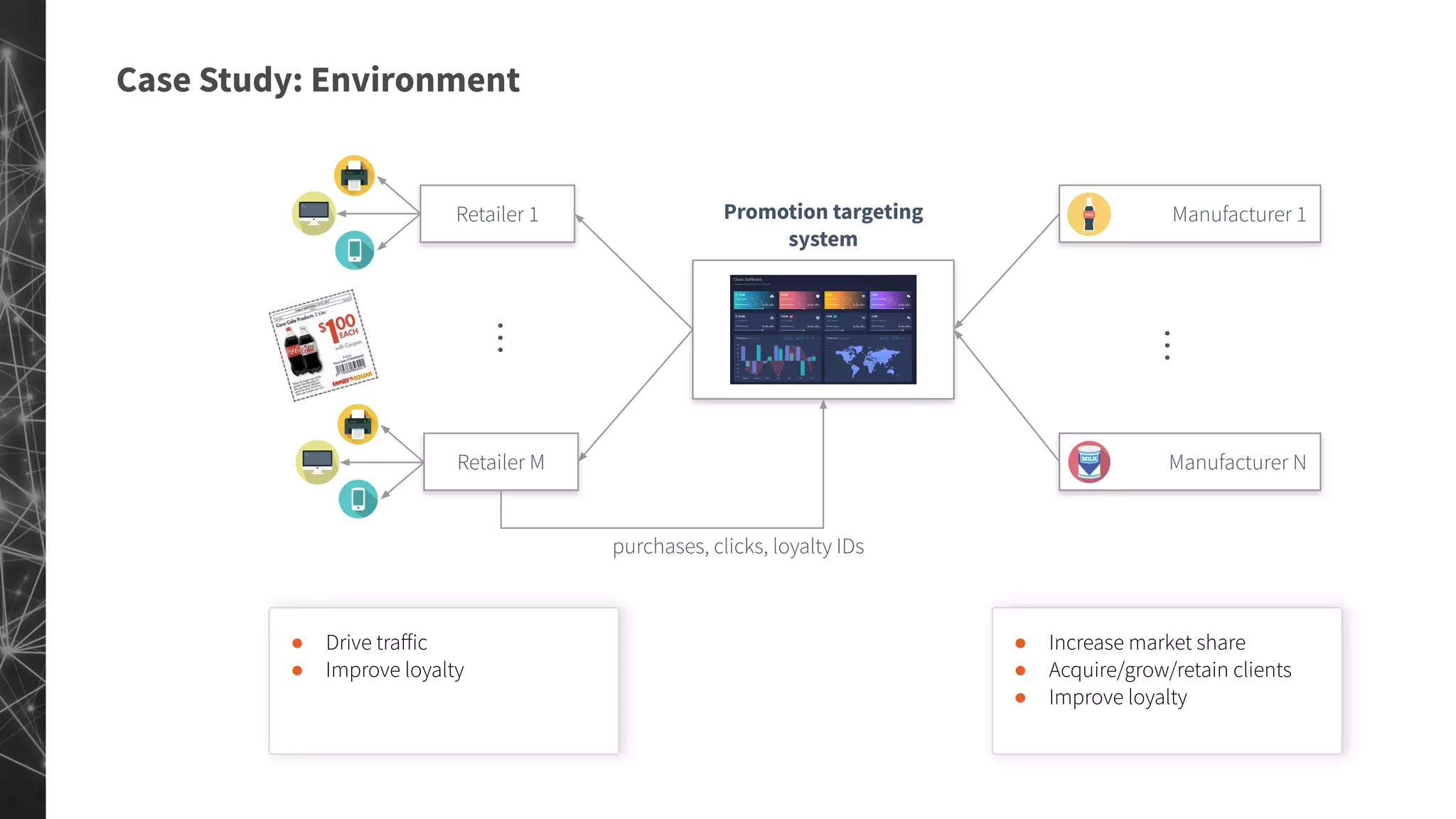
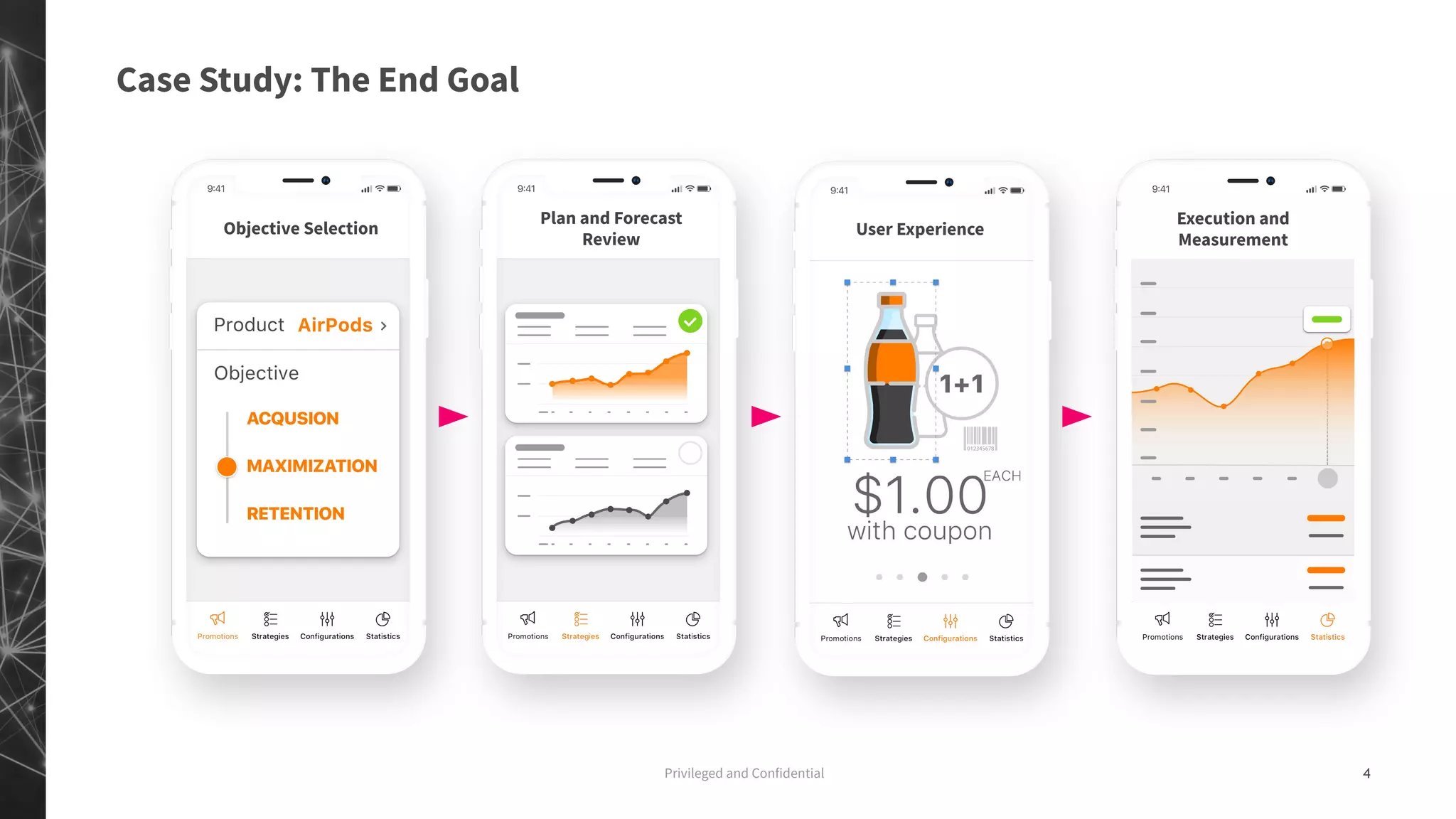
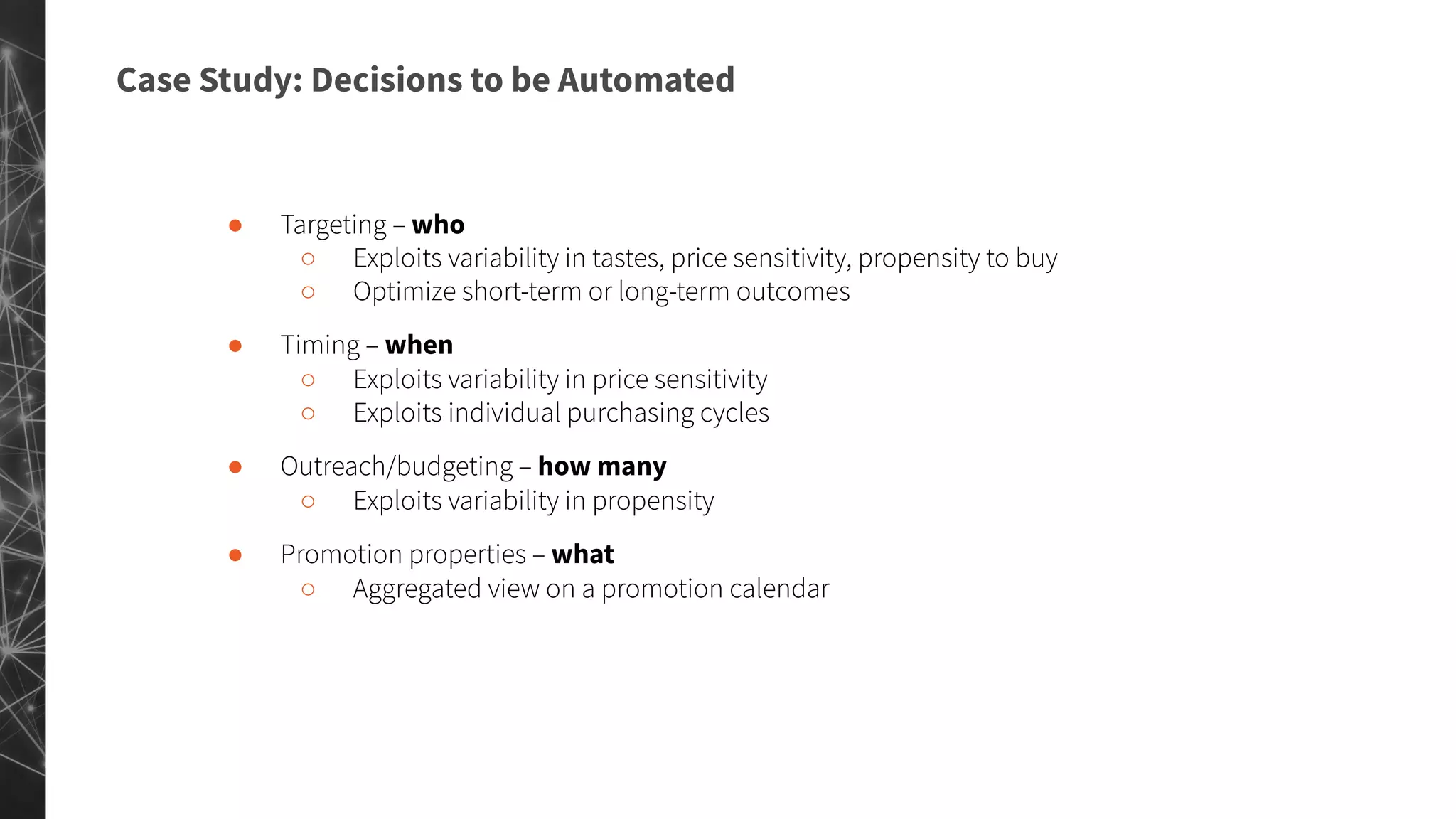
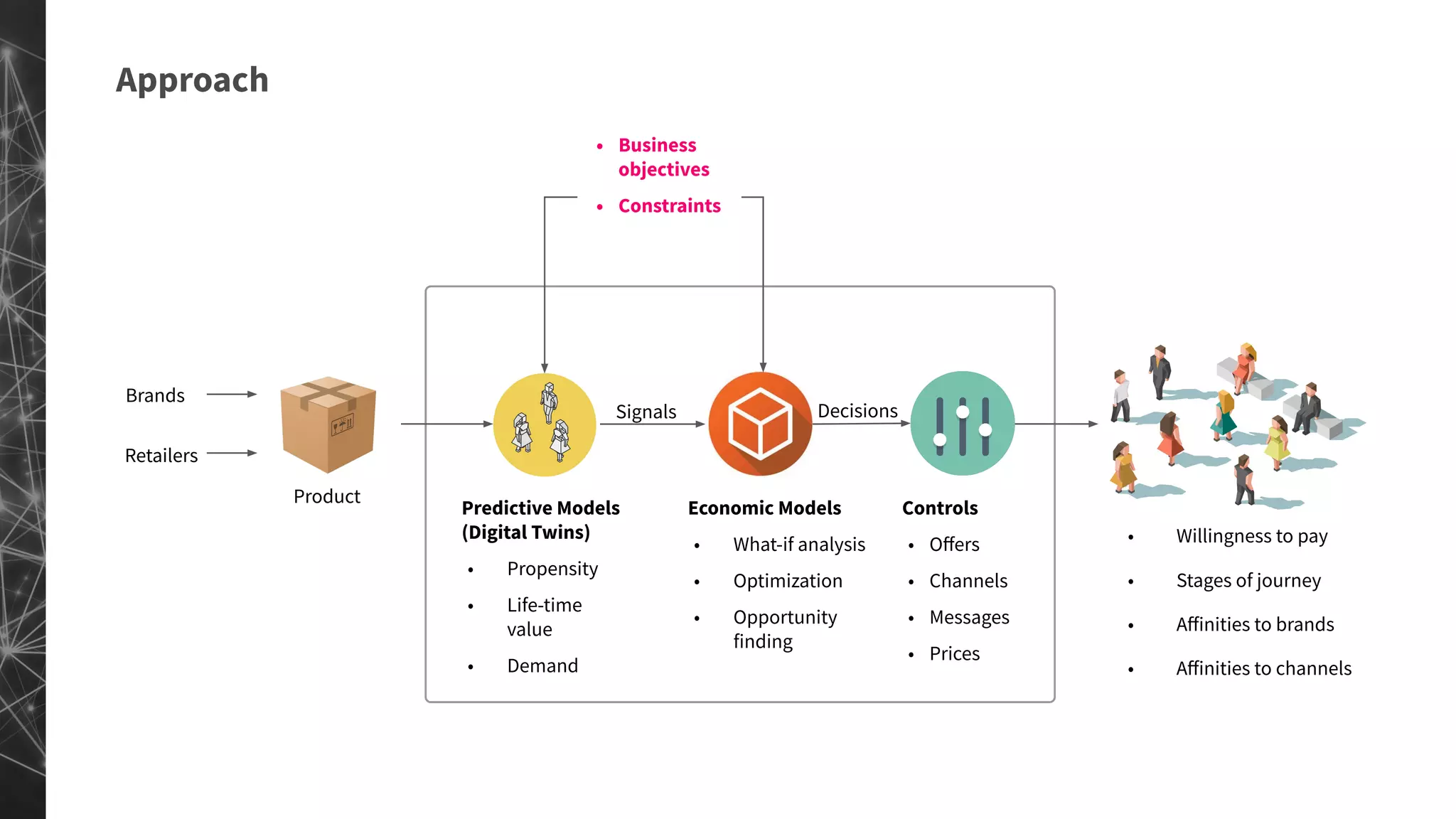
