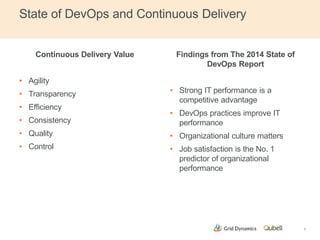
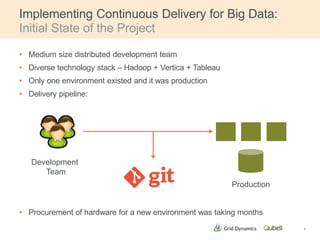
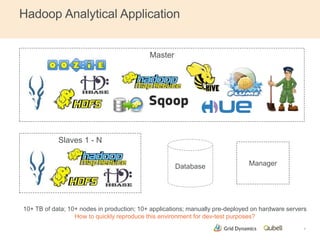
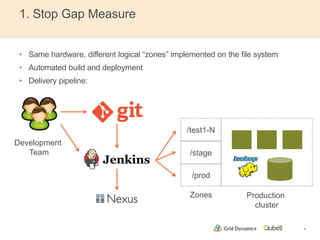
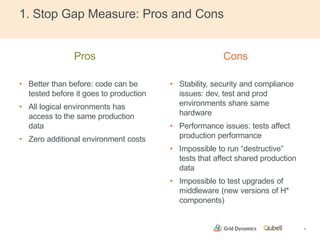
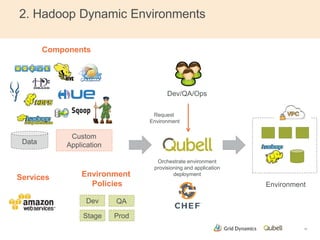
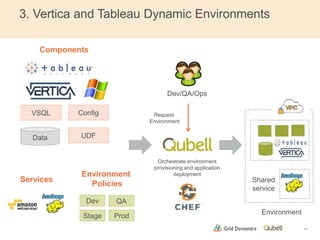
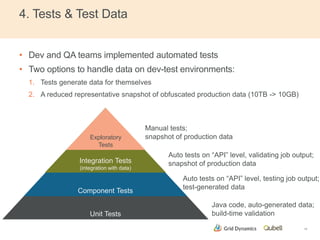
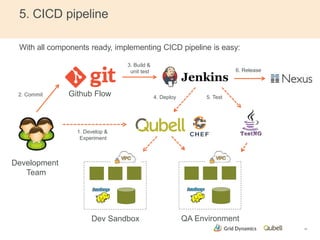
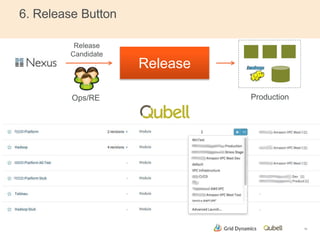
This document discusses implementing continuous delivery for big data applications using Hadoop, Vertica, and Tableau. It describes Grid Dynamics' initial state of developing these applications in a single production environment. It then outlines their steps to implement continuous delivery, including using dynamic environments provisioned by Qubell to enable automated testing and deployment. This reduced risks and increased efficiency by allowing experimentation and validation prior to production releases.