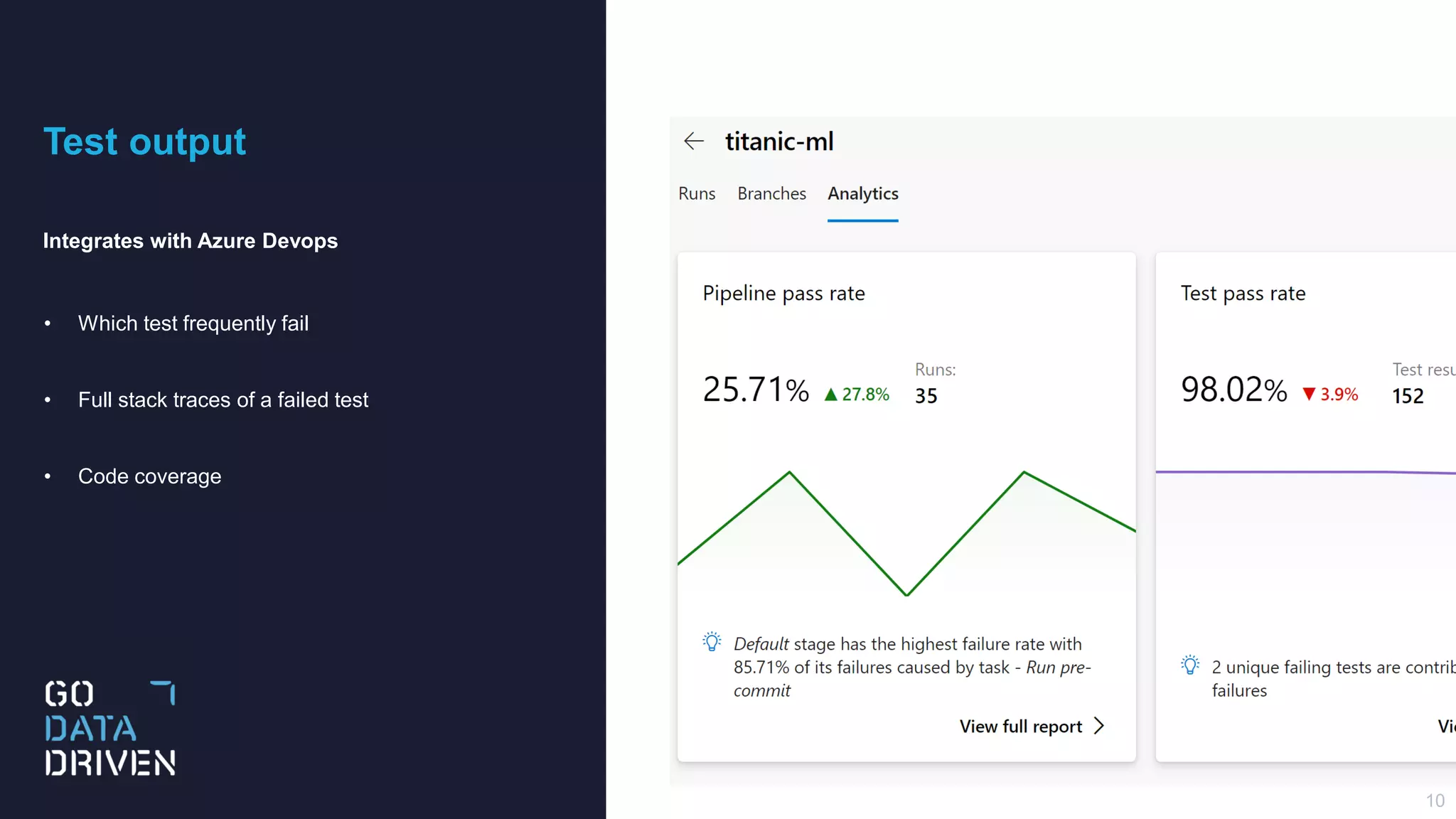
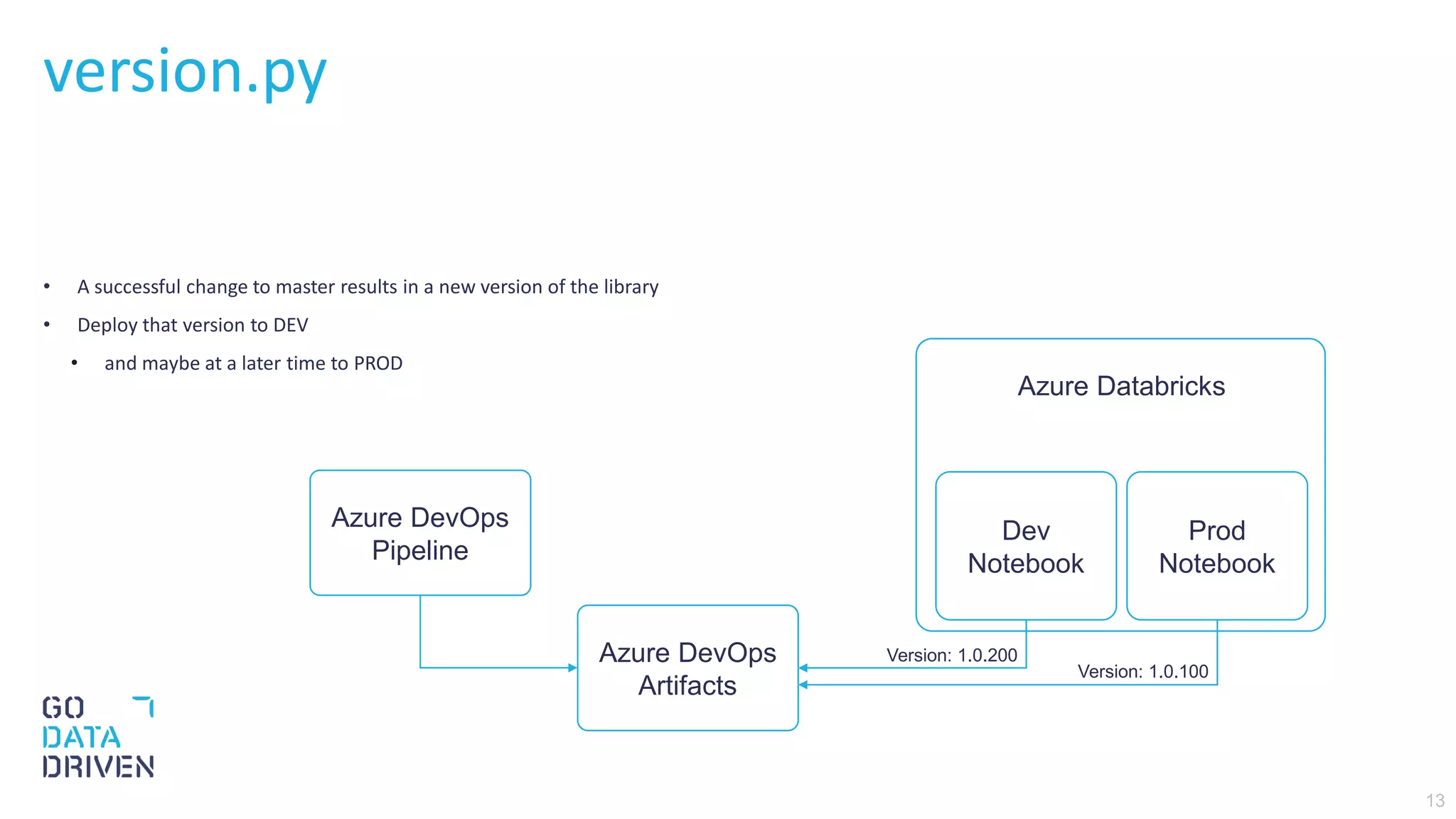
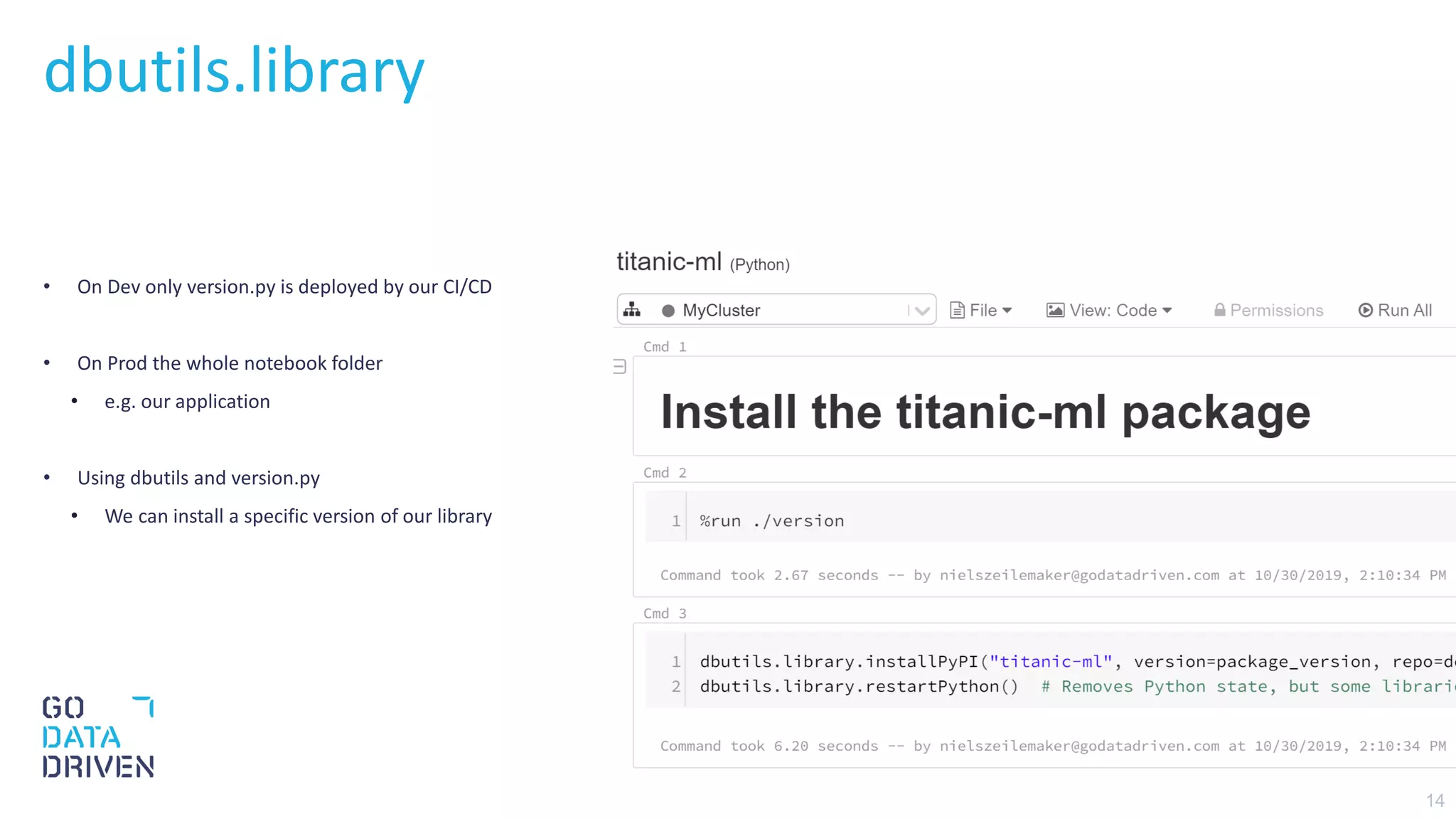
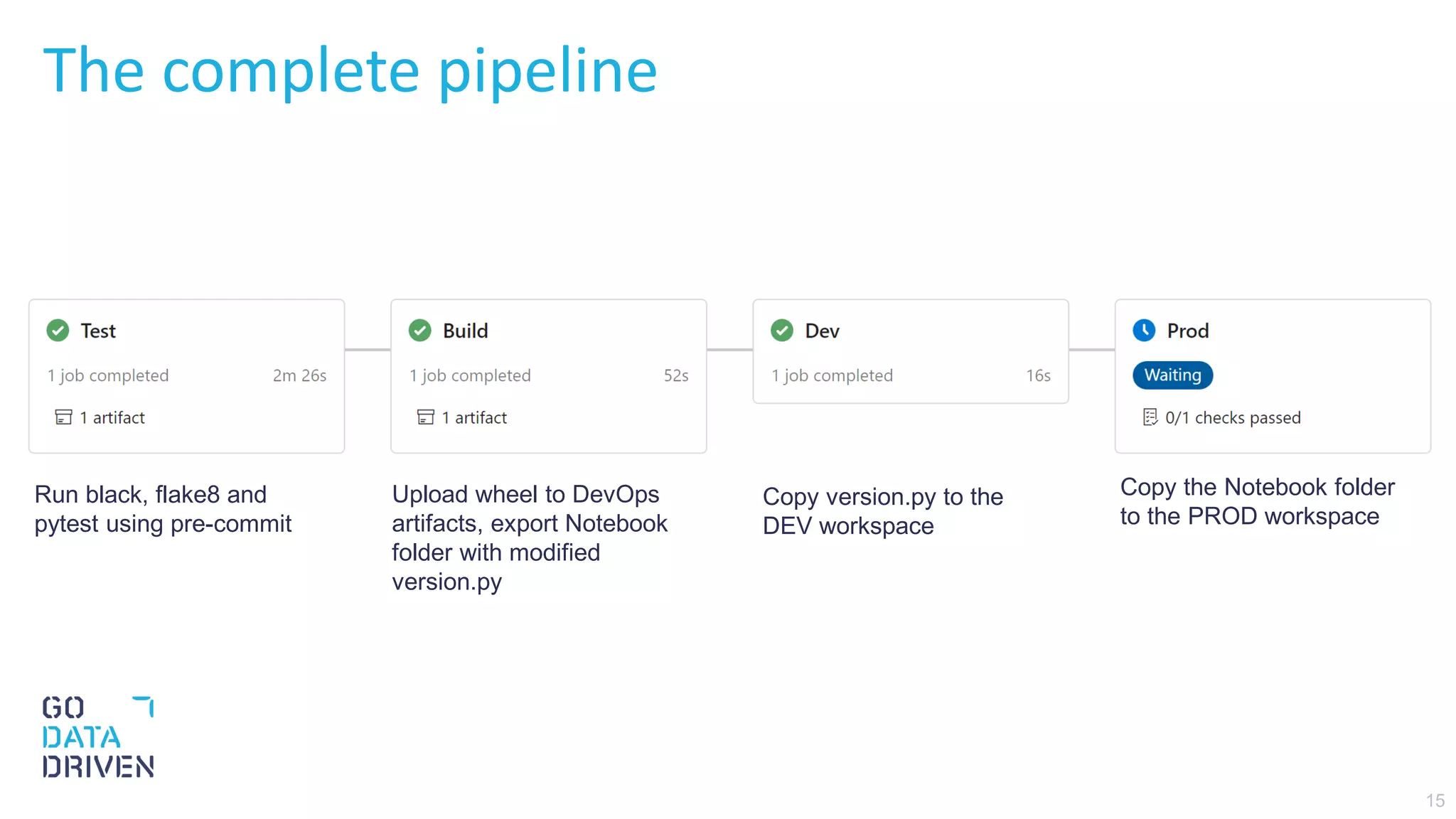
This document describes a CI/CD pipeline for automating deployment of Python code and notebooks to Azure Databricks. The pipeline uses Pre-Commit hooks to run linters and tests on commits. If tests pass, a Python wheel is built and published to Azure DevOps artifacts. The pipeline then copies the version file to the development workspace and copies the full notebook folder to production, allowing installation of the specific library version in notebooks. The goal is continuous deployment with testing at each stage to reliably deploy small code changes.