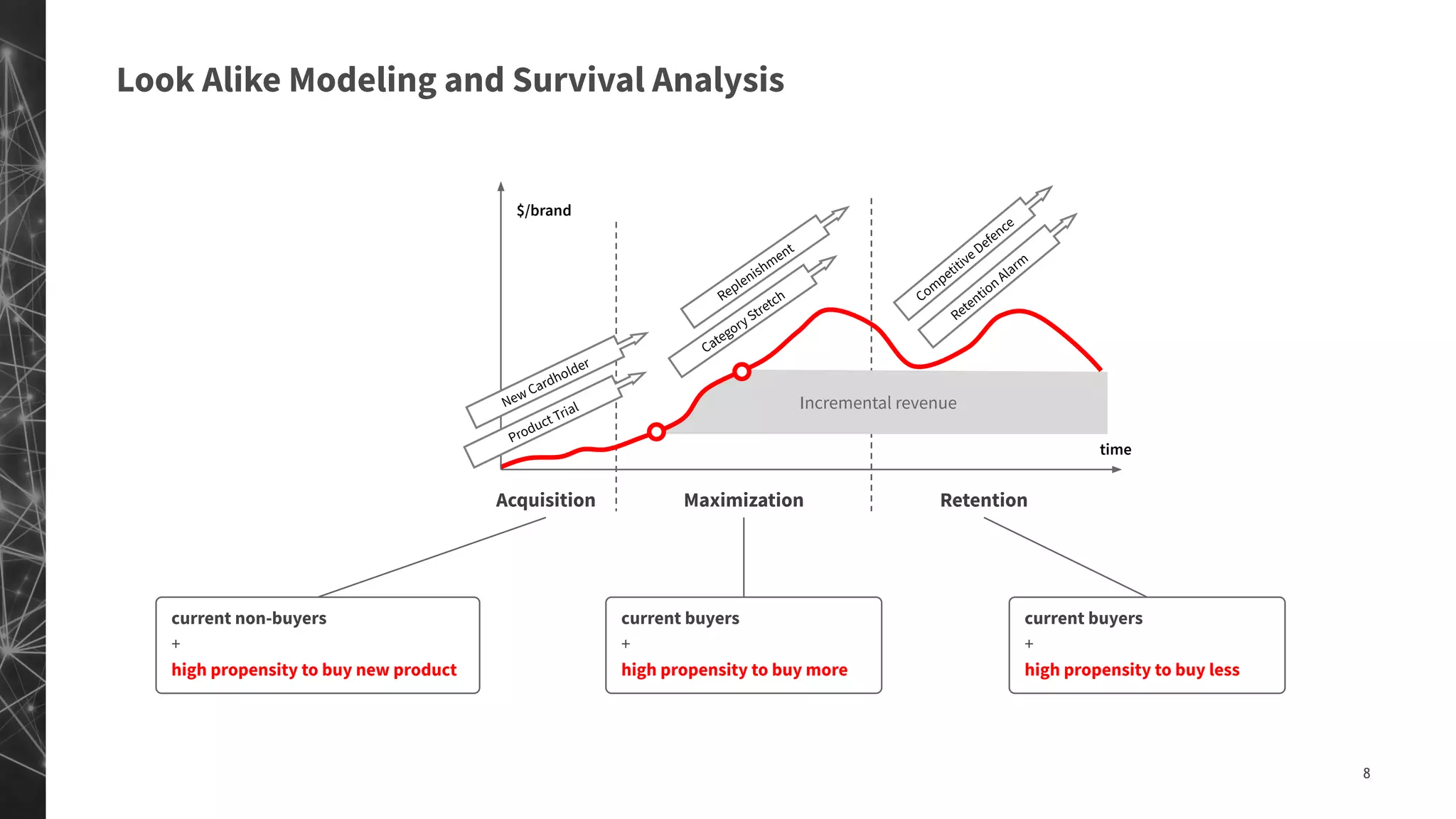
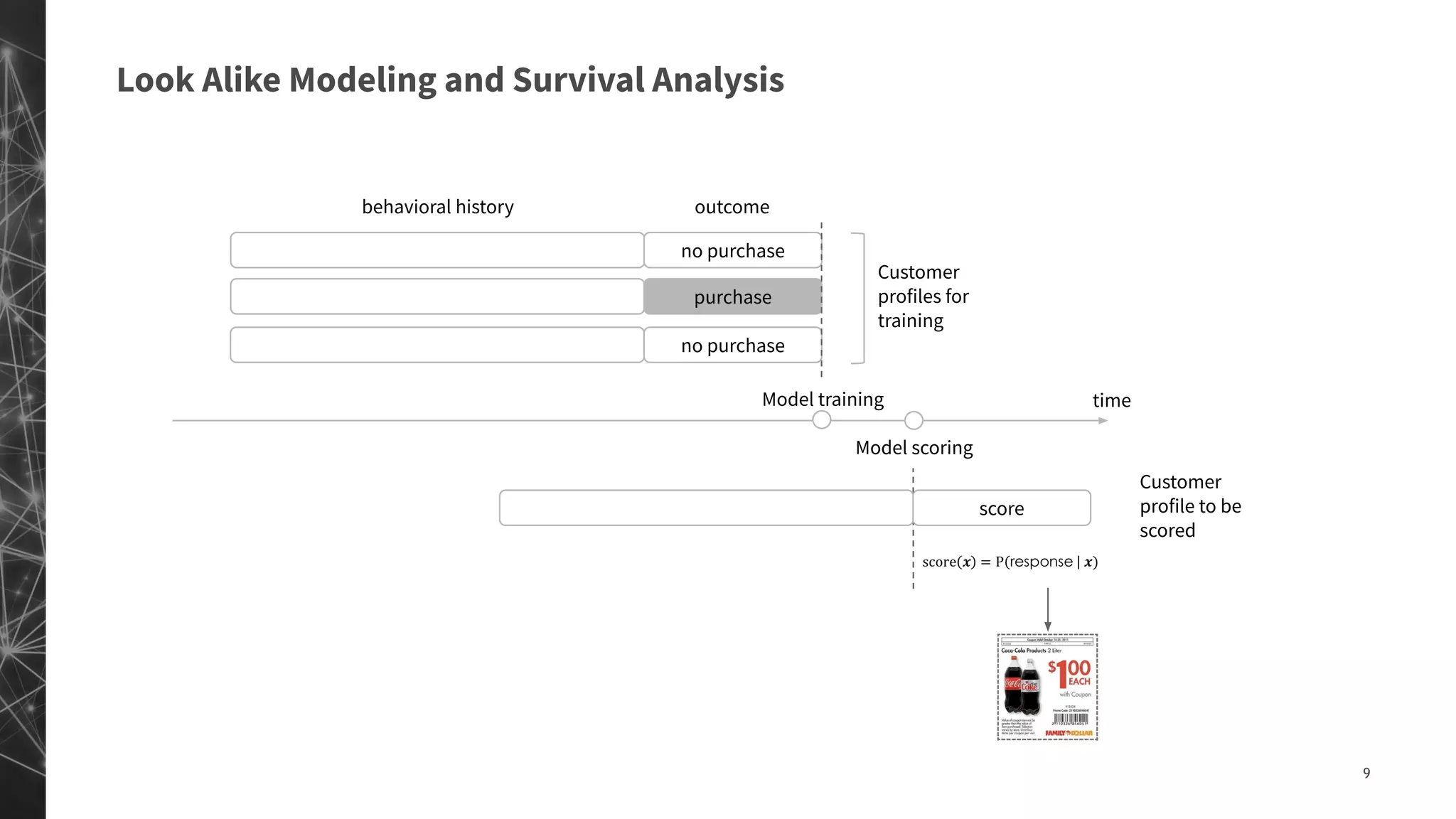
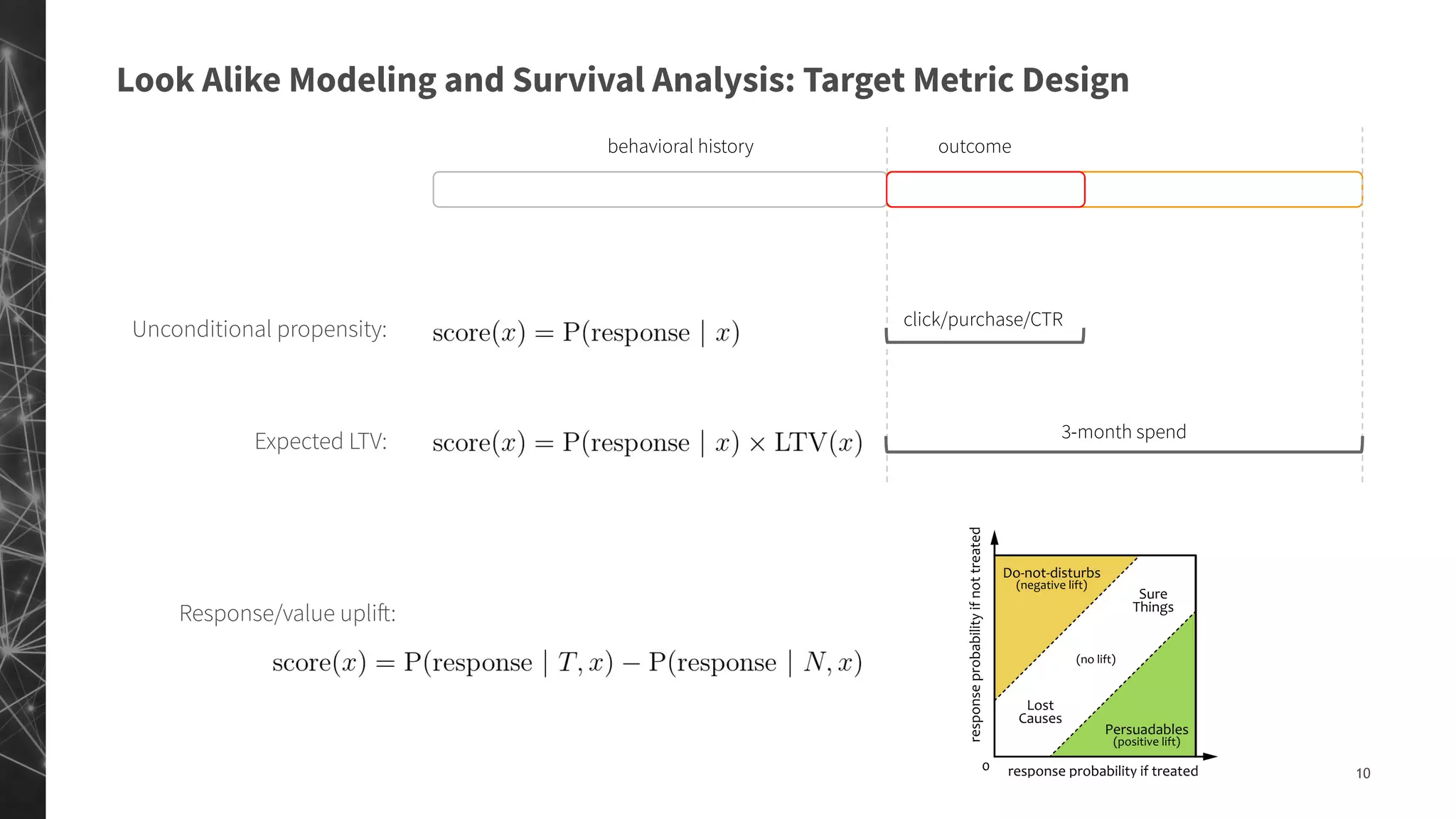
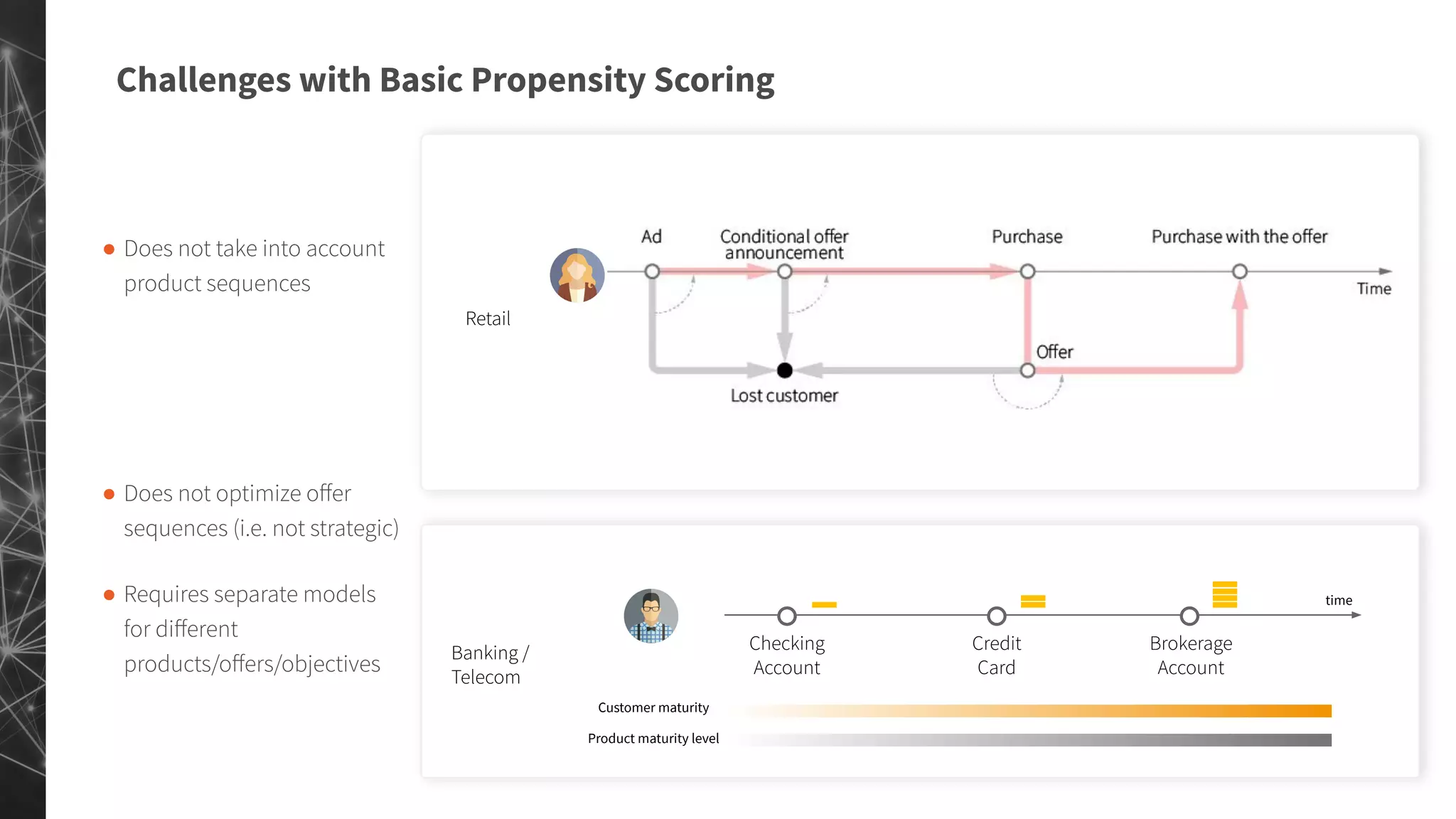
