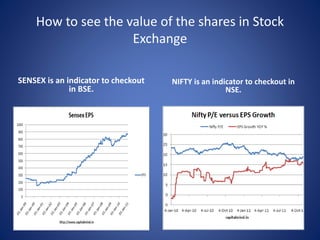
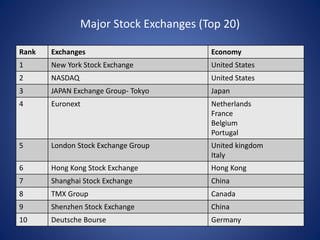
The document provides information about how the stock market works in India. It discusses opening a DEMAT account, which is similar to a bank account, to purchase and sell securities. The two major stock exchanges in India are the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) and National Stock Exchange (NSE). BSE was the first stock exchange established in Asia in 1875, while NSE was established in 1994 and operates electronically across India. The document also describes different types of speculators (bull, bear, stag, lame duck) and the roles of the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) and NSE certifications in regulating the stock market.