![Pre-Commit
.pre-commit-config.yaml
• In our case
• run black/Flake8 on each commit
• run pytest on each push
repos:
- repo: https://github.com/psf/black
rev: 19.3b0
hooks:
- id: black
- repo: https://github.com/pre-commit/pre-commit-hooks
rev: v2.3.0
hooks:
- id: flake8
- id: check-merge-conflict
- repo: https://github.com/godatadriven/pre-commit-docker-pyspark
rev: master
hooks:
- id: pyspark-docker
name: Run tests
entry: /entrypoint.sh python setup.py test
language: docker
pass_filenames: false
stages: [push]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/devopsdatabricks-191102095114/75/CI-CD-with-Azure-DevOps-and-Azure-Databricks-7-2048.jpg)
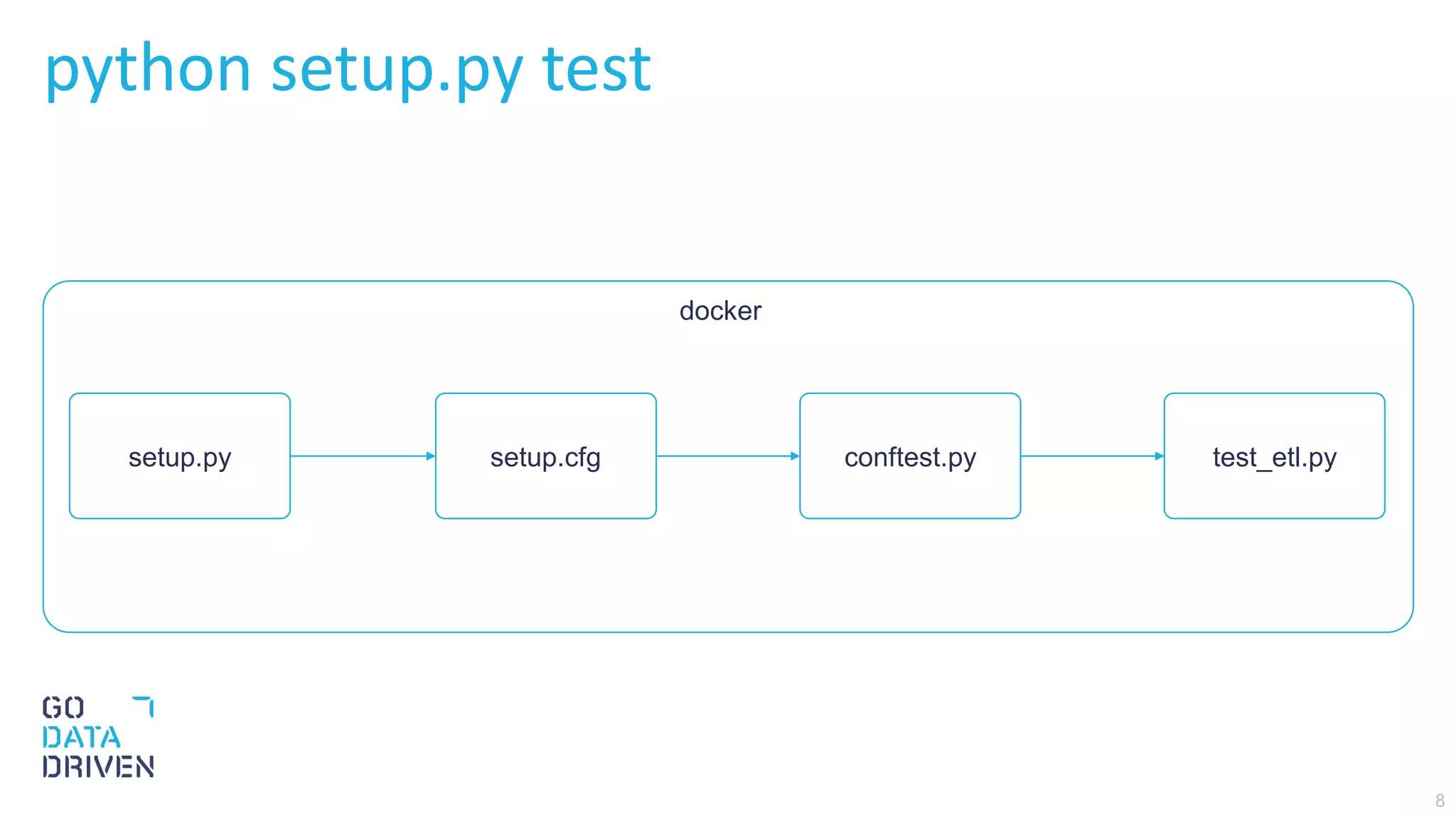
![9
Testing PySpark
conftest.py create pytest fixture called spark
def test_load_df(spark):
df = load_df(spark, "input/data.csv")
assert df.count() == 891
assert df.filter(df.Name == "Sandstrom, Miss. Marguerite Rut").count() == 1
def test_fill_na(spark):
input_df = spark.createDataFrame(
[(None, None, None)], "Age: double, Cabin: string, Fare: double"
)
output_df = fill_na(input_df)
output = df_to_list_dict(output_df)
expected_output = [{"Age": -0.5, "Cabin": "N", "Fare": -0.5}]
assert output == expected_output](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/devopsdatabricks-191102095114/75/CI-CD-with-Azure-DevOps-and-Azure-Databricks-9-2048.jpg)