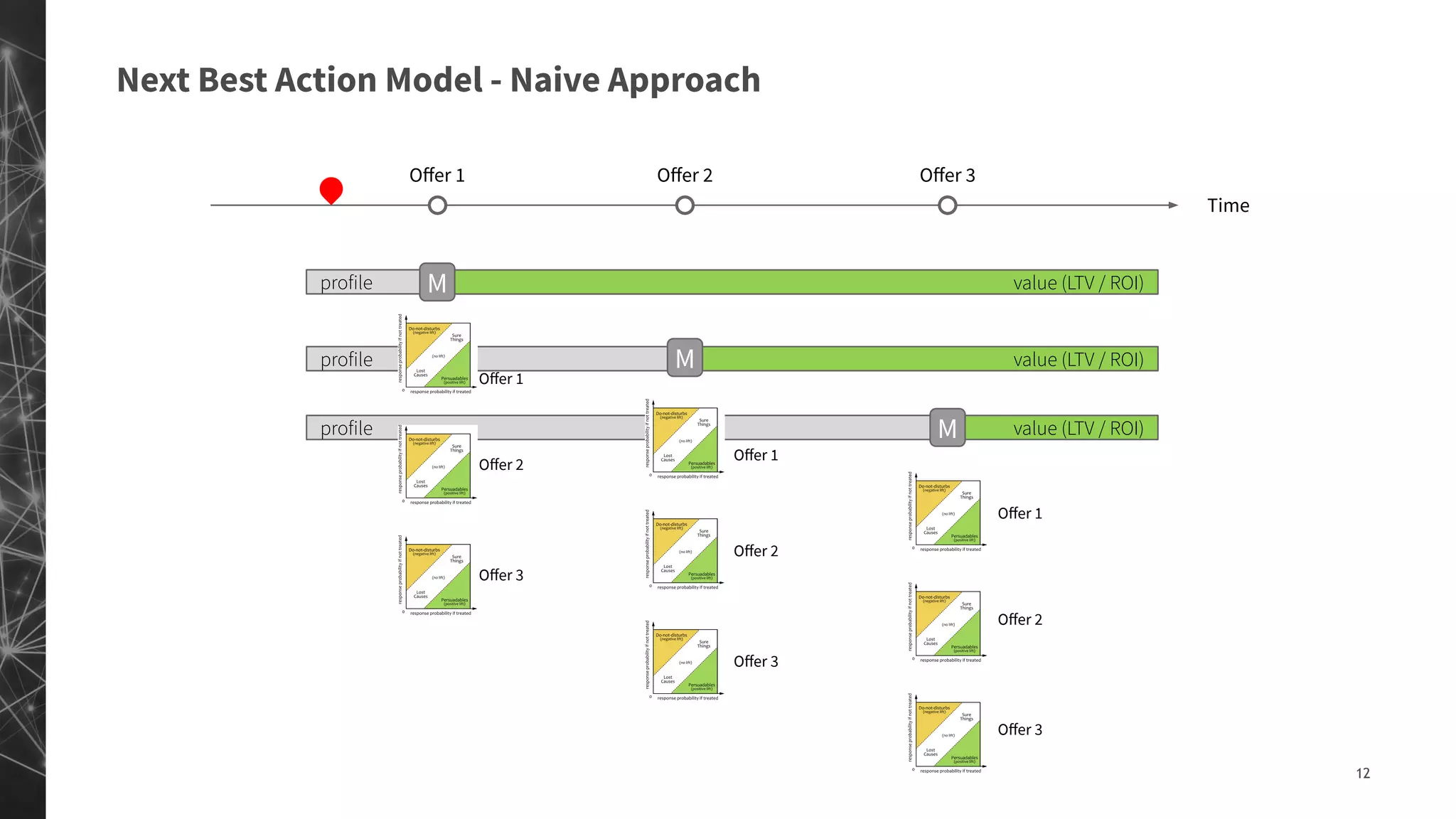
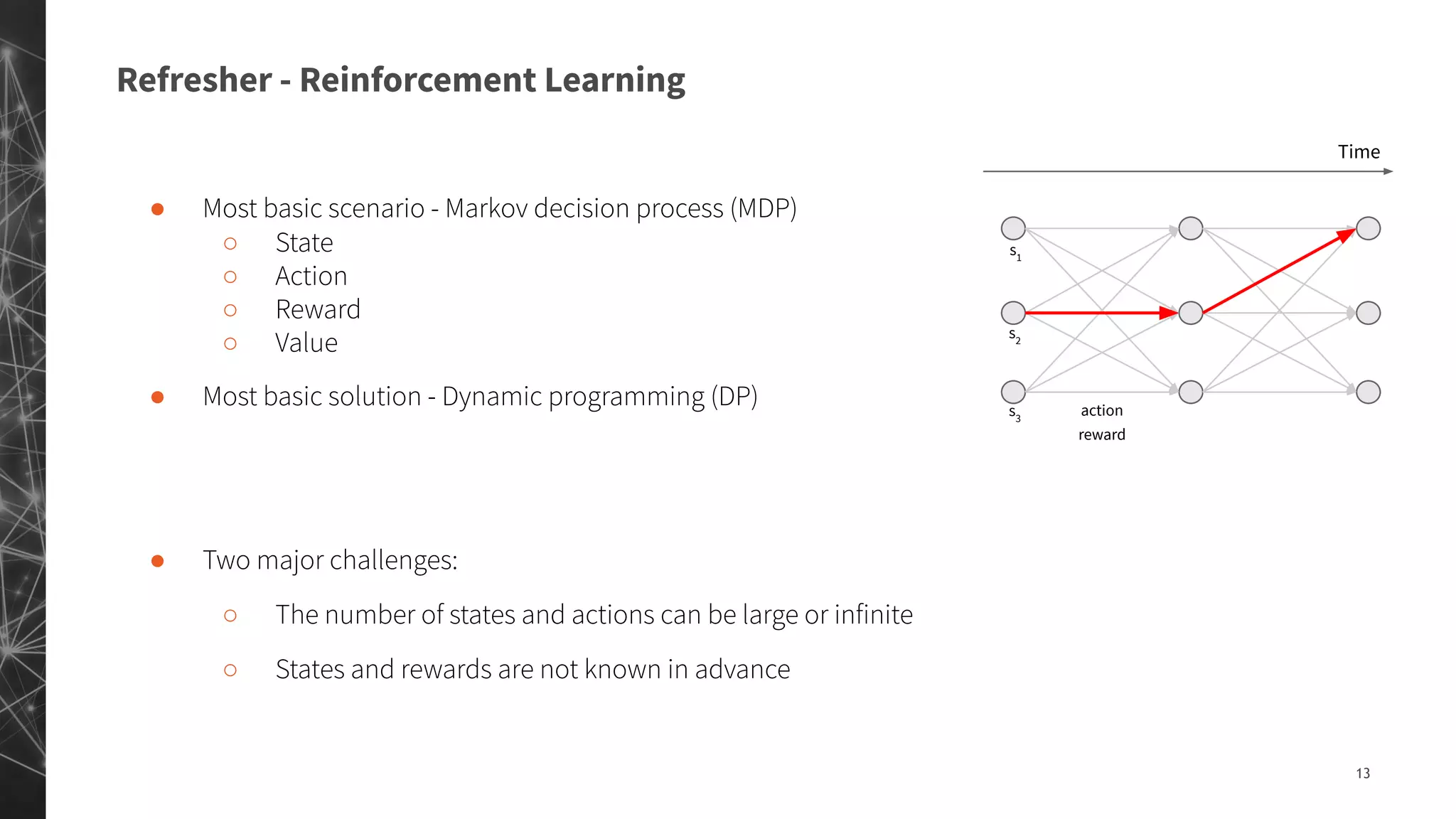
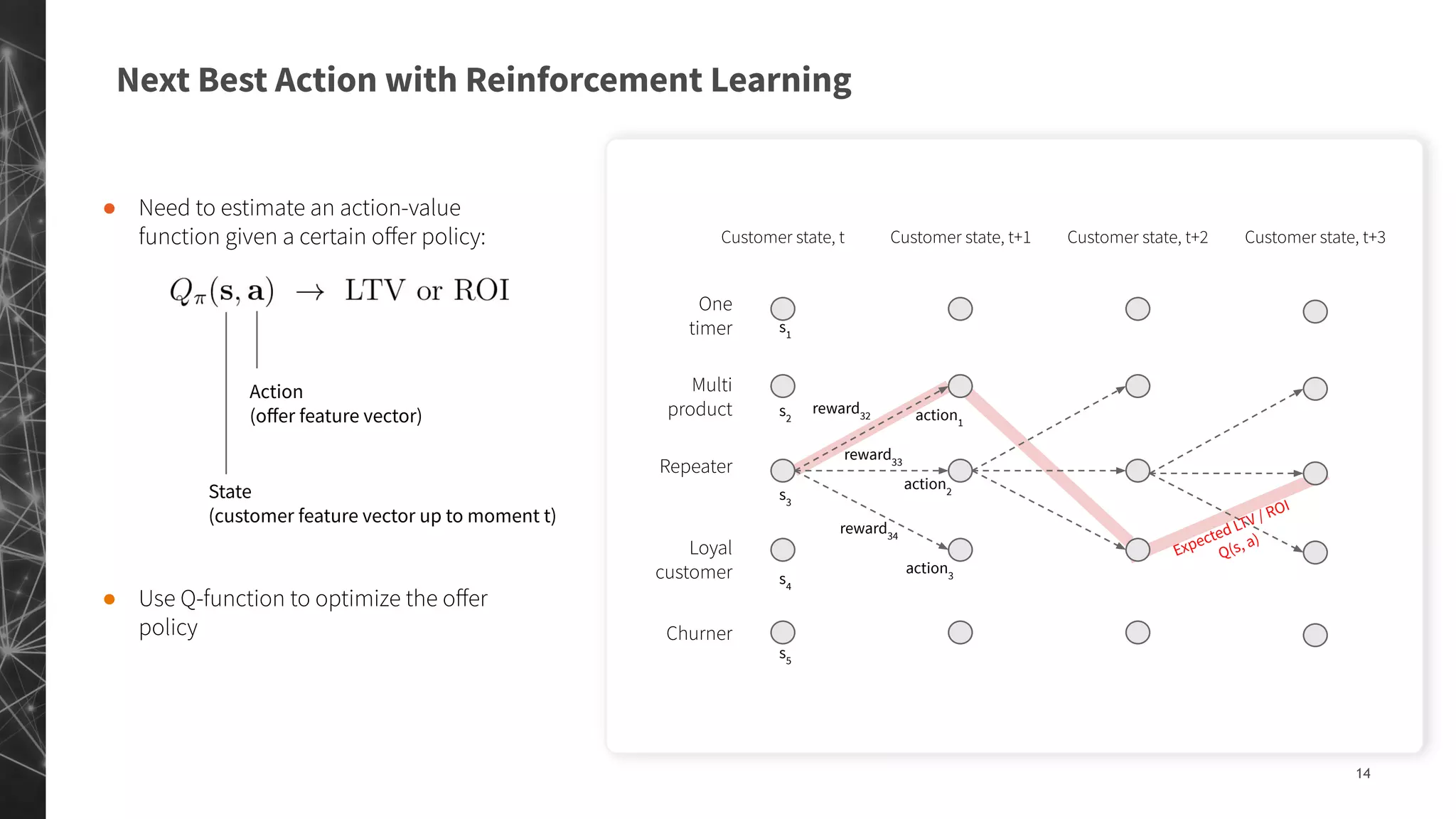
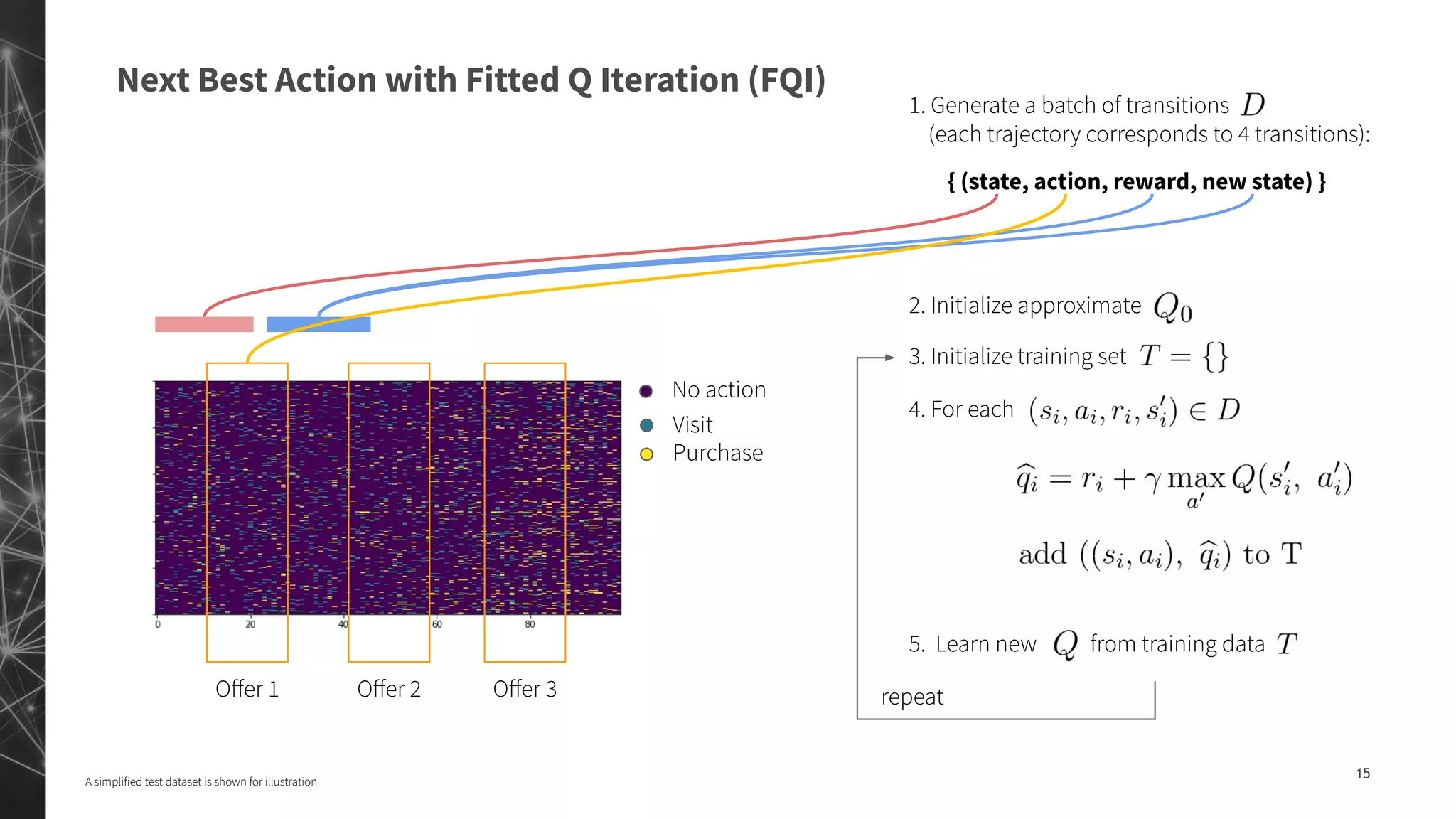
