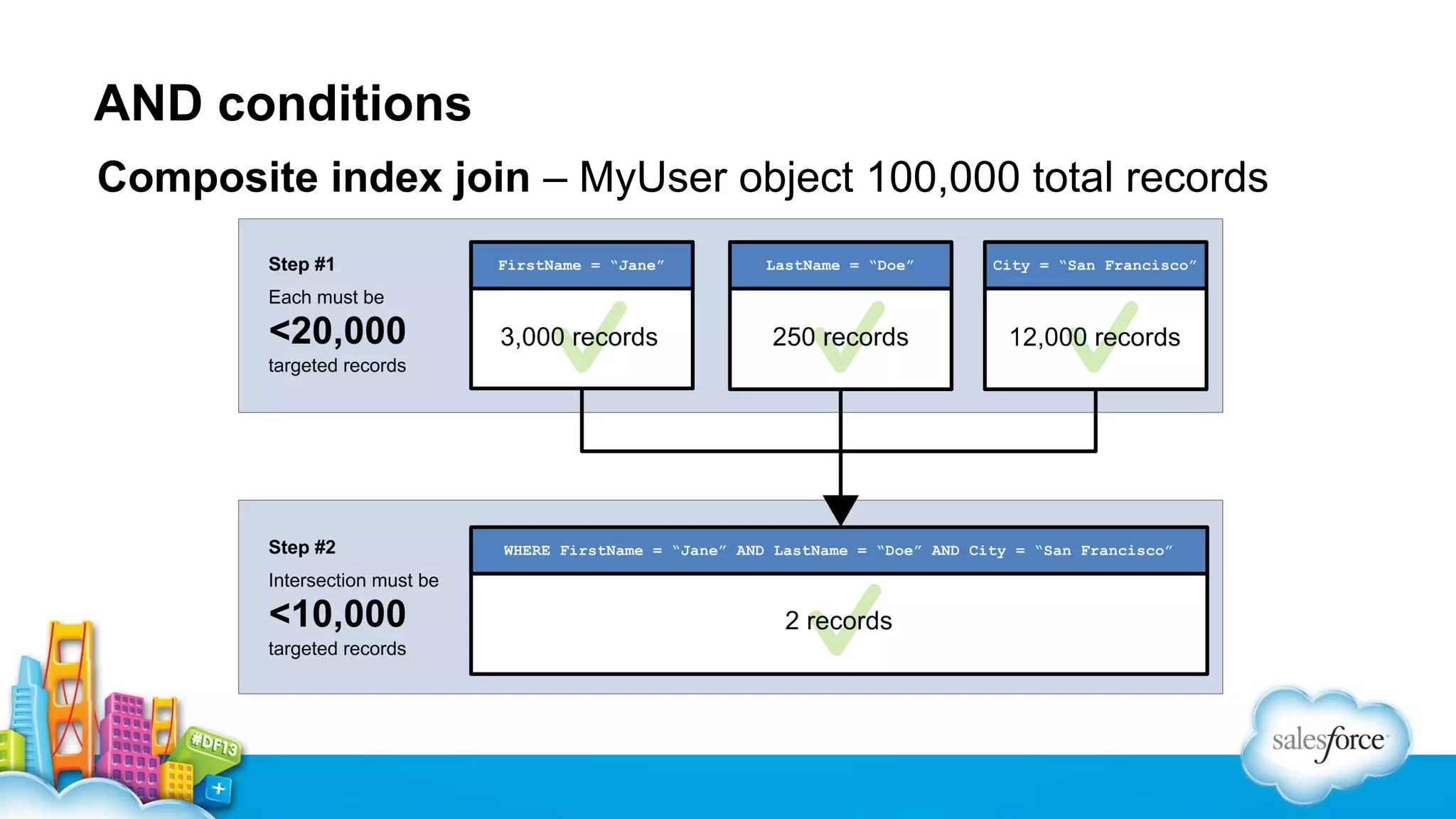
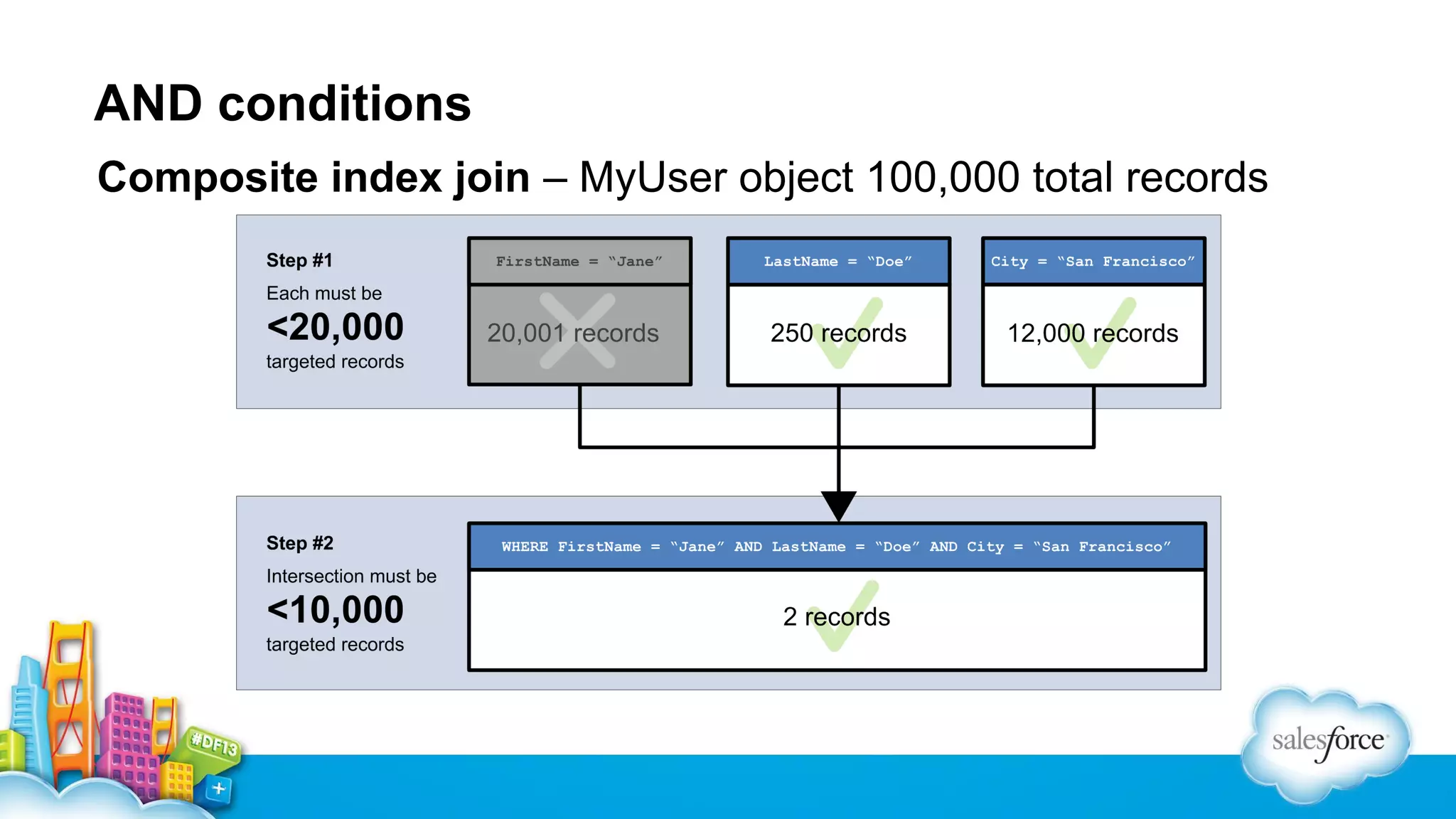
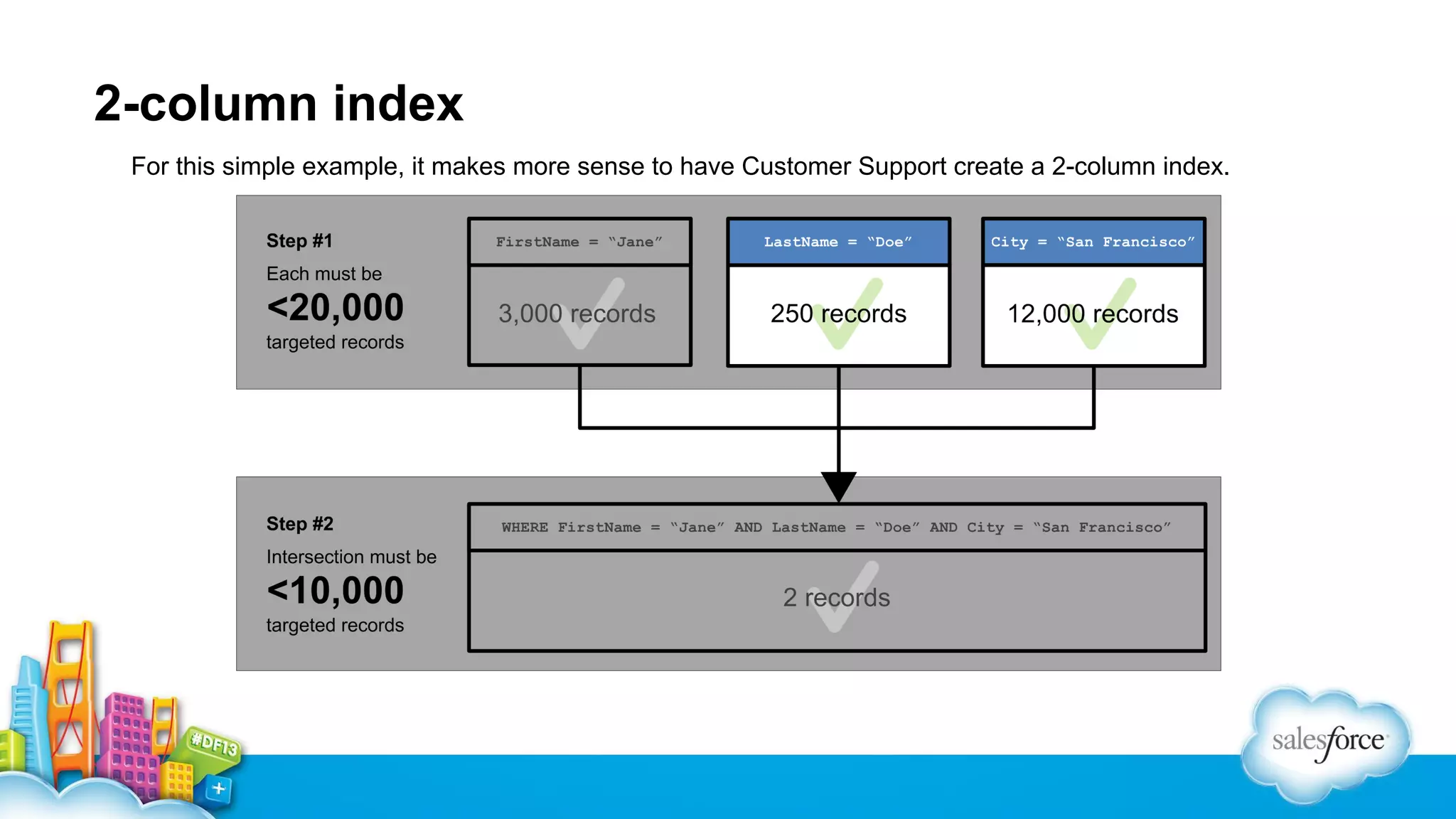
The document outlines performance tuning strategies for Visualforce and Apex on the Salesforce platform, focusing on issues like record lock contention, efficient queries, and debugging techniques. Key strategies include reducing parent-child data skews, utilizing selective filters in queries, and optimizing the ViewState in Visualforce pages. It suggests specific practices for managing batch Apex and APEX CPU limits while providing debugging tips to improve application performance.



































![Batch Apex start() method example
global Database.QueryLocator<SObject> start(Database.BatchableContext bc) {
return Database.getQueryLocator('SELECT Id FROM Account');
}
global void execute(Database.BatchableContext bc, List<Account> scope) {
List<Account> actualScope = [SELECT Id, Name, Description FROM Account
WHERE Rating__c IN
('Excellent','Good','Moderate’)
AND Id IN :scope];
for(Account acc : actualScope) { /* do something */ }
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/df13perftuningvfapexv41-131212223735-phpapp02/75/Performance-Tuning-for-Visualforce-and-Apex-47-2048.jpg)