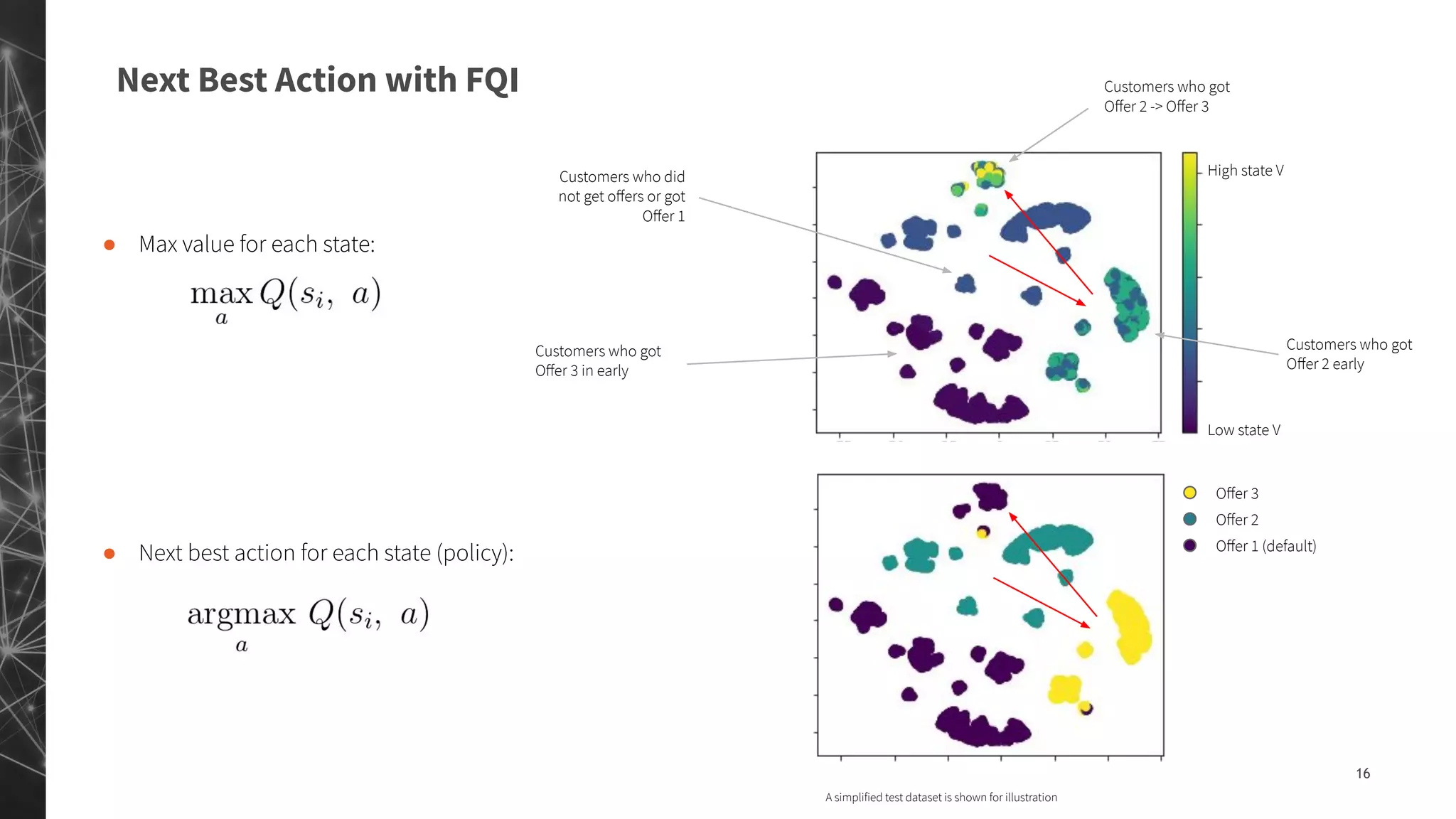
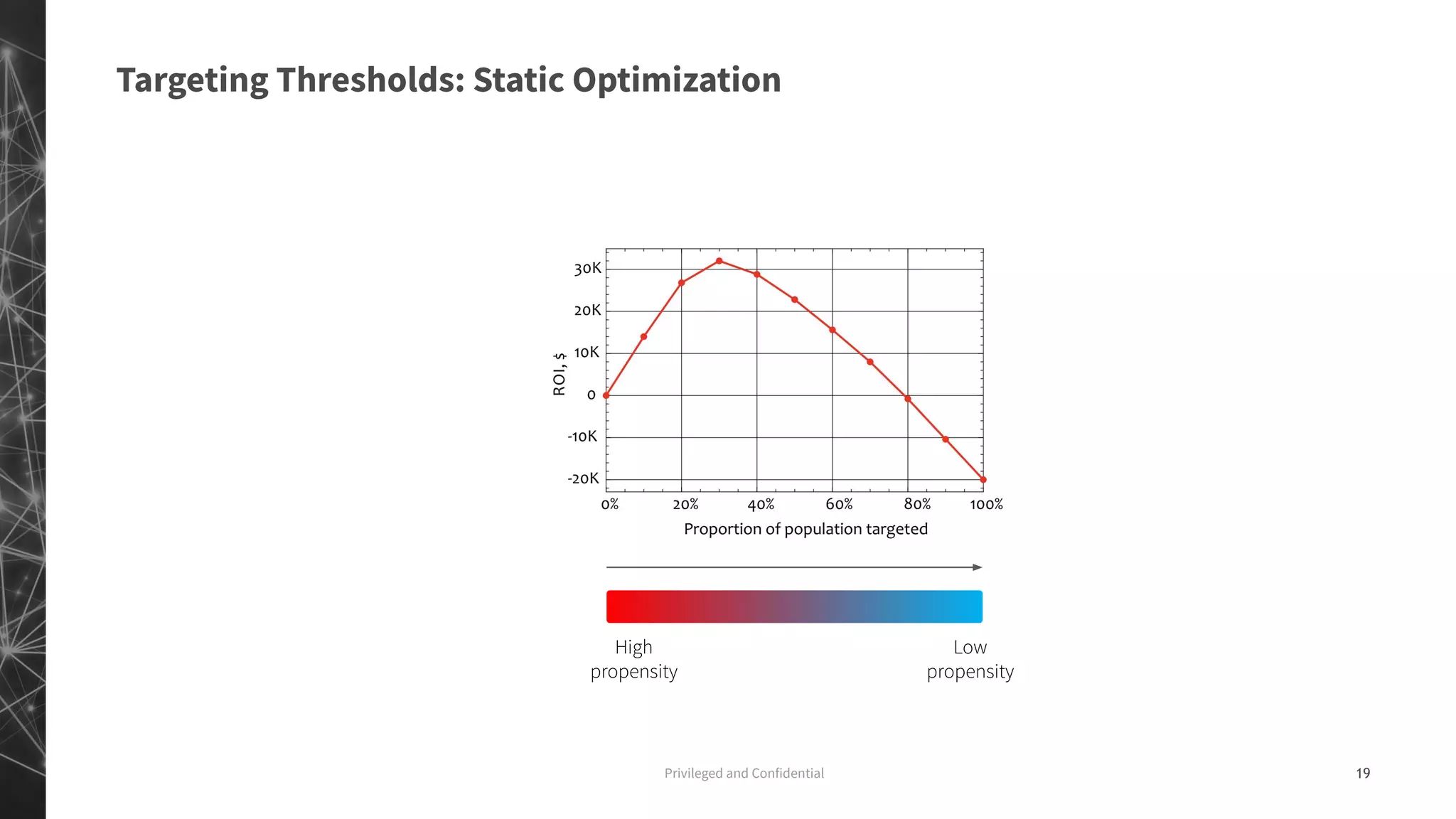
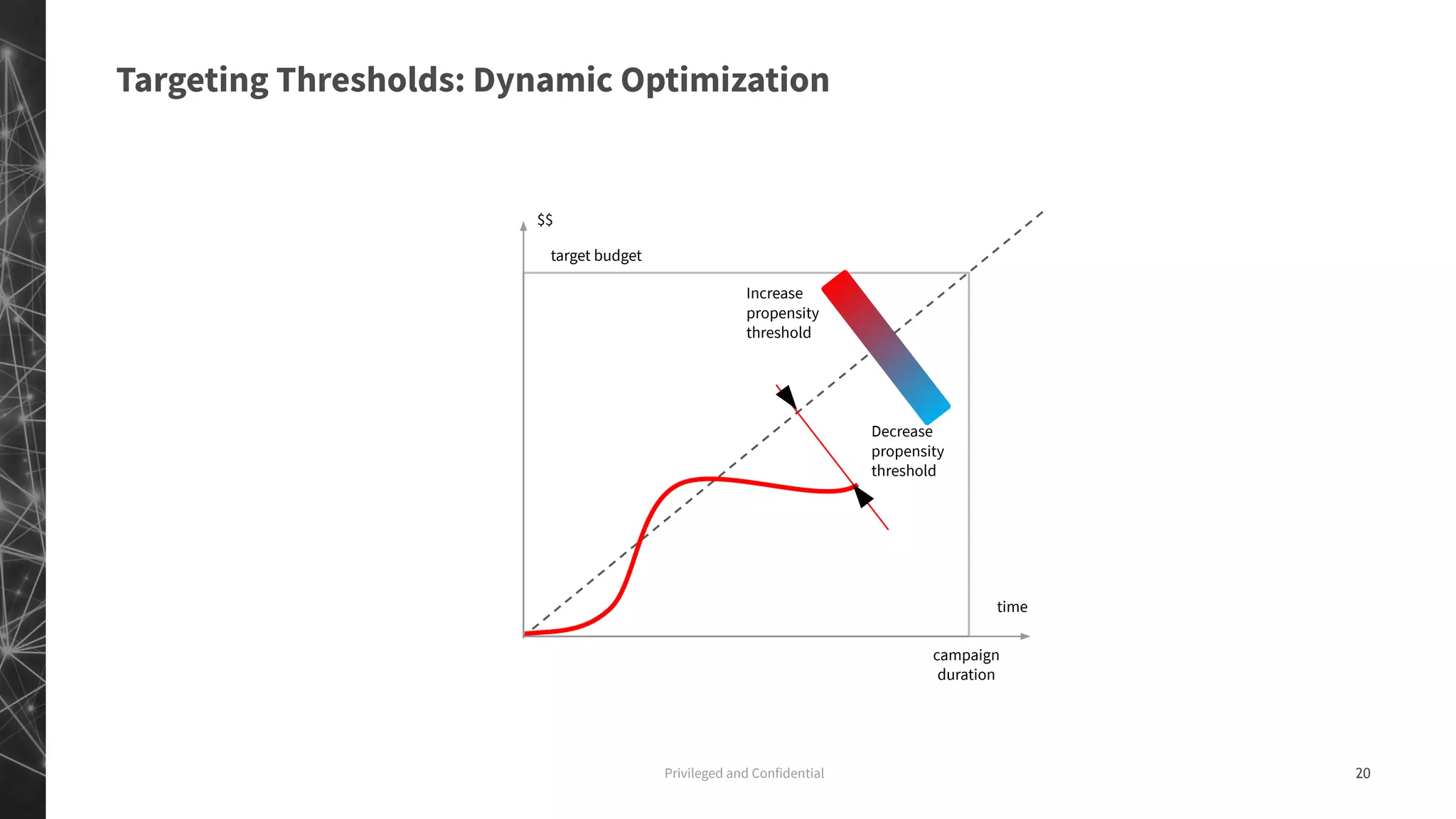
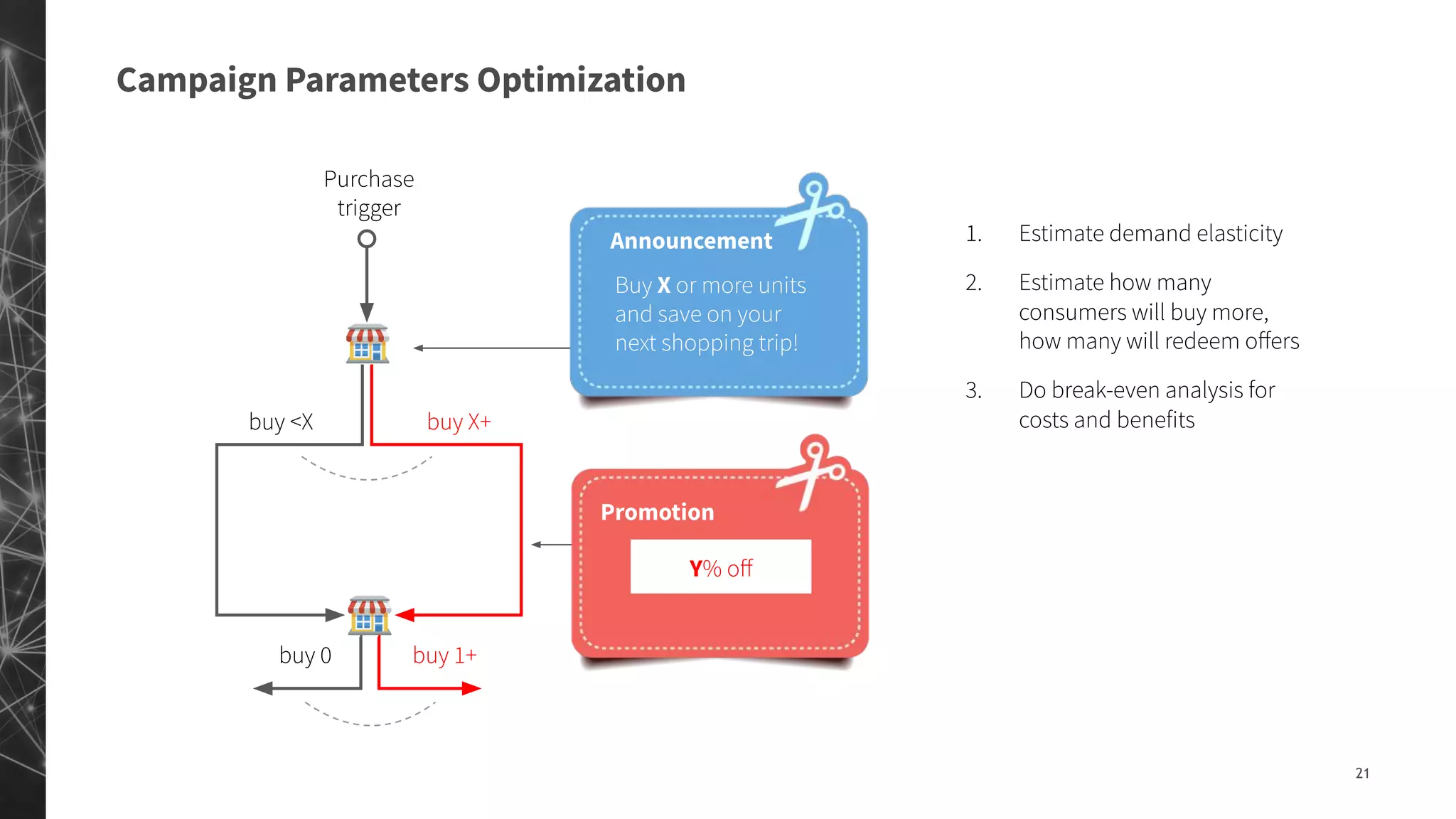
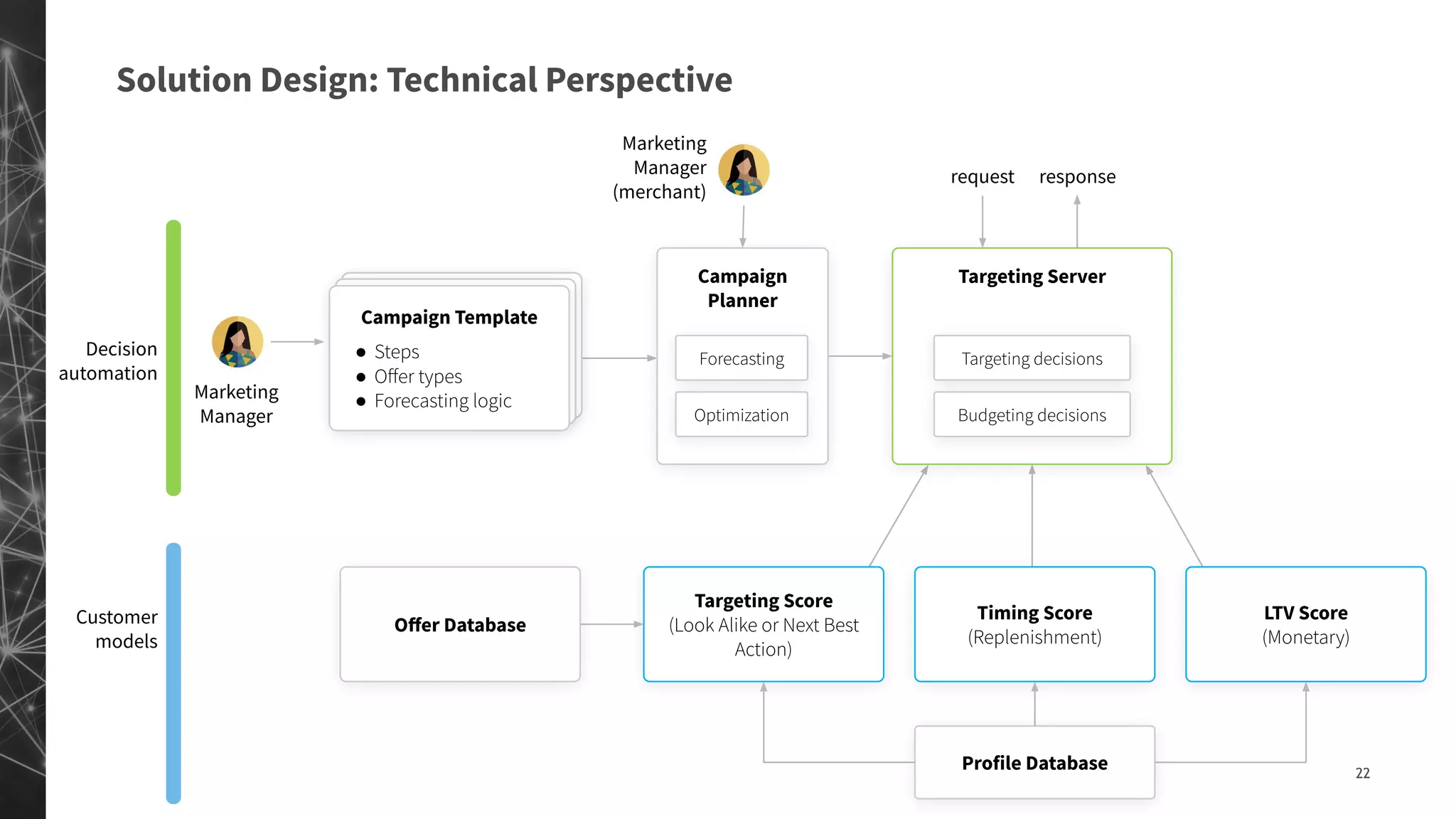
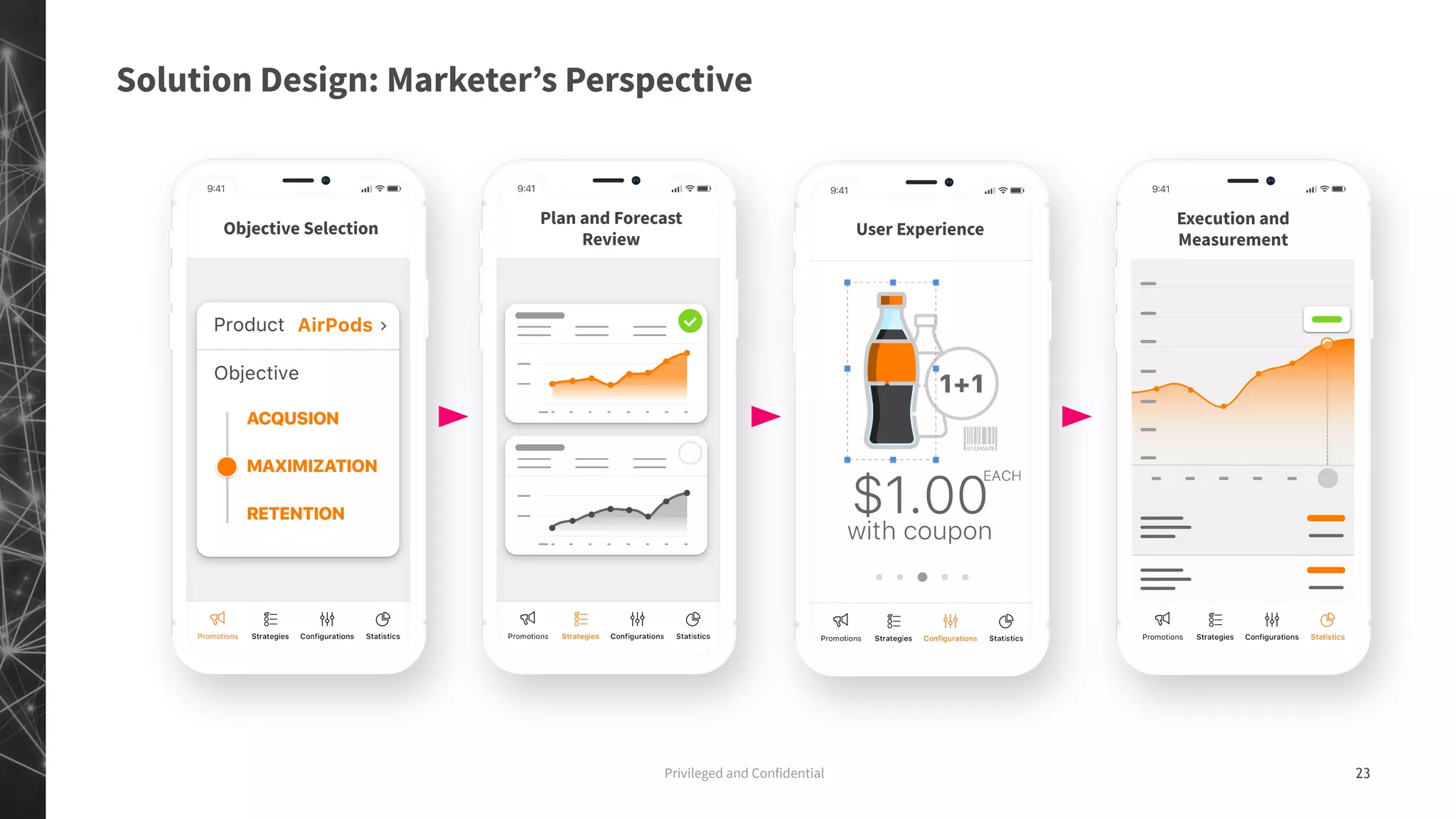
The document discusses a machine learning approach to customer intelligence in marketing operations, emphasizing the automation of micro-decisions in a complex retail environment. It presents case studies on targeting, timing, and outreach strategies for optimizing marketing efforts, along with methods such as propensity scoring and reinforcement learning. The document highlights challenges in traditional models and advocates for advanced predictive and dynamic optimization techniques to enhance campaign effectiveness.